(Press-News.org) Hamilton, ON (April 1, 2014) Researchers at McMaster University have discovered a key molecule that could lead to new therapies for people with celiac disease, an often painful and currently untreatable autoimmune disorder.
Celiac disease is a food sensitivity to dietary gluten contained in cereals. In people who are genetically predisposed, gluten containing food will trigger an immune response that leads to destruction of the intestinal lining, abdominal pain, changes in bowel habits, malnutrition and many other symptoms that include anemia, and neurological problems.
People with this disease cannot eat food containing wheat, rye or barley, which is a main source of protein intake in the western diet.
Researchers in the Farncombe Family Digestive Health Research Institute at McMaster University have discovered that a molecule, elafin, which is present in the intestine of healthy individuals, is significantly decreased in patients with celiac disease. The research was published in The American Journal of Gastroenterology.
When people with celiac disease eat food containing gluten , the digestive enzymes cannot digest it, and left over peptides from digestion induce inflammation. This inflammation is further amplified by an enzyme called tissue transglutaminase 2.
An intriguing finding of the research, say scientists, was that elafin, by interacting with the transglutaminase 2 enzyme, decreased the enzymatic reaction that increases the toxicity of peptides derived from gluten. In studies with mice, the researchers found that the administration of the elafin molecule protects the intestinal lining of the upper gut that is damaged by gluten.
Following a gluten-free diet is very difficult, because gluten is used not only in the food industry but in the cosmetic and pharmaceutical industries as a common, low cost filler.
"People who have to strictly avoid gluten for life often find this very difficult due to these hidden sources," said Elena Verdu, associate professor of Medicine in the Michael G. DeGroote School of Medicine. "There is a great need for a therapy that will protect patients with celiac disease from these accidental contaminations."
Verdu says the results raise the possibility of elafin administration or replacement as a new adjuvant therapy to the gluten free diet. "This would add flexibility to a restrictive lifelong diet, and increase patients' quality of life and potentially accelerate the healing of celiac lesions."
The research has implications beyond celiac disease.
Recently, gluten intolerance has been reported in patients who do not have celiac disease (non-celiac gluten sensitivity).
Development of new therapies such as this one could help in the management of common gastrointestinal disorders such as irritable bowel syndrome that could be also triggered by wheat containing food.
INFORMATION:
For further information:
Veronica McGuire
Media Relations
Faculty of Health Sciences
McMaster University
905-525-9140, ext. 22169
vmcguir@mcmaster.ca
Research finding could lead to new therapies for patients with gluten intolerance
Elafin decreases the enzymatic reaction that increases the toxicity of peptides derived from gluten
2014-04-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New screening tool to diagnose common sleep problem in children
2014-04-01
OTTAWA, Canada, April 1, 2014 — Clinical investigators at the Children's Hospital of Eastern Ontario (CHEO) have developed a new screening tool to help diagnose obstructive sleep apnea in children. Their findings are published in Pediatric Pulmonology.
Evidence suggests that adults with a large neck circumference are more likely to develop obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), especially males. As neck circumference varies by age and sex, there have been no reference ranges to diagnose pediatric OSA up until now. The new evidence-based diagnostic tool includes reference ranges ...
New test makes Parkinson's-like disorder of middle age detectable in young adulthood
2014-04-01
The very earliest signs of a debilitating neurodegenerative disorder, in which physical symptoms are not apparent until the fifth decade of life, are detectable in individuals as young as 30 years old using a new, sophisticated type of neuroimaging, researchers at UC Davis, the University of Illinois and UCLA have found.
People with the condition — fragile X-associated tremor/ataxia syndrome (FXTAS) — experience tremors, poor balance, cognitive impairments and Parkinsonism. The genetic condition results from a mutation in the fragile X mental retardation gene (FMR1). ...
Computers teach each other Pac-Man
2014-04-01
PULLMAN, Wash. – Researchers in Washington State University's School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science have developed a method to allow a computer to give advice and teach skills to another computer in a way that mimics how a real teacher and student might interact.
Matthew E. Taylor, WSU's Allred Distinguished Professor in Artificial Intelligence, reports on his method in the journal Connection Science. The work was funded in part by the National Science Foundation (NSF).
Researchers had the agents – as the virtual robots are called – act like true student ...
Nanosheets and nanowires
2014-04-01
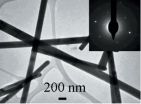
Researchers in China, [J. Appl. Cryst. (2014). 47, 527-531] have found a convenient way to selectively prepare germanium sulfide nanostructures, including nanosheets and nanowires, that are more active than their bulk counterparts and could open the way to lower cost and safer optoelectronics, solar energy conversion and faster computer circuitry.
Germanium monosulfide, GeS, is emerging as one of the most important "IV–VI" semiconductor materials with potential in opto-electronics applications for telecommunications and computing, and as an absorber of light for use ...
New discovery gives hope that nerves could be repaired after spinal cord injury
2014-04-01
A new discovery suggests it could one day be possible to chemically reprogram and repair damaged nerves after spinal cord injury or brain trauma.
Researchers from Imperial College London and the Hertie Institute, University of Tuebingen have identified a possible mechanism for re-growing damaged nerve fibres in the central nervous system (CNS). This damage is currently irreparable, often leaving those who suffer spinal cord injury, stroke or brain trauma with serious impairments like loss of sensation and permanent paralysis.
Published in Nature Communications today, ...
Neuromonitoring with pulse-train stimulation for implantation of thoracic pedicle screws
2014-04-01
Charlottesville, VA (April 1, 2014). Researchers from Syracuse, New York, report a new, highly accurate, neuromonitoring method that can be used during thoracic spine surgery to prevent malpositioning of pedicle screws such that they enter the spinal canal and possibly cause postoperative neurological impairment. Findings of this prospective, blinded, and randomized study are reported and discussed in two companion papers published today online, ahead of print, in the Journal of Neurosurgery: Spine, specifically "Neuromonitoring with pulse-train stimulation for implantation ...
Child support in Tennessee paternity actions
2014-04-01
Child support in Tennessee paternity actions
Article provided by Autry L. Jones, Attorney at Law
Visit us at http://www.autryjones.com
Tennessee law recognizes that both parents have legal duties to financially support their child, so when two parents do not live together, the law allows a Tennessee court to order child support. Child support arrangements usually involve one parent -- the one with whom the child does not live (or lives less) --paying money monthly to the custodial parent to help with the child's living expenses.
While people think of child support ...
Medical marijuana bill progresses through Florida legislature
2014-04-01
Medical marijuana bill progresses through Florida legislature
Article provided by Stanley E. Peacock, P.A.
Visit us at http://www.stanpeacocklaw.com
While a handful states have already decriminalized the recreational use of marijuana, others are still debating whether to approve the drug for medical purposes, including Florida. However, if one particular piece of Florida legislation eventually becomes law, medical marijuana may become a reality in the Sunshine State.
Recently, House Bill 843 passed a Florida House Appropriations Committee by a vote of 24-0; meaning ...
Special rules for workers over age 50 who apply for disability benefits
2014-04-01
Special rules for workers over age 50 who apply for disability benefits
Article provided by Law Offices of Judith S. Leland, APLC
Visit us at http://www.disabilitylawfirm.com
According to the Social Security Administration, more than 25 percent of today's 20-year-olds will be put out of work by a disabling condition before reaching the age of 67. A disability becomes more likely as workers age and their bodies become less resistant to injury and illness.
Fortunately, for qualifying disabled workers who have paid enough into the system, compensation may be available ...
Male military spouses more likely to face divorce, but may lack support
2014-04-01
Male military spouses more likely to face divorce, but may lack support
Article provided by Anthony C. Williams & Associates, PC
Visit us at http://www.anthonywilliamslaw.com
Today, women account for 15 percent of active duty U.S. military personnel. Married female armed service members are far more likely to divorce than their male counterparts. According to the Defense Department, the overall divorce rate in the military among both men and women was 3.4 percent in fiscal year 2013. But, 7.2 percent of women in the military reported a divorce during fiscal year ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
Johns Hopkins scientists engineer nanoparticles able to seek and destroy diseased immune cells
A hidden immune circuit in the uterus revealed: Findings shed light on preeclampsia and early pregnancy failure
Google Earth’ for human organs made available online
AI assistants can sway writers’ attitudes, even when they’re watching for bias
Still standing but mostly dead: Recovery of dying coral reef in Moorea stalls
3D-printed rattlesnake reveals how the rattle is a warning signal
Despite their contrasting reputations, bonobos and chimpanzees show similar levels of aggression in zoos
Unusual tumor cells may be overlooked factors in advanced breast cancer
Plants pause, play and fast forward growth depending on types of climate stress
University of Minnesota scientists reveal how deadly Marburg virus enters human cells, identify therapeutic vulnerability
Here's why seafarers have little confidence in autonomous ships
MYC amplification in metastatic prostate cancer associated with reduced tumor immunogenicity
[Press-News.org] Research finding could lead to new therapies for patients with gluten intoleranceElafin decreases the enzymatic reaction that increases the toxicity of peptides derived from gluten