(Press-News.org) WINSTON-SALEM – April 15, 2014 – Vitamin D deficiency and cognitive impairment are common in older adults, but there isn't a lot of conclusive research into whether there's a relationship between the two.
A new study from Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center published online ahead of print this month in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society enhances the existing literature on the subject.
"This study provides increasing evidence that suggests there is an association between low vitamin D levels and cognitive decline over time," said lead author Valerie Wilson, M.D., assistant professor of geriatrics at Wake Forest Baptist. "Although this study cannot establish a direct cause and effect relationship, it would have a huge public health implication if vitamin D supplementation could be shown to improve cognitive performance over time because deficiency is so common in the population."
Wilson and colleagues were interested in the association between vitamin D levels and cognitive function over time in older adults. They used data from the Health, Aging and Body composition (Health ABC) study to look at the relationship. The researchers looked at 2,777 well-functioning adults aged 70 to 79 whose cognitive function was measured at the study's onset and again four years later. Vitamin D levels were measured at the 12-month follow-up visit.
The Health ABC study cohort consists of 3,075 Medicare-eligible, white and black, well-functioning, community-dwelling older adults who were recruited between April 1997 and June 1998 from Pittsburgh, Pa., and Memphis, Tenn.
"With just the baseline observational data, you can't conclude that low vitamin D causes cognitive decline. When we looked four years down the road, low vitamin D was associated with worse cognitive performance on one of the two cognitive tests used," Wilson said. "It is interesting that there is this association and ultimately the next question is whether or not supplementing vitamin D would improve cognitive function over time."
Wilson said randomized, controlled trials are needed to determine whether vitamin D supplementation can prevent cognitive decline and definitively establish a causal relationship.
"Doctors need this information to make well-supported recommendations to their patients," Wilson said. "Further research is also needed to evaluate whether specific cognitive domains, such as memory versus concentration, are especially sensitive to low vitamin D levels."
INFORMATION:
The research is supported in part by the Intramural Research Program of the National Institutes of Health, National Institute on Aging and NIA Contracts N01-AG-6, N01-AG-6, and N01-AG-6 NIA Grants R01 AG028050 and R01 AG029364; and National Institute of Nursing Research Grant R01 NR012459.
Co-authors included Laurel Kilpatrick, M.D., University of Alabama at Birmingham; Kristine Yaffe, M.D., and Hilsa N. Ayonayon, Ph.D., both of University of California at San Francisco,;Jane A. Cauley, Dr.PH., University of Pittsburgh; Tamara B. Harris, M.D., M.S., and Eleanor M. Simonsick, Ph.D., both of the NIA; and James Lovato, M.S., Stephen B. Kritchevsky, Ph.D., Denise K. Houston, Ph.D., and Kaycee M. Sink, M.D., MAS, all of Wake Forest Baptist.
Study examines Vitamin D deficiency and cognition relationship
2014-04-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
NASA's TRMM Satellite adds up Tropical Cyclone Ita's Australian soaking
2014-04-15
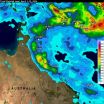
After coming ashore on April 11, Tropical Cyclone Ita dropped heavy rainfall over the weekend that caused flooding in many areas of northeastern Australia's state of Queensland. The Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission satellite known as TRMM gathered data on rainfall that was used to create a rainfall map at NASA.
TRMM is a satellite managed by both NASA and JAXA, the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency. At NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. Hal Pierce created a TRMM-based near-real time Multi-satellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA). The TMPA precipitation ...
The key to easy asthma diagnosis is in the blood
2014-04-15
MADISON, Wis. — Using just a single drop of blood, a team of University of Wisconsin-Madison researchers has developed a faster, cheaper and more accurate tool for diagnosing even mild cases of asthma.
This handheld technology — which takes advantage of a previously unknown correlation between asthmatic patients and the most abundant type of white blood cells in the body — means doctors could diagnose asthma even if their patients are not experiencing symptoms during their visit to the clinic.
The team described its findings in the journal Proceedings of the National ...
Girls' mental health suffers when romances unfold differently than they imagined
2014-04-15
WASHINGTON, DC, April 15, 2014 — A new study reveals that for adolescent girls, having a romantic relationship play out differently than they imagined it would has negative implications for their mental health.
"I found that girls' risk of severe depression, thoughts of suicide, and suicide attempt increase the more their relationships diverge from what they imagined," said the study's author Brian Soller, an assistant professor of sociology and a senior fellow of the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation Center for Health Policy at the University of New Mexico.
"Conversely, ...
Genetic pre-disposition toward exercise and mental development may be linked
2014-04-15
COLUMBIA, Mo. – University of Missouri researchers have previously shown that a genetic pre-disposition to be more or less motivated to exercise exists. In a new study, Frank Booth, a professor in the MU College of Veterinary Medicine, has found a potential link between the genetic pre-disposition for high levels of exercise motivation and the speed at which mental maturation occurs.
For his study, Booth selectively bred rats that exhibited traits of either extreme activity or extreme laziness. Booth then put the rats in cages with running wheels and measured how much ...
How mothers help children explore right and wrong
2014-04-15
Montreal, April 15, 2014 — There's no question that mothers want their children to grow up to be good people — but less is known about how they actually help their offspring sort out different types of moral issues.
According to a new study published in Developmental Psychology and led by Holly Recchia, assistant professor in Concordia's Department of Education and the Centre for Research in Human Development, many mums talk to their kids in ways that help them understand moral missteps.
The study — co-written by Cecilia Wainryb, Stacia Bourne and Monisha Pasupathi ...
Biologists develop nanosensors to visualize movements and distribution of plant hormone
2014-04-15
Biologists at UC San Diego have succeeded in visualizing the movement within plants of a key hormone responsible for growth and resistance to drought. The achievement will allow researchers to conduct further studies to determine how the hormone helps plants respond to drought and other environmental stresses driven by the continuing increase in the atmosphere's carbon dioxide, or CO2, concentration.
A paper describing their achievement appears in the April 15 issue of the scientific journal eLife and is accessible at: http://elife.elifesciences.org/lookup/doi/10.7554/elife.01739 ...
Pharmacist-led interventions show high success rates for post-stroke care
2014-04-15
A new study from the Faculty of Medicine & Dentistry is looking at nurse- and pharmacist-led interventions to improve the standard of care for patients who have suffered minor stroke or transient ischemic attack, also known as "mini stoke."
"What we were finding was that six months or 12 months after their stroke, a lot of patients still had uncontrolled blood pressure and uncontrolled cholesterol," said Finlay McAlister (MD '90), lead author of the study. "[This factor] puts the patients at an increased risk of recurrent events, including strokes, heart attacks, amputation ...
Photo: Tiger beetle's chase highlights mechanical law
2014-04-15
ITHACA, N.Y. – If an insect drew a line as it chased its next meal, the resulting pattern would be a tangled mess. But there's method to that mess, says Jane Wang, a Cornell University professor of mechanical engineering and physics, who tries to find simple physical explanations for complex, hardwired animal behaviors.
Photo: https://cornell.box.com/tbeetle
It turns out the tiger beetle, known for its speed and agility, does an optimal reorientation dance as it chases its prey at blinding speeds. Publishing online April 9 in the Journal of the Royal Society Interface, ...
Researchers transplant regenerated esophagus
2014-04-15
Tissue engineering has been used to construct natural oesophagi, which in combination with bone marrow stem cells have been safely and effectively transplanted in rats. The study, published in Nature Communications, shows that the transplanted organs remain patent and display regeneration of nerves, muscles, epithelial cells and blood vessels.
The new method has been developed by researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden, within an international collaboration lead by Professor Paolo Macchiarini. The technique to grow human tissues and organs, so called tissue engineering, ...
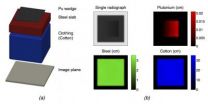
Sensitive detection method may help impede illicit nuclear trafficking
2014-04-15
WASHINGTON D.C., April 15, 2014 -- According to the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) the greatest danger to nuclear security comes from terrorists acquiring sufficient quantities of plutonium or highly enriched uranium (HEU) to construct a crude nuclear explosive device. The IAEA also notes that most cases of illicit nuclear trafficking have involved gram-level quantities, which can be challenging to detect with most inspection methods.
According to a new study appearing this week in the Journal of Applied Physics, coupling commercially available spectral X-ray ...