(Press-News.org) For the first time, a field test has demonstrated that elevated levels of carbon dioxide inhibit plants' assimilation of nitrate into proteins, indicating that the nutritional quality of food crops is at risk as climate change intensifies.
Findings from this wheat field-test study, led by a UC Davis plant scientist, will be reported online April 6 in the journal Nature Climate Change.
"Food quality is declining under the rising levels of atmospheric carbon dioxide that we are experiencing," said lead author Arnold Bloom, a professor in the Department of Plant Sciences.
"Several explanations for this decline have been put forward, but this is the first study to demonstrate that elevated carbon dioxide inhibits the conversion of nitrate into protein in a field-grown crop," he said.
The assimilation, or processing, of nitrogen plays a key role in the plant's growth and productivity. In food crops, it is especially important because plants use nitrogen to produce the proteins that are vital for human nutrition. Wheat, in particular, provides nearly one-fourth of all protein in the global human diet.
Many previous laboratory studies had demonstrated that elevated levels of atmospheric carbon dioxide inhibited nitrate assimilation in the leaves of grain and non-legume plants; however there had been no verification of this relationship in field-grown plants.
Wheat field study
To observe the response of wheat to different levels of atmospheric carbon dioxide, the researchers examined samples of wheat that had been grown in 1996 and 1997 in the Maricopa Agricultural Center near Phoenix, Ariz.
At that time, carbon dioxide-enriched air was released in the fields, creating an elevated level of atmospheric carbon at the test plots, similar to what is now expected to be present in the next few decades. Control plantings of wheat were also grown in the ambient, untreated level of carbon dioxide.
Leaf material harvested from the various wheat tests plots was immediately placed on ice, and then was oven dried and stored in vacuum-sealed containers to minimize changes over time in various nitrogen compounds.
A fast-forward through more than a decade found Bloom and the current research team able to conduct chemical analyses that were not available at the time the experimental wheat plants were harvested.
In the recent study, the researchers documented that three different measures of nitrate assimilation affirmed that the elevated level of atmospheric carbon dioxide had inhibited nitrate assimilation into protein in the field-grown wheat.
"These field results are consistent with findings from previous laboratory studies, which showed that there are several physiological mechanisms responsible for carbon dioxide's inhibition of nitrate assimilation in leaves," Bloom said.
3 percent protein decline expected
Bloom noted that other studies also have shown that protein concentrations in the grain of wheat, rice and barley — as well as in potato tubers — decline, on average, by approximately 8 percent under elevated levels of atmospheric carbon dioxide.
"When this decline is factored into the respective portion of dietary protein that humans derive from these various crops, it becomes clear that the overall amount of protein available for human consumption may drop by about 3 percent as atmospheric carbon dioxide reaches the levels anticipated to occur during the next few decades," Bloom said.
While heavy nitrogen fertilization could partially compensate for this decline in food quality, it would also have negative consequences including higher costs, more nitrate leaching into groundwater and increased emissions of the greenhouse gas nitrous oxide, he said.
INFORMATION:
In addition to Bloom, the research team on this study included Martin Burger, currently in UC Davis' Department of Land, Air and Water Resources; and Bruce A. Kimball and Paul J. Pinter, both of the U.S. Department of Agriculture's U.S. Arid-Land Agricultural Research Center in Maricopa, Ariz.
Funding for the study was provided by the National Science Foundation and the National Research Initiative competitive grants program of the U.S. Department of Agriculture's National Institute of Food and Agriculture.
About UC Davis
For more than 100 years, UC Davis has been one place where people are bettering humanity and our natural world while seeking solutions to some of our most pressing challenges. Located near the state capital, UC Davis has more than 33,000 students, over 2,500 faculty and more than 21,000 staff, an annual research budget of over $750 million, a comprehensive health system and 13 specialized research centers. The university offers interdisciplinary graduate study and more than 100 undergraduate majors in four colleges — Agricultural and Environmental Sciences, Biological Sciences, Engineering, and Letters and Science. It also houses six professional schools — Education, Law, Management, Medicine, Veterinary Medicine and the Betty Irene Moore School of Nursing.
Media contacts:
Arnold Bloom, Plant Sciences, (530) 752-1743, ajbloom@ucdavis.edu
Pat Bailey, UC Davis News Service, (530) 752-9843, pjbailey@ucdavis.edu
Field study shows why food quality will suffer with rising CO2
2014-04-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers find arid areas absorb unexpected amounts of atmospheric carbon
2014-04-06
PULLMAN, Wash.—Researchers led by a Washington State University biologist have found that arid areas, among the biggest ecosystems on the planet, take up an unexpectedly large amount of carbon as levels of carbon dioxide increase in the atmosphere. The findings give scientists a better handle on the earth's carbon budget—how much carbon remains in the atmosphere as CO2, contributing to global warming, and how much gets stored in the land or ocean in other carbon-containing forms.
"It has pointed out the importance of these arid ecosystems," said R. Dave Evans, a WSU professor ...
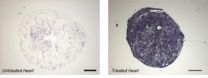
Friedreich's ataxia -- an effective gene therapy in an animal model
2014-04-06
The transfer, via a viral vector, of a normal copy of the gene deficient in patients, allowed to fully and very rapidly cure the heart disease in mice. These findings are published in Nature Medicine on 6 April, 2014.
Friedreich's ataxia is a severe, rare hereditary disorder which combines progressive neuro-degeneration, impaired heart function and an increased risk of diabetes. The condition affects one in every 50,000 birth. There is currently no effective treatment for this disease. In most cases, Friedreich's ataxia starts in adolescence with impaired balance and ...
Smoking visibility mapped for the first time
2014-04-06
The visibility of smoking in city streets has for the first time anywhere been mapped, in new research from the University of Otago, Wellington, New Zealand.
The research found that up to 116 smokers outside bars/cafés could be seen from any one location in the outdoor public areas of downtown Wellington (e.g. on a footpath). Of 2600 people observed in the outdoor areas of bars and cafés, 16% were smoking, with a higher proportion than this in evenings.
Data from observations across the downtown area were mapped by the researchers, producing a record of the street ...
Blood test could provide rapid, accurate method of detecting solid cancers
2014-04-06
STANFORD, Calif. — A blood sample could one day be enough to diagnose many types of solid cancers, or to monitor the amount of cancer in a patient's body and responses to treatment. Previous versions of the approach, which relies on monitoring levels of tumor DNA circulating in the blood, have required cumbersome and time-consuming steps to customize it to each patient or have not been sufficiently sensitive.
Now, researchers at the Stanford University School of Medicine have devised a way to quickly bring the technique to the clinic. Their approach, which should be broadly ...
Self-assembled superlattices create molecular machines with 'hinges' and 'gears'
2014-04-06
VIDEO:
This video shows the motion of nanoparticles in neighboring layers of the superlattice as pressure is applied.
Click here for more information.
A combined computational and experimental study of self-assembled silver-based structures known as superlattices has revealed an unusual and unexpected behavior: arrays of gear-like molecular-scale machines that rotate in unison when pressure is applied to them.
Computational and experimental studies show that the superlattice ...
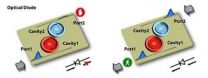
Groundbreaking optical device could enhance optical information processing, computers
2014-04-06
At St. Paul's Cathedral in London, a section of the dome called the Whispering Gallery makes a whisper audible from the other side of the dome as a result of the way sound waves travel around the curved surface. Researchers at Washington University in St. Louis have used the same phenomenon to build an optical device that may lead to new and more powerful computers that run faster and cooler.
Lan Yang, PhD, associate professor of electrical and systems engineering, and her collaborators have developed an essential component of these new computers that would run on light. ...
Columbia scientists identify key cells in touch sensation
2014-04-06
VIDEO:
This video shows a Merkel cell responding to touch.
Click here for more information.
NEW YORK, NY, April 6, 2014 — In a study published in the April 6 online edition of the journal Nature, a team of Columbia University Medical Center researchers led by Ellen Lumpkin, PhD, associate professor of somatosensory biology, solve an age-old mystery of touch: how cells just beneath the skin surface enable us to feel fine details and textures.
Touch is the last frontier of ...
Catman Cohen -- "Knocking Bones & Kissing Shadows"
2014-04-06
Shadow musician, Catman Cohen, proposes to create a new CD that will be a radical departure from his past efforts. "Knocking Bones & Kissing Shadows" will aim to be the exemplar of what is considered desirable in contemporary music. Catman's 5th CD will be a raw and passionate sonic dance...sexual to the nth degree....mindless to the max....and contrived in service of a 24 hour round-the-clock orgiastic party. The music will pound and throb, the airhead lyrics will extol nothing other the celebration of genital satisfaction, buying expensive stuff, getting high, and ...
WellBiz Brands Names Abby Lee as Chief Marketing Officer
2014-04-06
WellBiz Brands, Inc., parent company to Elements Massage and Fitness Together , announced the appointment of Abby Lee as the company's new Chief Marketing Officer.
Lee has a strong background in brand marketing and advertising, most recently serving as the Vice President of Brand Marketing and Sponsorships at RE/MAX where she managed and implemented media and marketing campaigns in more than 100 U.S. markets and coordinated national and local sponsorships. At WellBiz, Lee will be responsible for overseeing marketing initiatives that support new client trial, boost membership ...
2014 Loveland Art Studio Tour Seeks Artists
2014-04-06
The 6th Annual Loveland Art Studio Tour (LAST) has issued a call for artists for its 2014 event. Applications are available here via CallForEntry at https://www.callforentry.org/festivals_unique_info.php?ID=1880&sortby=fair_name&apply=yes.
When: Applications accepted through May 10. Artists notified May 20.
Event Dates: October 11 & 12 and October 18 & 19, 2014, 10:00 a.m. to 5:00 p.m. daily.
LAST seeks passionate, unique, interesting artists who have an individual style. Because one of the event's goals is to educate the community about art, artists ...