(Press-News.org) A new report quantifies for the first time how much our food choices affect pollutant nitrogen emissions, climate change and land-use across Europe.
The executive summary of the European Nitrogen Assessment Special Report on Nitrogen and Food, 'Nitrogen on the Table', was released today (Friday 25 April 2014). The Special report provides an assessment of what would happen if Europe were to decrease its consumption of meat and dairy products. It shows how much cutting down on meat and dairy in our diets would reduce nitrogen air and water pollution, and greenhouse gas emissions, while freeing up large areas of farmland for other purposes such as food export or bioenergy. It also considers the health benefits of reduced meat consumption. The full report is published next month.
Report lead author Henk Westhoek, program manager for Agriculture and Food at PBL (the Netherlands Environmental Assessment Agency) said, "The report shows that the nitrogen footprint of meat and dairy is considerably higher than that from plant-based products. If all people within the EU would halve their meat and dairy consumption, this would reduce greenhouse gas emissions from agriculture by 25 to 40%, and nitrogen emissions by 40%. The EU could become a major exporter of food products, instead of a major importer of for example soy beans."
The work has been conducted by the 'Task Force on Reactive Nitrogen' of the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE). In 2011 the Task Force produced the first 'European Nitrogen Assessment' (ENA) which showed that better nitrogen management will help reduce air, water and soil pollution, greenhouse gas emissions, simultaneously reducing threats to human health, biodiversity and food security.
Co-author of the report Prof Mark Sutton, an Environmental Physicist at the UK's Centre for Ecology and Hydrology, said, "Human's use of nitrogen is a major societal challenge that links environment, food security, and human health. There are many ways in which society could improve the way it uses nitrogen, and this includes actions by farmers and by ourselves. Our new study shows that adopting a demitarian* diet across Europe would reduce nitrogen pollution levels by about 40%, which is similar to what could be achieved by adopting low-emission farming practices."
The UNECE Task Force on Reactive Nitrogen is tasked with providing policy makers in the Convention on Long-range Transboundary Air Pollution with scientific evidence to support international decision making on environmental policies, especially as these link air pollution with water, soil, climate and biodiversity.
Professor Sutton said, "As the EU now starts to renegotiate the National Emissions Ceilings Directive, it is an open question to what extent countries will emphasize technical measures or such behavioural changes. One of the major barriers to action is the international trade in food commodities. The result is that countries fear that tackling nitrogen pollution will reduce their international competitiveness. The present study shows that there is huge power for pollution control in simply reducing our meat and dairy consumption."
Dr Alessandra Di Marco, a co-author of the study and researcher at the Air Pollution Unit of the Italian National Agency for New Technologies, Energy and Sustainable Economic Development, has been involved in a number of food pilot projects in Italian schools. She said, "The school food pilot projects in Italy have shown added value environmental benefits and health benefits associated with 'smart food'. This is a new concept in Italian schools where children are informed about health principle of nutrition, but it still misses the connection with environmental co-benefits of the healthy choice. Increasing the awareness of dietary choice in children is the starting point for cleaning the environment."
INFORMATION: END
Nitrogen pollution, climate and land use: Why what we eat matters
2014-04-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
A civil war inside our cells: Scientists show how our bodies fight off 'jumping genes'
2014-04-25
ANN ARBOR, Mich. — There's a civil war going on inside every one of the 37 trillion cells in your body. Now, University of Michigan scientists have uncovered how your cells keep this war from causing too much collateral damage.
On one side of the battle: your "regular" DNA, which provides the day-to-day instructions for life. On the other side: tiny bits of rogue DNA that hide like spies between genes in your own DNA. From time to time, these rogue bits of DNA spin off a copy of themselves and "jump" to another DNA location – often causing harmful mutations when they ...
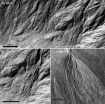
Traces of recent water on Mars
2014-04-25
The southern hemisphere of Mars is home to a crater that contains very well-preserved gullies and debris flow deposits. The geomorphological attributes of these landforms provide evidence that they were formed by the action of liquid water in geologically recent time.
Evidence of liquid water
When sediment on a slope becomes saturated with water, the mixture may become too heavy to remain in place, leading to a flow of debris and water as a single-phase unit. This is called a debris flow. Debris flows on Earth often cause significant material destruction and even human ...
Tsetse fly genetic code sequenced
2014-04-25
Scientists at the University of Liverpool have been part of a ten-year project which has successfully sequenced the genetic code of the tsetse fly – making major advances in disease control possible.
Tsetse flies are unique to Africa and can infect people bitten by them with sleeping sickness, a disease which damages the nervous system and is fatal if untreated. This kills over 250,000 people each year.
Traditional methods of control such as releasing sterile males, trapping and pesticide spraying are expensive and difficult to implement. Sleeping sickness can also ...
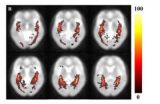
Quantitative volumetric analysis of the optic radiation in the normal human brain
2014-04-25
The optic radiation is a dense fiber tract that emerges from the lateral geniculate nucleus and continues to the occipital visual cortex. Especially, the optic radiation is an important fiber structure that conveys visual information from the lateral geniculate nucleus to the primary visual cortex in the occipital lobe. Current studies have focused on the anatomical characteristics of optic radiation fiber tracts in individual brains and on comparisons of the anatomical characteristics of the optic radiation fiber tracts between patient and control groups. Therefore, no ...
Climate change: Don't wait until you can feel it
2014-04-25
Washington, D.C.— Despite overwhelming scientific evidence for the impending dangers of human-made climate change, policy decisions leading to substantial emissions reduction have been slow. New work from Carnegie's Katharine Ricke and Ken Caldeira focuses on the intersection between personal and global impacts. They find that even as extreme weather events influence those who experience them to support policy to address climate change, waiting for the majority of people to live through such conditions firsthand could delay meaningful action by decades. Their findings ...
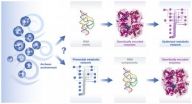
Reconstructed ancient ocean reveals secrets about the origin of life
2014-04-25
HEIDELBERG, 25 April 2014 – Researchers from the University of Cambridge have published details about how the first organisms on Earth could have become metabolically active. The results, which are reported in the journal Molecular Systems Biology, permit scientists to speculate how primitive cells learned to synthesize their organic components – the molecules that form RNA, lipids and amino acids. The findings also suggest an order for the sequence of events that led to the origin of life.
A reconstruction of Earth's earliest ocean in the laboratory revealed the spontaneous ...
Metabolism may have started in our early oceans before the origin of life
2014-04-25
The chemical reactions behind the formation of common metabolites in modern organisms could have formed spontaneously in the earth's early oceans, questioning the events thought to have led to the origin of life.
In new research funded by the Wellcome Trust, researchers at the University of Cambridge reconstructed the chemical make-up of the earth's earliest ocean in the laboratory. The team found the spontaneous occurrence of reaction sequences which in modern organisms enable the formation of molecules essential for the synthesis of metabolites such as amino acids, ...
Apps, Touch Tablets Bringing Mobility to Chemical Research Industry
2014-04-25
The formula for success in the chemical research industry is beginning to take shape outside of the traditional laboratory setting.
Touch-enabled software and tablets are transforming chemical researchers' workflows, bringing time-savings and mobile capability to professionals who are used to desktop computers and the pen-and-paper mentality.
For example, the updated Mobile Reagents scientific app from Eidogen-Sertanty now offers a Windows* 8 version for touch devices built on Intel architecture, and allows mobile access to more than 17 million chemical product variations ...
3rd Twin's New Single, '3rd,' 'Leaks' Online Ahead of Release of Underground Mixtape
2014-04-25
The wait is over there has been a leak of 3rd Twin's new hit from the highly anticipated "50 artist 50 states" Underground Mixtape, slated for release May 9th. 3rd Twin, Portland, Oregon's best lyricist is back with a vengeance with "3rd" "leaked" online Sunday night.
"3rd" #1 wit a bullet 50 artist 50 states is 3rd Twin at his best displaying his clever word play and powerful punchlines. "3rd" is a definite anthem and club banger and great follow up to his first single "Future in ya Stuntin," which caused quite the stir on the internet, creating a huge buzz as he shot ...
Charleston Culinary Tours Presents a Special Taste of the Market on May 15th at 6:30pm on Anson St. to Celebrate our Civil Servants, Military, Hometown Heroes and Local Community Leaders.
2014-04-25
Charleston Culinary Tours presents a special Taste of the Market on May 15th at 6-8:30pm at the Palmetto Carriage lot on Anson Street by the City Market that celebrates local civil servants, military personnel, hometown heroes and community leaders. For devotion to duty and sacrifice of self, they will receive a discounted admission of $5 (saving $5) and other giveaways with uniform or ID badge. Additionally, Charleston Culinary Tours is offering 10% off on culinary tours and 20% off any Mixology Tour in May, June or July with sign up at the Taste of the Market. The mission ...