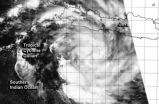
(Press-News.org) NASA's Aqua satellite passed over the reborn tropical cyclone known as Gillian on March 21 and captured a visible image of the storm, located just south of the island of Java.
Java is highly populated island of Indonesia that includes the capital city of Jakarta. Java is divided into four provinces, East, West and Central Java and Banten. There are also two special regions of Java called Jakarta and Yogyakarta.
The MODIS instrument that flies aboard Aqua captured a visible image of Gillian on March 21 at 06:55 UTC/2:55 a.m. EDT. The image showed bands of thunderstorms wrapping around the center of circulation that stretched from the north to the east and southwest. Only the northwestern quadrant appeared to have a fragmented band. The NOAA-19 polar orbiting satellite showed that Gillian is a symmetric and compact system with improved central convection.
Gillian initially formed on March 10 in the northern Gulf of Carpentaria, part of the Southern Pacific Ocean. After a brief landfall in Queensland's Cape York Peninsula it weakened to a remnant low, moved northwest and entered the Southern Indian Ocean where it just re-formed into a tropical storm.
At 0900 UTC/5 a.m. EDT, Tropical Cyclone Gillian's maximum sustained winds were near 35 knots/40 mph/62 kph. It was centered near 9.6 south and 108.2 east, just south of Java and about 834 nautical miles/959.8 miles/1,545 km north-northwest of Learmonth, Australia. Gillian was moving to the west at 16 knots/18.4 mph/ 29.6 kph.
The Indonesian Tropical Cyclone Warning Center in Jakarta has issued watches and warnings across parts of Java and Sumatra for heavy rain and rough surf.
Gillian is expected to move west and once past Christmas Island, the Australian Bureau of Meteorology and the Joint Typhoon Warning Center expect it to move southwest while intensifying to hurricane-force over open waters of the Southern Indian Ocean.
INFORMATION:
NASA sees Tropical Cyclone Gillian reborn near Java
2014-03-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
NASA's Aqua satellite sees Tropical System 94W affecting Philippines
2014-03-21
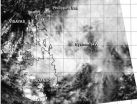
The tropical low pressure area centered just east of the southern Philippines appeared more organized on visible imagery from NASA's Aqua satellite on March 21. System 94W appears to be developing and the Philippine authorities have already issued warnings on the system locally designated as "Caloy."
The MODIS instrument (Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured a visible image of System 94W coming together east of the southern Philippines on March 21 at 5:25 UTC/1:25 a.m. EDT. The image revealed a circulation with ...
Deep ocean current may slow due to climate change, Penn research finds
2014-03-21
Far beneath the surface of the ocean, deep currents act as conveyer belts, channeling heat, oxygen, carbon and nutrients around the globe.
A new study by the University of Pennsylvania's Irina Marinov and Raffaele Bernardello and colleagues from McGill University has found that recent climate change may be acting to slow down one of these conveyer belts, with potentially serious consequences for the future of the planet's climate.
"Our observations are showing us that there is less formation of these deep waters near Antarctica," Marinov said. "This is worrisome because, ...
Pushing and pulling: Using strain to tune a new quantum material
2014-03-21
Research into a recently discovered class of materials shows they have the necessary characteristics to develop ultra-energy efficient electronics. Topological insulators (TI) are three-dimensional materials that conduct electricity on their surfaces, while the interior insulates.
Their surfaces are particularly unique because the motion of the electrons is "protected" by symmetry, meaning electrons will keep moving without scattering even when they encounter defects and contamination.
In fact, electrons on the surface of TIs move so robustly scientists are trying ...
Computers spot false faces better than people
2014-03-21
TORONTO, ON — A joint study by researchers at the University of California San Diego and the University of Toronto has found that a computer system spots real or faked expressions of pain more accurately than people can. The work, titled "Automatic Decoding of Deceptive Pain Expressions," is published in the latest issue of Current Biology.
"The computer system managed to detect distinctive dynamic features of facial expressions that people missed," said Marian Bartlett, research professor at UC San Diego's Institute for Neural Computation and lead author of the study. ...
Characteristics of lung cancers arising in germline EGFR T790M mutation carriers
2014-03-21
DENVER –Two studies are providing new insight into germline epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) T790M mutation in familial non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). The findings suggest the need for tailored approaches for early detection and treatment, as well as for genetic testing to identify carriers.
"These studies now solidify the fact that routine clinical management of lung cancer now has to include the awareness of this inherited cancer syndrome," wrote David P. Carbone, MD, PhD, President-Elect of the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer ...
Ground-improvement methods might protect against earthquakes
2014-03-21
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. — Researchers from the University of Texas at Austin's Cockrell School of Engineering are developing ground-improvement methods to help increase the resilience of homes and low-rise structures built on top of soils prone to liquefaction during strong earthquakes.
Findings will help improve the safety of structures in Christchurch and the Canterbury region in New Zealand, which were devastated in 2010 and 2011 by a series of powerful earthquakes. Parts of Christchurch were severely affected by liquefaction, in which water-saturated soil temporarily ...
Forests crucial to green growth
2014-03-21
NAIROBI, Kenya (21 March 2014) ----The value of forests and tree-based ecosystems extends far beyond carbon sequestration; they are the foundation of sustainable societies.
A new report, launched in Jakarta, Indonesia on 21 March - the International Day of Forests – promotes REDD+ and the Green Economy as together providing a new pathway to sustainable development that can benefit all nations. It claims this approach can conserve and even boost the economic and social benefits forests provide to human society.
Building Natural Capital – How REDD+ Can Support a Green ...
Pathogens in cheese
2014-03-21
Listeria is a rod-shaped bacterium highly prevalent in the environment and generally not a threat to human health. One species however, Listeria monocytogenes, can cause listeriosis, a very dangerous disease. This pathogen can be present in raw milk and soft cheeses, smoked fish, raw meat and ready-to-eat products. In Austria, health care providers are required to report all cases of listeriosis, which can be fatal particularly for patients with weakened immune systems. In 2009 and 2010, a dairy in Hartberg (Styria, Austria) produced Quargel cheese contaminated with Listeria ...
In rats, diffuse brain damage can occur with no signs of 'concussion,' reports study in Neurosurgery
2014-03-21
Philadelphia, Pa. (March 21, 2014) – A standard experimental model of concussion in rats causes substantial brain damage—but no behavioral changes comparable to those seen in patients with concussion, reports a study in the April issue of Neurosurgery, official journal of the Congress of Neurological Surgeons. The journal is published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, a part of Wolters Kluwer Health.
The results highlight the "disconnect" between preclinical and clinical studies of concussion, according to the report by Dr. Charles L. Rosen of West Virginia University, ...
Genetic evidence for single bacteria cause of sepsis identified for the first time
2014-03-21
An international team of academics, including Professor Marco Oggioni from the University of Leicester's Department of Genetics, has studied how localised infections can turn into the dangerous systematic disease sepsis – and has identified for the first time through genetic evidence that a single bacteria could be the cause.
The study, which has been published in the academic journal PLOS Pathogens, examined the events that lead to sepsis by Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus), a major human pathogen, in mice. They found that in most cases the bacteria causing sepsis ...