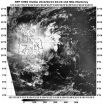
(Press-News.org) Tropical Depression Peipah has been very stubborn and has moved over the southern and central Philippines bringing clouds, showers and gusty winds. NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite captured an image that showed Peipah's clouds covering the Visayas and Mindanao regions of the country.
The VIIRS instrument aboard NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite captured a visible look at the remnant clouds associated with former Tropical Depression Peipah on April 14 at 4:24 UTC/12:24 a.m. EDT. The Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) instrument collects visible and infrared imagery and global observations of land, atmosphere, cryosphere and oceans. Peipah is a broad area of low pressure and its remnant clouds covered the central region of the Philippines called the Visayas region, and Mindanao, the southern region. Microwave satellite imagery confirmed that the low-level part of the storm is still poorly defined and convection (rising air that builds thunderstorms that make up a tropical cyclone) has not improved.
On April 14 at 0900 UTC/5 a.m. EDT, Peipah's remnants were centered near 9.7 north latitude and 130.8 east longitude, about 360 nautical miles/414 miles/666.7 km northwest of Zamboanga, Philippines. Maximum sustained winds were estimated as high as 20 knots/23.0 mph/37.2 kph.
According to the Joint Typhoon Warning Center, Peipah's remnants have a medium chance for regenerating in the next couple of days as it moves slowly in a westerly direction.
INFORMATION:
NASA sees remnants of Tropical Depression Peipah over Southern Philippines
2014-04-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Pharmacists can significantly improve blood pressure, cholesterol in stroke patients
2014-04-14
Stroke patients managed by a pharmacist had a 12.5% improvement in blood pressure and low-density lipoprotein (LDL), or "bad" cholesterol levels compared with a control group, according to a clinical trial published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal).
Patients who have a stroke or "mini stroke" (transient ischemic attack) are at high risk of adverse cardiovascular events. Management of high blood pressure and cholesterol after a stroke is important because it can substantially reduce the risk of a negative event; however, many patients receive suboptimal care. ...
'MicroRNA' could be key target for bowel cancer treatment
2014-04-14
Scientists found that the molecule, called microRNA 135b, is a vital 'worker' employed by several important cancer genes to drive the growth of bowel cancers.
Drugs targeted at the microRNA could knock out the effects of multiple cancer-causing mutations at once, while tests for it could identify patients with the most aggressive disease, the researchers believe.
The research was carried out by an international team including scientists based at The Institute of Cancer Research, London, the University of Glasgow and Ohio State University in the US.
Scientists tested ...
Study identifies a likely key driver of colorectal cancer development and progression
2014-04-14
COLUMBUS, Ohio – A new study identifies a molecule that is a probable driving force in colorectal cancer and suggests that the molecule could be an important target for colorectal cancer treatment and a valuable biomarker of tumor progression.
The study of microRNA-135b (miR-135b) in two animal models and human tumors was published in the journal Cancer Cell and was led by researchers at The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center – Arthur G. James Cancer Hospital and Richard J. Solove Research Institute (OSUCCC – James) and at the University of Glasgow in ...
Dietary supplement use among US adults more prevalent than previously thought
2014-04-14
Washington, D.C., April 14, 2014—Dietary supplement use by U.S. adults is more prevalent than indicated by published data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (NHANES), according to a new article in the peer-reviewed Journal of the American College of Nutrition (JACN). The review article is based on five consecutive years of online market research studies, conducted by Ipsos Public Affairs for the Council for Responsible Nutrition (CRN).
According to Annette Dickinson, Ph.D., corresponding author and a consultant for CRN, "This new review adds to ...
Young dads at high risk of depression, too
2014-04-14
CHICAGO --- Depression can hit young fathers hard -- with symptoms increasing dramatically during some of the most important years of their children's lives, a new Northwestern Medicine® study has found.
Depressive symptoms increased on average by 68 percent over the first five years of fatherhood for these young men, who were around 25 years old when they became fathers and whom lived in the same home as their children. The results of the study were published April 14 in the journal Pediatrics.
This study is the first to identify when young fathers are at increased ...
Osteoporosis drugs appear to impede cell membrane repair
2014-04-14
AUGUSTA, Ga. –A class of drugs widely used to treat osteoporosis appears to impede a cell's ability to repair a protective outer membrane that helps determine what enters and exits, researchers report.
The inability to quickly repair a membrane is lethal to a cell and may help explain the rare and serious side effect of jawbone destruction that can occur following dental work in patients taking these drugs, said Caroline Lewis, a sophomore at the Medical College of Georgia at Georgia Regents University.
"The bottom line is it inhibits cell membrane repair in two distinct ...
Long-term antibiotic treatment for Q fever causes weight gain
2014-04-14
Scientists have unearthed still more evidence that antibiotics can contribute to obesity. Research published ahead of print in the journal Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy suggests that patients on long-term antibiotic treatment gained weight and had significant changes in their gut microbiota.
The study, led by Didier Raoult, of Aix-Marseille University, Marseille, France, followed 48 patients who were being treated long-term with doxycycline and hydroxychloroquine for Q fever, and 34 control subjects. Nearly one quarter of the treated patients gained anywhere ...
Shiny quantum dots brighten future of solar cells
2014-04-14
A house window that doubles as a solar panel could be on the horizon, thanks to recent quantum-dot work by Los Alamos National Laboratory researchers in collaboration with scientists from University of Milano-Bicocca (UNIMIB), Italy. Their project demonstrates that superior light-emitting properties of quantum dots can be applied in solar energy by helping more efficiently harvest sunlight.
"The key accomplishment is the demonstration of large-area luminescent solar concentrators that use a new generation of specially engineered quantum dots," said lead researcher Victor ...
UT Dallas study: Youth who fail to envision future commit more crimes
2014-04-14
In a UT Dallas study involving serious youth offenders, the answer to one open-ended question predicted the teenagers' offending patterns for the next seven years: "How long do you think you'll live?"
According to the study, having little hope for the future encourages offending over time.
Author Dr. Alex Piquero said the study found those who don't view a very long life ahead of them offend at very high rates and commit more serious offenses, while those who believe they're going to die much later in life offend much less.
"In a lot of distressed communities and for ...
Device turns flat surface into spherical antenna
2014-04-14
WASHINGTON D.C., April 14, 2014 -- By depositing an array of tiny, metallic, U-shaped structures onto a dielectric material, a team of researchers in China has created a new artificial surface that can bend and focus electromagnetic waves the same way an antenna does.
This breakthrough, which the team is calling the first broadband transformation optics metasurface lens, may lead to the creation of new types of antennas that are flat, ultra low-profile or conformal to the shape of curved surfaces.
The new lens, described in AIP Publishing's journal Applied Physics Letters, ...