(Press-News.org) New research shows sugary drinks are the worst offenders in the fight against youth obesity and recommends that B.C. schools fully implement healthy eating guidelines to reduce their consumption.
Data from the 2008 Adolescent Health survey among 11,000 grade seven to 12 students in British Columbia schools indicates sugary drinks like soda increased the odds of obesity more than other foods such as pizza, french fries, chips and candies.
The study, published today in the International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity, found that students in schools where sugary drinks were available consumed them more often and were more likely to be obese on the BMI scale.
"This study adds to the mounting literature that shows the high concentration of sugar in soft drinks contributes to obesity in adolescents," says lead author Louise Mâsse, an associate professor in the University of British Columbia's School of Population and Public Health, and a scientist at the Child & Family Research Institute at BC Children's Hospital.
In 2005, the B.C. government released guidelines for healthy eating that suggested sugary drinks not be sold in schools, but Mâsse says full implementation is necessary to help address obesity trends.
"Schools have an important role in promoting healthy dietary habits," says Mâsse. "For example, students who are moderate consumers of these types of beverages were 60 per cent less likely to consume them in the schools that followed healthy nutrition guidelines.
"Creating an environment within the school that is more conducive to healthy eating will likely provide the greatest benefit in supporting healthy weights among adolescents."
INFORMATION:
BACKGROUND | SUGARY DRINKS AND OBESITY
About the study
Unlike the U.S., Canada does not have a national breakfast or school lunch program that is subsidized by the federal government. In B.C., provincial government guidelines to regulate the school food environment were first written in 2005, but full implementation was only expected in the 2008/2009 school year, after the data were collected for this paper. The B.C. government revised these guidelines in 2010 and 2013.
The study is based on survey results from over 11,000 students collected by the McCreary Centre Society, as well as a nutritional and physical activity school environment survey sent to public school principals. The data were linked, which resulted in an analytic sample of 174 schools (67 middle schools, 105 high schools, and two kindergarten to grade 12 schools from 36 districts).
Funding for this study was provided by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR).
Study partners
UBC's School of Population and Public Health provides a vibrant, interdisciplinary academic environment at a critical time in the development of public health in Canada and around the world. One of the most research-intensive units at UBC, with a long history of public health engagement, the School offers six graduate-level academic programs, as well as a residency program. For more information, visit http://www.spph.ubc.ca
The Child & Family Research Institute (CFRI) conducts discovery, translational and clinical research to benefit the health of children and their families. CFRI is supported by BC Children's Hospital Foundation and works in close partnership with the University of British Columbia, BC Children's Hospital, and BC Women's Hospital & Health Centre (agencies of the Provincial Health Services Authority). For more information, visit http://www.cfri.ca.
Sugary drinks weigh heavily on teenage obesity
2014-03-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Research: Less invasive technique possible in vulvar cancer treatment
2014-03-26
A team of researchers from Women & Infants Hospital of Rhode Island commanded a national stage to present the results of a study evaluating the use of sentinel lymph node dissection in women with vulvar malignancies, and then follow the patients for complications and recurrence.
The team – Drs. Richard G. Moore, Dario Roque, Carolyn McCourt, Ashley Stuckey, Paul A. DiSIlvestro, James Sung, Margaret Steinhoff, Cornelius Granai III, and Katina Robison – presented their work at the annual meeting of the Society of Gynecologic Oncologists (SGO) in Tampa. The oral presentation ...
Lack of coronin 1 protein causes learning deficits and aggressive behavior
2014-03-26
This news release is available in German.
Organisms must be able to sense signals from the outside and translate these into biochemical cues in order to adequately respond to their environment. This capability is also required to process information that reaches the brain. Within the brain, stimulation of neurons activates genes that are required, for example for learning and memory. In collaboration with an international and interdisciplinary team the research group led by Prof. Jean Pieters from the Biozentrum, University of Basel, has now uncovered the role of ...
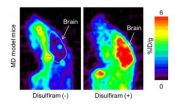
Using PET scanning to evaluate therapies of Menkes disease
2014-03-26
Scientists at the RIKEN Center for Life Science Technologies have used PET imaging to visualize the distribution in the body of copper, which is deregulated in Menkes disease, a genetic disorder, using a mouse model. This study lays the groundwork for PET imaging studies on human Menkes disease patients to identify new therapy options.
Menkes disease, though rare, is a fearsome genetic disorder. Most affected babies die within the first few years of life. The disease is caused by an inborn fault in the body's ability to absorb copper. The standard treatment today for ...
Diabetes: Good self-management helps to reduce mortality
2014-03-26
Scientists of the Institute of Health Economics and Health Care Management (IGM) and of the Institute of Epidemiology II (EPI II) at Helmholtz Zentrum München (HMGU), together with colleagues of the German Diabetes Center (DDZ) in Düsseldorf, investigated the association between self-management behavior and mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes. HMGU and the DDZ are partners in the German Center for Diabetes Research (DZD).
High self-management index – low mortality
340 study participants with type 2 diabetes were interviewed with regard to their patient behavior ...
Real-life CSI: What can investigators really tell from gunshot residue?
2014-03-26
The popular TV series "CSI" is fiction, but every day, real-life investigators and forensic scientists collect and analyze evidence to determine what happened at crime scenes. In a study published in the ACS journal Analytical Chemistry, scientists say they have developed a more rapid and accurate method that could allow crime scene investigators to tell what kind of ammunition was shot from a gun based on the residue it left behind.
Igor K. Lednev and Justin Bueno point out that when someone fires a gun, burnt particles from the bullet spray out of the weapon onto a ...
Electroacupuncture at Conception and Governor vessels and hUCB-MSCs for cerebral ischemia
2014-03-26
Mesenchymal stem cell transplantation is a novel means of treating cerebral ischemia/reperfusion, and can promote angiogenesis and neurological functional recovery. Acupuncture at Conception and Governor vessels also has positive effects as a treatment for cerebral ischemia/reperfusion. Therefore, Prof. Haibo Yu and co-workers from Affiliated Shenzhen Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine in China hypothesized that electro-acupuncture at Conception and Governor vessels plus mesenchymal stem cell transplantation may have better therapeutic ...
Beer marinade could reduce levels of potentially harmful substances in grilled meats
2014-03-26
The smells of summer — the sweet fragrance of newly opened flowers, the scent of freshly cut grass and the aroma of meats cooking on the backyard grill — will soon be upon us. Now, researchers are reporting that the very same beer that many people enjoy at backyard barbeques could, when used as a marinade, help reduce the formation of potentially harmful substances in grilled meats. The study appears in ACS' Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry.
I.M.P.L.V.O. Ferreira and colleagues explain that past studies have shown an association between consumption of grilled ...
Research produces strong evidence for a new class of antidepressant drugs
2014-03-26
Scientists have shown for the first time that a chemical in the brain called galanin is involved in the risk of developing depression.
And the research, undertaken by a European research team, points to a strong reason to develop drugs that modify galanin functioning as a new class of antidepressant drug.
Galanin is a neuropeptide (a small protein) that was discovered and investigated over 30 years ago by various groups including the Swedish scientist Tomas Hokfelt. He is one of the senior authors of the paper published in the journal PNAS.
Professor Hokfelt and ...
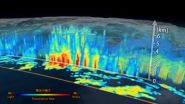
First images available from NASA-JAXA global rain and snowfall satellite
2014-03-26
NASA and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) have released the first images captured by their newest Earth-observing satellite, the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory, which launched into space Feb. 27.
The images show precipitation falling inside a March 10 cyclone over the northwest Pacific Ocean, approximately 1,000 miles east of Japan. The data were collected by the GPM Core Observatory's two instruments: JAXA's Dual-frequency Precipitation Radar (DPR), which imaged a three-dimensional cross-section of the storm; and, NASA's GPM Microwave ...
The advantages of entering the workforce in a recession
2014-03-26
Despite the well-documented disadvantages of graduating from college during a recession, could graduates actually be happier with their jobs in the long run?
A new article from Administrative Science Quarterly examines whether earning a college or graduate degree in a recession or an economic boom has lasting effects on job satisfaction. Across three studies, well-educated graduates who entered the workforce during economic downturns were happier with their work than those who first searched for jobs during more prosperous times. In fact, they were happier with their ...