(Press-News.org) To reproduce or to conquer the world? Surprisingly, bacteria also face this problem. Theoretical biophysicists at Ludwig-Maximilians-Universitaet (LMU) in Munich have now shown how these organisms should decide how best to preserve their species.
The bacterium Bacillus subtilis is quite adaptable. It moves about in liquids and on agar surfaces by means of flagella. Alternatively, it can stick to an underlying substrate. Actually, the bacteria proliferate most effectively in this stationary state, while motile bacteria reproduce at a notably lower rate.
In order to sustain and extend the colony, bacteria primarily require sufficient nutrients. Moving slowly would mean that nutrients are soon used up, but adventurous bacteria that decide to move out fast in search of the land of Cockaigne may end up feeling lonely.
"Should I stay or should I go?"
Which strategy offers the best prospects for the organisms? Should one specialize in growth or migration, or be a generalist and steer a balanced course? This is the question that has been addressed by theoretical biophysicists in LMU Professor Erwin Frey's group at the NIM (Nanosystems Initiative Munich). "We have developed a special mathematical model in which these strategies compete with each other," explains Matthias Reiter, first author of the study. "And this model enables us to prove that generalists are most successful."
Up to now such experiments have only been performed on homogeneous bacterial cultures consisting of genetically identical cells. The LMU theorists are the first to calculate the behavior of heterogeneous Bacillus subtilis populations. For this purpose, they assign a fixed migration rate to each bacterium, which is inherited by its progeny. This rate determines the proportion of time the organisms spend in a motile state, as opposed to being engaged in nutrient uptake and proliferation. In the simulated scenario, the bacteria are, for instance, seeded at the center of a plate containing nutrients. They gradually consume the nutrients available locally and are forced to colonize unpopulated territory.
Fighting for the best spots
The model reveals that, initially, there is intense competition for the limited resources at the edge of the occupied territory. During this phase, individuals that reproduce fast and occupy as much space as possible are at an advantage. But they are soon superseded by colonies of generalists, which devote equal time to migration and proliferation. These gradually spread out, forming sectors as shown in the Figure.
The Munich theorists explain this behavior in terms of the invasion speed of so-called Fisher fronts. This speed is maximal in the case of a balance between growth and motility. Initially, colonies that steer a middle course form individual sectors, until they eventually occupy the entire invasion front.
"We intend to test our findings experimentally in cooperation with biologists, in order to compare our theory with experimental work," Erwin Frey says. "It would even be possible to extend the model to more complex ecosystems, since it can, in principle, be transferred to all range-expansion phenomena in which growth and motility are complementary skills."
INFORMATION: END
Theoretical biophysics: Adventurous bacteria
2014-04-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
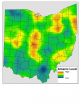
Significant baseline levels of arsenic found in Ohio soils are due to natural processes
2014-04-16
RICHLAND, Wash. – Geologic and soil processes are to blame for significant baseline levels of arsenic in soil throughout Ohio, according to a study published recently in the Journal of Environmental Quality.
The analysis of 842 soil samples from all corners of Ohio showed that every single sample had concentrations higher than the screening level of concern recommended by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. The findings should not alarm the public, say the authors, who note that regulatory levels typically are set far below those thought to be harmful. Rather, the ...
Preterm births, multiples, and fertility treatment
2014-04-16
While it is well known that fertility treatments are the leading cause of increases in multiple gestations and that multiples are at elevated risk of premature birth, these results are not inevitable, concludes an article in Fertility and Sterility. The article identifies six changes in policy and practice that can reduce the odds of multiple births and prematurity, including expanding insurance coverage for in vitro fertilization (IVF) and improving doctor-patient communications about the risks associated with twins.
Financial pressures provide a powerful incentive for ...
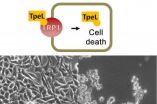
Gate for bacterial toxins found
2014-04-16
Prof. Dr. Dr. Klaus Aktories and Dr. Panagiotis Papatheodorou from the Institute of Experimental and Clinical Pharmacology and Toxicology of the University of Freiburg have discovered the receptor responsible for smuggling the toxin of the bacterium Clostridium perfringens into the cell. The TpeL toxin, which is formed by C. perfringens, a pathogen that causes gas gangrene and food poisoning. It is very similar to the toxins of many other hospital germs of the genus Clostridium. The toxins bind to surface molecules and creep into the body cell, where they lead to cell death. ...
Scientists explain how memories stick together
2014-04-16
LA JOLLA—Scientists at the Salk Institute have created a new model of memory that explains how neurons retain select memories a few hours after an event.
This new framework provides a more complete picture of how memory works, which can inform research into disorders liked Parkinson's, Alzheimer's, post-traumatic stress and learning disabilities.
"Previous models of memory were based on fast activity patterns," says Terry Sejnowski, holder of Salk's Francis Crick Chair and a Howard Hughes Medical Institute Investigator. "Our new model of memory makes it possible to ...
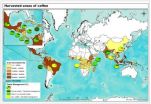
Shade grown coffee shrinking as a proportion of global coffee production
2014-04-16
The proportion of land used to cultivate shade grown coffee, relative to the total land area of coffee cultivation, has fallen by nearly 20 percent globally since 1996, according to a new study by scientists from The University of Texas at Austin and five other institutions.
The study's authors say the global shift toward a more intensive style of coffee farming is probably having a negative effect on the environment, communities and individual farmers.
"The paradox is that there is greater public interest than ever in environmentally friendly coffee, but where coffee ...
Synapses -- stability in transformation
2014-04-16
This news release is available in German. Synapses are the points of contact at which information is transmitted between neurons. Without them, we would not be able to form thoughts or remember things. For memories to endure, synapses sometimes have to remain stable for very long periods. But how can a synapse last if its components have to be replaced regularly? Scientists from the Max Planck Institute of Neurobiology in Martinsried near Munich have taken a decisive step towards answering this question. They have succeeded in demonstrating that when a synapse is formed, ...
Scratching the surface: Microbial etchings in impact glass and the search for life on Mars
2014-04-16
Boulder, Colo., USA – Haley M. Sapers and colleagues provide what may be the first report of biological activity preserved in impact glass. Recent research has suggested that impact events create novel within-rock microbial habitats. In their paper, "Enigmatic tubular features in impact glass," Sapers and colleagues analyze tubular features in hydrothermally altered impact glass from the Ries Impact Structure, Germany, that are remarkably similar to the bioalteration textures observed in volcanic glasses.
The authors note that mineral-forming processes cannot easily ...
Cancer drugs block dementia-linked brain inflammation, UCI study finds
2014-04-16
Irvine, Calif., April 16, 2014 — A class of drugs developed to treat immune-related conditions and cancer – including one currently in clinical trials for glioblastoma and other tumors – eliminates neural inflammation associated with dementia-linked diseases and brain injuries, according to UC Irvine researchers.
In their study, assistant professor of neurobiology & behavior Kim Green and colleagues discovered that the drugs, which can be delivered orally, eradicated microglia, the primary immune cells of the brain. These cells exacerbate many neural diseases, including ...
Recycling industrial waste water
2014-04-16
A research group composed of Dr. Martin Prechtl, Leo Heim and their colleagues at the University of Cologne's Department of Chemistry has discovered a new method of generating hydrogen using water and formaldehyde. The generation of hydrogen from liquids is of particular interest when it comes to fuel cell technologies. The results of the project, entitled "Selective and mild hydrogen production using water and formaldehyde", have recently been published in the journal Nature Communications.
Among other applications, the new approach can be used to recycle industrial ...
Research uncovers DNA looping damage tied to HPV cancer
2014-04-16
It's long been known that certain strains of human papillomavirus (HPV) cause cancer. Now, researchers at The Ohio State University have determined a new way that HPV might spark cancer development – by disrupting the human DNA sequence with repeating loops when the virus is inserted into host-cell DNA as it replicates.
Worldwide, HPV causes about 610,000 cases of cancer annually, accounting for about five percent of all cancer cases and virtually all cases of cervical cancer. Yet, the mechanisms behind the process aren't yet completely understood.
This study, recently ...