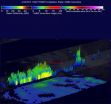
(Press-News.org) Tropical Cyclone Jack had weakened to a tropical depression when NASA and JAXA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite passed above on April 22, 2014 at 1120 UTC/7:20 a.m. EDT.
At that time, TRMM found that Jack was devoid of almost all rainfall near the tropical cyclone's center. Outside the center was a different story, however. That's where TRMM's precipitation radar instrument found rain falling at a rate of over 130mm/hr (about 5.1 inches) in a band of thunderstorms that stretched from east of Jack's center to the south. Some of the thunderstorms even stretched as high as 15 km (9.3 miles).
Wind shear continued to pummel the tropical cyclone and by April 23, Jack had fizzled in the Southern Indian Ocean.
INFORMATION:
Text credit: Harold F. Pierce
SSAI/NASA Goddard Space Flight Center
NASA sees last vestiges of Tropical Depression Jack
2014-04-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
EARTH Magazine: Faking quakes at full scale
2014-04-23
Alexandria, Va. – On a muggy day in mid-July 2009, a lone seven-story condominium complex northwest of Kobe, Japan, was violently shaken by an earthquake. Onlookers watched the 23-unit, wood-frame tower sway and bounce while, inside the building, furniture toppled and plates clattered to the floor. No one was hurt during the highly localized event and there was only minimal damage, in part because the building's wooden skeleton had been augmented to better resist earthquake shaking, but also because the whole event — from the seismicity to the partially furnished building ...
Some astronauts at risk for cognitive impairment, animal studies suggest
2014-04-23
Johns Hopkins scientists report that rats exposed to high-energy particles, simulating conditions astronauts would face on a long-term deep space mission, show lapses in attention and slower reaction times, even when the radiation exposure is in extremely low dose ranges.
The cognitive impairments — which affected a large subset, but far from all, of the animals — appear to be linked to protein changes in the brain, the scientists say. The findings, if found to hold true in humans, suggest it may be possible to develop a biological marker to predict sensitivity to radiation's ...
Gold nanoparticles help target, quantify breast cancer segments in a living cell
2014-04-23
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - Purdue University researchers have developed a way to detect and measure cancer levels in a living cell by using tiny gold particles with tails of synthetic DNA.
A team led by Joseph Irudayaraj, professor of agricultural and biological engineering, used gold nanoparticles to target and bind to fragments of genetic material known as BRCA1 messenger RNA splice variants, which can indicate the presence and stage of breast cancer. The number of these mRNA splice variants in a cell can be determined by examining the specific signal that light produces ...
Study identifies enzymes that help fix cancer-causing DNA defects
2014-04-23
Purdue University researchers have identified an important enzyme pathway that helps prevent new cells from receiving too many or too few chromosomes, a condition that has been directly linked to cancer and other diseases.
Mark Hall, associate professor of biochemistry, found that near the end of cell division, the enzyme Cdc14 activates Yen1, an enzyme that ensures any breaks in DNA are fully repaired before the parent cell distributes copies of the genome to daughter cells. This process helps safeguard against some of the most devastating genome errors, including the ...
A key to enjoying massive online photo files may be giving up some control
2014-04-23
PITTSBURGH—The ability of individuals to store and instantly access thousands of their photos online has become a commonplace luxury, but the sheer size of these archives can be intimidating. Researchers at Carnegie Mellon University and Microsoft Research Cambridge, UK, have found people might actually enjoy their collections more by giving up a bit of control and learning to wait.
Their 14-month study showed that people reflected more on past events and developed a renewed interest in their online photos when a device called Photobox would randomly print four or five ...
AGU: Odds of storm waters overflowing Manhattan seawall up 20-fold, new study shows
2014-04-23
WASHINGTON, D.C. -- Maximum water levels in New York harbor during major storms have risen by nearly two and a half feet since the mid-1800s, making the chances of water overtopping the Manhattan seawall now at least 20 times greater than they were 170 years ago, according to a new study. Whereas sea-level rise, which is occurring globally, has raised water levels along New York harbor by nearly a foot and a half since the mid-19th century, the research shows that the maximum height of the city's "once-in-10-years" storm tide has grown additionally by almost a foot in that ...
Study finds long-term survival of human neural stem cells transplanted into primate brain
2014-04-23
Putnam Valley, NY. (Apr. 23 2014) – A team of researchers in Korea who transplanted human neural stem cells (hNSCs) into the brains of nonhuman primates and assessed cell survival and differentiation after 22 and 24 months found that the hNSCs had differentiated into neurons at 24 months and did not cause tumors.
The study will be published in a future issue of Cell Transplantation but is currently freely available on-line as an unedited early e-pub at: http://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/cog/ct/pre-prints/content-ct1117Antonucci2.
The hNSCs were labeled with magnetic ...
Scientists identify source of mysterious sound in the Southern Ocean
2014-04-23
Scientists have conclusive evidence that the source of a unique rhythmic sound, recorded for decades in the Southern Ocean and called the "bio-duck," is the Antarctic minke whale (Balaenoptera bonaerensis). First described and named by submarine personnel in the 1960s who thought it sounded like a duck, the bio-duck sound has been recorded at various locations in the Southern Ocean, but its source has remained a mystery, until now.
In February 2013, an international team of researchers deployed acoustic tags on two Antarctic minke whales in Wilhelmina Bay off the western ...
Autologous stem cell therapy improves motor function in chronic stroke victims
2014-04-23
Putnam Valley, NY. (Apr. 23, 2014) – People who have had a stroke, often suffer motor deficits with little potential to restore neurological function. However, a study conducted in Taiwan, that will be published in a future issue of Cell Transplantation, but is currently freely available on-line as an unedited early e-pub at: http://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/cog/ct/pre-prints/content-ct1168Chen, has found that when one group of stroke victims had their own peripheral blood stem cells (PBSCs) injected directly into the brain and a similar group did not, those who received ...
Too many chefs: Smaller groups exhibit more accurate decision-making
2014-04-23
The trope that the likelihood of an accurate group decision increases with the abundance of brains involved might not hold up when a collective faces a variety of factors — as often happens in life and nature. Instead, Princeton University researchers report that smaller groups actually tend to make more accurate decisions while larger assemblies may become excessively focused on only certain pieces of information.
The findings present a significant caveat to what is known about collective intelligence, or the "wisdom of crowds," wherein individual observations — even ...