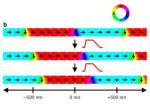
(Press-News.org) Researchers at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) have achieved a major breakthrough in the development of methods of information processing in nanomagnets. Using a new trick, they have been able to induce synchronous motion of the domain walls in a ferromagnetic nanowire. This involved applying a pulsed magnetic field that was perpendicular to the plane of the domain walls. "This is a radically new solution," explained Professor Mathias Kläui of the Institute of Physics of Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz. "It enables us to move domain walls synchronously over a relatively large distance without them returning to their original position." This is essential for permanent data storage, because data would otherwise be lost if domain walls were not collectively displaced in a controlled manner. The research was carried out in cooperation with the working groups of Professor Stefan Eisebitt at TU Berlin and Professor Gisela Schütz of the Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems in Stuttgart. The results were published in the journal Nature Communications at the end of March.
Magnetic nanowires have small regions of uniform magnetization called domains, which can be used as storage units (bits). The site where domains of different alignment meet each other is called a domain wall. Information can be stored in the domain, and read and processed by means of the movement of the domain walls. The method has the great advantage that the information – as in the case of magnetic data storage in general – cannot be easily lost. This contrasts with semiconductor-based storage systems, such as RAM in PCs, which lose all stored information without power. In addition, no fragile moving parts are required such as the read/write head of a hard disk.
It has not previously proved possible to induce the required controlled and synchronized movement of multiple domain walls using magnetic fields. The most obvious approach would be to apply a magnetic field in the direction in which the magnetization runs in the tiny nanowires. However, this has been shown to be ineffective, as there is loss of data. Mathias Kläui and his group took a radically new path. They decided to apply a pulsed magnetic field perpendicularly to the in-plane magnetized domain walls. As the Mainz researchers found in their model system, it is possible to customize the asymmetric field pulses that provide the forward- and backward-oriented forces that act on domain walls. Data can thus be moved within the storage medium in a controlled manner.
The participating physicists at Mainz University first tried out their concept in the context of micromagnetic simulations and then tested it experimentally. For this purpose, they recorded images of the magnetic arrangement in the tiny nanowires with the help of the electron storage ring BESSY II of the Helmholtz Center Berlin for Materials and Energy (HZB). As expected from the simulation, they observed displacement of the domain walls in a direction that was consistent with the model. The scientists also calculated the energy that would be necessary for the experimentally observed domain wall motion and came to the conclusion that the energy consumption of the proposed system would be quite cost-effective compared with the best components currently available.
"The results are very promising. We assume that the necessary paradigm shift will be facilitated by this new approach and it will prove possible to develop a method of efficient and controlled synchronous motion of the domain walls in nanowires," said Kläui. This would pave the way for the development of non-volatile spintronic components of the next generation, which could be used in a wide range of applications for data storage as well as logic and sensor modules.
INFORMATION: END
Domain walls in nanowires cleverly set in motion
Domain walls can be synchronously displaced using magnetic field pulses / An important prerequisite for the development of nano-components for data storage and sensor technology
2014-04-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Montreal researchers explain how our immune system kills abnormal blood cells
2014-04-08
A team of researchers at the IRCM, led by André Veillette, MD, explains how our immune system kills abnormal blood cells. Their discovery, recently published in the Journal of Experimental Medicine, could eventually lead to new treatment avenues for leukemia, lymphoma and certain types of infectious viral diseases.
"Our team is studying how natural killer cells can eliminate abnormal hematopoietic (blood) cells," explains Dr. Veillette, Director of the Molecular Oncology research unit at the IRCM. "NK (natural killer) cells are crucial to the immune system and play a ...
How coughs and sneezes float farther than you think
2014-04-08
The next time you feel a sneeze coming on, raise your elbow to cover up that multiphase turbulent buoyant cloud you're about to expel.
That's right: A novel study by MIT researchers shows that coughs and sneezes have associated gas clouds that keep their potentially infectious droplets aloft over much greater distances than previously realized.
"When you cough or sneeze, you see the droplets, or feel them if someone sneezes on you," says John Bush, a professor of applied mathematics at MIT, and co-author of a new paper on the subject. "But you don't see the cloud, ...
Gothenburg scientist in Nature: Climate models underestimate costs to future generations
2014-04-08
The seven scientists behind the article, due to be published 10 April, conclude that the reports by the UN climate panel serve an important function in setting the agenda for climate research. Yet the most important role of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) is to inform the global political discussion on how the harm caused by climate change should be handled.
Thomas Sterner, expert on policy instruments to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, is a Coordinating Lead Author of one key chapter on policy instruments in the Working Group III of the Fifth Assessment ...
Are women in Iran who use Facebook less likely to wear a veil?
2014-04-08
New Rochelle, NY, April 8, 2014—Use of social media such as Facebook can influence attitudes and behaviors among people of all countries and cultures. Among women in Iran, the duration and amount of daily Facebook activity is associated with their desire to wear a traditional head-covering and their willingness to display pictures of themselves without a veil, according to an article in Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available free on the Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social ...
New research may provide effective nonsurgical treatment for knee osteoarthritis
2014-04-08
New Rochelle, NY, April 8, 2014—A new nonsurgical approach to treating chronic pain and stiffness associated with knee osteoarthritis has demonstrated significant, lasting improvement in knee pain, function, and stiffness. This safe, two-solution treatment delivered in a series of injections into and around the knee joint is called prolotherapy, and is described in The Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available free on The Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine website.
David ...
Breast cancer cell subpopulation cooperation can spur tumor growth
2014-04-08
Subpopulations of breast cancer cells sometimes cooperate to aid tumor growth, according to Penn State College of Medicine researchers, who believe that understanding the relationship between cancer subpopulations could lead to new targets for cancer treatment.
Cancers contain genetically different subpopulations of cells, called subclones. Researchers have long known that these mutant subclones aggressively compete with one another to become the dominant tumor cell population. However, in some cases it seems that no single subclone can achieve dominance on its own. ...
Tracking sugar movement in plants
2014-04-08
A new study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences by scientists at the University of Queensland, Australia, overturns a long-held theory in plant science [see:http://www.bnl.gov/newsroom/news.php?a=11631]. Researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory who are co-authors on this paper conducted critical radiotracer studies that support the new theory that plant sugars play a dominant role in regulating branching at plant stems. While branching has relevance in agriculture, it is also very important in bioenergy ...
Dartmouth researchers identify potential therapeutic target for deadly brain cancer
2014-04-08
(Lebanon, NH, 4/8/14) Researchers from the Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth will present a scientific poster on Tuesday, April 8, 2014 at the American Association of Cancer Researchers conference in San Diego, CA. The research identifies a potential characteristic for predicting outcome in a deadly form of brain cancer known as glioblastoma multiforme.
Existing therapies based on genetic information have failed to effectively treat glioblastomas. Therefore, researchers are aggressively looking to find new molecular targets for this aggressive brain tumor.
Dartmouth ...
Novel plant biotechnology approach for sustainable production of pharmaceutical compounds
2014-04-08
European scientists have made ground-breaking discoveries for improving the efficiency of the production of pharmaceuticals through plant biotechnology. Biotechnological production offers a cost-effective and environmentally friendly alternative to the chemical synthesis of rare and complex pharmaceutical compounds currently isolated from plants. The results have been achieved in the European SmartCell project coordinated by VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland.
Several expensive anticancer alkaloid blockbusters used in chemotherapy, such as terpenoid indole alkaloids ...
New breast cancer results illustrate promise and potential of I-SPY 2 trial
2014-04-08
In an innovative clinical trial led by UC San Francisco, the experimental drug neratinib along with standard chemotherapy was found to be a beneficial treatment for some women with newly diagnosed, high-risk breast cancer.
Additionally, researchers learned that an algorithm used in the adaptive, randomized trial known as I-SPY 2 was highly effective at predicting the success of the treatment regimen in the patients who have HER2-positive/HR-negative disease.
The finding marks the second drug "graduation" within the I-SPY 2 trial model, which is designed to accelerate ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Novel camel antimicrobial peptides show promise against drug-resistant bacteria
Scientists discover why we know when to stop scratching an itch
A hidden reason inner ear cells die – and what it means for preventing hearing loss
Researchers discover how tuberculosis bacteria use a “stealth” mechanism to evade the immune system
New microscopy technique lets scientists see cells in unprecedented detail and color
Sometimes less is more: Scientists rethink how to pack medicine into tiny delivery capsules
Scientists build low-cost microscope to study living cells in zero gravity
The Biophysical Journal names Denis V. Titov the 2025 Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator awardee
Scientists show how your body senses cold—and why menthol feels cool
Scientists deliver new molecule for getting DNA into cells
Study reveals insights about brain regions linked to OCD, informing potential treatments
Does ocean saltiness influence El Niño?
2026 Young Investigators: ONR celebrates new talent tackling warfighter challenges
Genetics help explain who gets the ‘telltale tingle’ from music, art and literature
Many Americans misunderstand medical aid in dying laws
Researchers publish landmark infectious disease study in ‘Science’
New NSF award supports innovative role-playing game approach to strengthening research security in academia
Kumar named to ACMA Emerging Leaders Program for 2026
AI language models could transform aquatic environmental risk assessment
New isotope tools reveal hidden pathways reshaping the global nitrogen cycle
Study reveals how antibiotic structure controls removal from water using biochar
Why chronic pain lasts longer in women: Immune cells offer clues
Toxic exposure creates epigenetic disease risk over 20 generations
More time spent on social media linked to steroid use intentions among boys and men
New study suggests a “kick it while it’s down” approach to cancer treatment could improve cure rates
Milken Institute, Ann Theodore Foundation launch new grant to support clinical trial for potential sarcoidosis treatment
New strategies boost effectiveness of CAR-NK therapy against cancer
Study: Adolescent cannabis use linked to doubling risk of psychotic and bipolar disorders
Invisible harms: drug-related deaths spike after hurricanes and tropical storms
Adolescent cannabis use and risk of psychotic, bipolar, depressive, and anxiety disorders
[Press-News.org] Domain walls in nanowires cleverly set in motionDomain walls can be synchronously displaced using magnetic field pulses / An important prerequisite for the development of nano-components for data storage and sensor technology