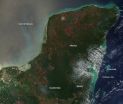
(Press-News.org) April is in the middle of the dry season, which runs from January through May in this region, and naturally coincides with fire season. Farmers often use fire to return nutrients to the soil and to clear the ground of unwanted plants. Fire helps enhance crops and grasses for pasture. Some of the fires in this image may be wildfires, with natural (lightning) or accidental (human) sources. As the dry season progresses, the number of fires tend to grow, as does the blanket of smoke which settles over the land, and although the fire may help the farmers get their lands ready for planting season, unfortunately, the fires also produce smoke that degrades air quality.
This natural-color satellite image was collected by the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) aboard the Terra satellite on April 24, 2014. Actively burning areas, detected by MODIS's thermal bands, are outlined in red. Each hot spot, which appears as a red mark, is an area where the thermal detectors on the MODIS instrument recognized temperatures higher than background. When accompanied by plumes of smoke, as in this image, such hot spots are diagnostic for fire.
INFORMATION:NASA image courtesy Jeff Schmaltz, MODIS Rapid Response Team. Caption: NASA/Goddard, Lynn Jenner END
Fires in the Yucatan Peninsula in April 2014
2014-04-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Function found for mysterious heart disease gene
2014-04-25
OTTAWA, April 24, 2014 - A new study from researchers at the University of Ottawa Heart Institute (UOHI), published today in Cell Reports, sheds light on a mysterious gene that likely influences cardiovascular health. After five years, UOHI researchers now know how one genetic variant works and suspect that it contributes to the development of heart disease through processes that promote chronic inflammation and cell division.
Researchers at the Ruddy Canadian Cardiovascular Genetics Centre had initially identified a variant in a gene called SPG7 as a potential contributor ...
Study finds almost half of homeless men had traumatic brain injury in their
2014-04-25
TORONTO, April 25, 2014—Almost half of all homeless men who took part in a study by St. Michael's Hospital had suffered at least one traumatic brain injury in their life and 87 per cent of those injuries occurred before the men lost their homes.
While assaults were a major cause of those traumatic brain injuries, or TBIs, (60 per cent) many were caused by potentially non-violent mechanisms such as sports and recreation (44 per cent) and motor vehicle collisions and falls (42 per cent).
The study, led by Dr. Jane Topolovec-Vranic, a clinical researcher in the hospital's ...
UNC researchers link aging to cellular interactions that occur across generations
2014-04-25
April 24, 2014
CHAPEL HILL, N.C. – The evidence for what causes aging has typically been limited to the study of a single organism's lifespan; our cells divide many times throughout our lives and eventually cause organs and our bodies to age and break down. But new research from the UNC School of Medicine suggests that how we age might depend on cellular interactions that we inherit from ancestors throughout many generations.
By studying the reproductive cells of nematodes – tiny worms found in soil and compost bins – Shawn Ahmed, PhD, an associate professor of genetics, ...
Scripps Florida scientists find connection between gene mutation, key symptoms of autism
2014-04-25
JUPITER, FL – April 25, 2014 – Scientists have known that abnormal brain growth is associated with autism spectrum disorder. However, the relationship between the two has not been well understood.
Now, scientists from the Florida campus of The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) have shown that mutations in a specific gene that is disrupted in some individuals with autism results in too much growth throughout the brain, and yet surprisingly specific problems in social interactions, at least in mouse models that mimic this risk factor in humans.
"What was striking is ...
Are almonds an optimal snack?
2014-04-25
Modesto, CA (April 25, 2014) - Six new almond-related research studies will be presented next week in San Diego at the American Society of Nutrition (ASN)'s Scientific Sessions and Annual Meeting, held in conjunction with Experimental Biology 2014 (EB). The conference attracts an international audience of approximately 13,000 leading scientists specializing in various health disciplines.
The science presented will reveal new insights on the effects of almond consumption on overall diet quality and health status, abdominal adiposity, measures of appetite and satiety, and ...
New sensor molecules have potential for early cancer detection
2014-04-25
A research team lead by Academy Professor Kari Rissanen at the University of Jyväskylä has discovered a new water-soluble fluorescent detection system that is extremely sensitive to pyrophosphate (PPi).
Pyrophosphate has a key role in energy transduction, DNA replication and other metabolic processes that are dysregulated in cancer cells.
The discovery might lead to the development of a method for early detection of cancer cells.
The team developed a simple metal complex which shows an intense orange fluorescent color in the presence of very low concentration of pyrophosphate ...
Researchers at LSTM part of the international team to sequence the tsetse genome
2014-04-25
Researchers from LSTM are among those who have sequenced the genome of a species of tsetse fly (Glossina morsitans). The outcomes of this research will be invaluable to understanding more about the tsetse and other insect vector biology, knowledge which can be applied to improving the current vector control methods and may lead to more effective and affordable control strategies.
A paper summarising some of the findings will be published in the journal Science today, with more specific and in depth analyses of various aspects of tsetse biology being published as a collection ...
Know your enemy
2014-04-25
Researchers at Aarhus University, Denmark, have drawn up the most detailed 'image of the enemy' to date of one of the body's most important players in the development of Parkinson's disease. This provides much greater understanding of the battle taking place when the disease occurs – knowledge that is necessary if we are to understand and treat Parkinsonism. However, it also raises an existential question because part of the conclusion is that we do not live forever!
Parkinson's disease is one of the most common neurological disorders, with about 7000 people suffering ...
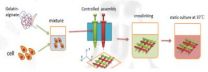
3D printing cancer tumors
2014-04-25
Drexel's Wei Sun, PhD, Albert Soffa chair professor in the College of Engineering, has devised a method for 3D printing tumors that could soon be taking cancer research out of the petri dish.
Using a mixture of cervical cancer cells and a hydrogel substance that resembles an ointment balm, Sun can print out a tumor model that can be used for studying their growth and response to treatment. This living model will give cancer researchers a better look at how tumors behave and a more accurate measure of how they respond to treatment.
"This is the first time to report ...
Study reaffirms soy-dairy protein blend increases muscle mass
2014-04-25
A new study published online in the Journal of Applied Physiology shows additional benefits of consuming a blend of soy and dairy proteins after resistance exercise for building muscle mass. Researchers from the University of Texas Medical Branch found that using a protein blend of soy, casein and whey post-workout prolongs the delivery of select amino acids to the muscle for an hour longer than using whey alone. It also shows a prolonged increase in amino acid net balance across the leg muscle during early post-exercise recovery, suggesting prolonged muscle building. ...