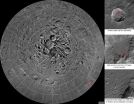
(Press-News.org) Scientists, using cameras aboard NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO), have created the largest high resolution mosaic of our moon's north polar region. The six-and-a-half feet (two-meters)-per-pixel images cover an area equal to more than one-quarter of the United States.
Web viewers can zoom in and out, and pan around an area. Constructed from 10,581 pictures, the mosaic provides enough detail to see textures and subtle shading of the lunar terrain. Consistent lighting throughout the images makes it easy to compare different regions.
"This unique image is a tremendous resource for scientists and the public alike," said John Keller, LRO project scientist at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Md. "It's the latest example of the exciting insights and data products LRO has been providing for nearly five years."
The images making up the mosaic were taken by the two LRO Narrow Angle Cameras, which are part of the instrument suite known as the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter Camera (LROC). The cameras can record a tremendous dynamic range of lit and shadowed areas.
"Creation of this giant mosaic took four years and a huge team effort across the LRO project," said Mark Robinson, principal investigator for the LROC at Arizona State University in Tempe. "We now have a nearly uniform map to unravel key science questions and find the best landing spots for future exploration."
The entire image measures 931,070 pixels square – nearly 867 billion pixels total. A complete printout at 300 dots per inch – considered crisp resolution for printed publications – would require a square sheet of paper wider than a professional U.S. football field and almost as long. If the complete mosaic were processed as a single file, it would require approximately 3.3 terabytes of storage space. Instead, the processed mosaic was divided into millions of small, compressed files, making it manageable for users to view and navigate around the image using a web browser.
LRO entered lunar orbit in June 2009 equipped with seven instrument suites to map the surface, probe the radiation environment, investigate water and key mineral resources, and gather geological clues about the moon's evolution.
Researchers used additional information about the moon's topography from LRO's Lunar Orbiter Laser Altimeter, as well as gravity information from NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory (GRAIL) mission, to assemble the mosaic. Launched in September 2011, the GRAIL mission, employing twin spacecraft named Ebb and Flow, generated a gravity field map of the moon -- the highest resolution gravity field map of any celestial body.
LRO is managed by Goddard for the Science Mission Directorate (SMD) at NASA Headquarters in Washington. LROC was designed and built by Malin Space Science Systems and is operated by the University of Arizona. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, Calif., managed the GRAIL mission for SMD.
INFORMATION:
For more information about LRO, visit:
http://www.nasa.gov/lro
To access the complete collection of LROC images, visit:
http://lroc.sese.asu.edu/
To view the image with zoom and pan capability, visit:
http://lroc.sese.asu.edu/gigapan
NASA releases first interactive mosaic of lunar north pole
2014-03-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Fierce 2012 magnetic storm barely missed Earth
2014-03-18
Earth dodged a huge magnetic bullet from the sun on July 23, 2012.
According to University of California, Berkeley, and Chinese researchers, a rapid succession of coronal mass ejections – the most intense eruptions on the sun – sent a pulse of magnetized plasma barreling into space and through Earth's orbit. Had the eruption come nine days earlier, it would have hit Earth, potentially wreaking havoc with the electrical grid, disabling satellites and GPS, and disrupting our increasingly electronic lives.
The solar bursts would have enveloped Earth in magnetic fireworks ...
New statistical models could lead to better predictions of ocean patterns
2014-03-18
COLUMBIA, Mo. – The world's oceans cover more than 72 percent of the earth's surface, impact a major part of the carbon cycle, and contribute to variability in global climate and weather patterns. However, accurately predicting the condition of the ocean is limited by current methods. Now, researchers at the University of Missouri have applied complex statistical models to increase the accuracy of ocean forecasting that can influence the ways in which forecasters predict long-range events such as El Nińo and the lower levels of the ocean food chain—one of the world's ...
Early detection of childhood eye cancer doesn't always improve survival, prevent eye loss
2014-03-18
For the most common form of childhood eye cancer, unilateral retinoblastoma, shortening the time from the first appearance of symptoms to diagnosis of disease has no bearing on survival or stage of the disease, according to a study by researchers at Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health in partnership with the Hospital Infantil de Mexico. The results appear online in the journal Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention.
Because retinoblastoma is easily detectable by shining a light into a child's eye—often as a "cat's eye" reflection revealed through ...
The precise reason for the health benefits of dark chocolate: Mystery solved
2014-03-18
DALLAS, March 19, 2014 — The health benefits of eating dark chocolate have been extolled for centuries, but the exact reason has remained a mystery –– until now. Researchers reported here today that certain bacteria in the stomach gobble the chocolate and ferment it into anti-inflammatory compounds that are good for the heart.
Their findings were unveiled at the 247th National Meeting & Exposition of the American Chemical Society (ACS), the world's largest scientific society. The meeting, attended by thousands of scientists, features more than 10,000 reports on new advances ...
Building heart tissue that beats
2014-03-18
DALLAS, March 18, 2014 — When a heart gets damaged, such as during a major heart attack, there's no easy fix. But scientists working on a way to repair the vital organ have now engineered tissue that closely mimics natural heart muscle that beats, not only in a lab dish but also when implanted into animals. They presented their latest results at the 247th National Meeting & Exposition of the American Chemical Society (ACS), the world's largest scientific society.
The talk was one of more than 10,000 being presented at the meeting, which continues here through Thursday.
"Repairing ...
Bees capable of learning feats with tasty prize in sight
2014-03-18
They may have tiny brains, but bumblebees are capable of some remarkable learning feats, especially when they might get a tasty reward, according to two studies by University of Guelph researchers.
PhD student Hamida Mirwan and Prof. Peter Kevan, School of Environmental Sciences, are studying bees' ability to learn by themselves and from each other.
In the first study, published in February in Animal Cognition, the researchers found bees capable of learning to solve increasingly complex problems.
The researchers presented bees with a series of artificial flowers that ...
Sauder research shows why innovation takes a nosedive
2014-03-18
A new UBC study reveals that corporate leaders are victims of herd mentality when adopting new innovations, sometimes with deadly consequences.
The paper, by Sauder School of Business Associate Professor Marc-David L. Seidel and INSEAD Professor Henrich R. Greve, shows leaders tend to pursue innovations, even as complex as airplanes, based on early adoption by competitors not close scrutiny of the technical merits.
"Business leaders tend to panic when new innovations are about to hit the market. They scramble to buy an apparent early leader," says Seidel. "Sometimes ...
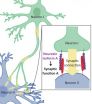
Stanford researchers survey protein family that helps the brain form synapses
2014-03-18
Neuroscientists and bioengineers at Stanford are working together to solve a mystery: how does nature construct the different types of synapses that connect neurons -- the brain cells that monitor nerve impulses, control muscles and form thoughts.
In a paper published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Thomas C. Südhof, M.D., a professor of molecular and cellular physiology, and Stephen R. Quake, a professor of bioengineering, describe the diversity of the neurexin family of proteins.
Neurexins help to create the synapses that connect neurons. Think ...
TGen-led study spotlights dog DNA role in developing new therapies for human cancers
2014-03-18
PHOENIX, Ariz. — March 17, 2014 — Using genomic analysis to study cancer in dogs can help develop new therapies for humans with cancer, according to a proof-of-concept study led by the National Cancer Institute (NCI) and the Translational Genomics Research Institute (TGen).
Pure-breed dogs, whose genetics have been standardized by hundreds of years of human intervention, provide highly predictable genetic models useful in designing clinical trials, in which specific drugs are matched to the molecular profiles of human patients, according to the study published today in ...
Kessler Foundation researchers link body temperature to relapsing-remitting MS and fatigue
2014-03-18
West Orange, NJ. March 18, 2014. Kessler Foundation researchers have demonstrated for the first time ever that body temperature is elevated endogenously in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS) and linked to worse fatigue. The article was published ahead of print on Feb. 21, 2014 in Archives of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation. Sumowski J, Leavitt V: Body temperature is elevated and linked to fatigue in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis, even without heat exposure. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2014.02.004.
Researchers measured body temperature in 50 patients with ...