(Press-News.org) SAN DIEGO, Calif. April 28, 2014 – A morning and evening ritual of tart cherry juice may help you sleep better at night, suggests a new study presented today at the Experimental Biology 2014 meeting. Researchers from Louisiana State University found that drinking Montmorency tart cherry juice twice a day for two weeks helped increase sleep time by nearly 90 minutes among older adults with insomnia.
These findings were presented Monday, April 28, at the "Dietary Bioactive Components: Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Effects of Dietary Bioactive Components" section of the annual meeting of the American Society of Nutrition, which is being held in conjunction with the Experimental Biology 2014 meeting in San Diego. The findings have been submitted for publication in a peer-reviewed journal.
Insomnia is a common health problem among older adults, impacting an estimated 23 to 34 percent of the population ages 65 and older. Insomnia – defined as trouble sleeping on average more than three nights per week – can be an annoyance for some, but long-lasting sleeplessness can seriously affect health, especially in the elderly.
Insomnia is linked to a higher prevalence of chronic pain, high blood pressure, type 2 diabetes and a decline of cognitive function, or dementia. Individuals with insomnia may turn to sleeping pills; however, these sedative medications have been found to increase risk of falls in the elderly – which makes it increasingly important to find more natural sleep-aids without these apparent side effects, said co-author Frank L. Greenway, MD, director of the outpatient research clinic at the Pennington Biomedical Research Center at Louisiana State University.
"Sleeping pills may be an option for younger insomniacs, but for older people these medications quadruple the risk of falling, which can lead to broken hips and, often, earlier death," Greenway said.
For the randomized crossover clinical trial, seven older adults (average age 68) with insomnia consumed 8 ounces of tart cherry juice twice daily for two weeks, followed by a two-week washout period, then a two-week period when another beverage was consumed (placebo). Greenway and his colleagues studied their slumber in a controlled setting, using overnight polysomnography to evaluate sleep efficiency, such as sleep onset and duration. Participants also completed questionnaires related to sleep, fatigue, depression and anxiety. Additionally, blood work was conducted on each participant.
The researchers found that those who drank the Montmorency tart cherry juice in the morning and at night were able to sleep more than an hour longer each night (averaging 84 minutes) compared to the placebo, and their sleep tended to be more efficient.
Montmorency tart cherries are a natural source of melatonin, a hormone that helps regulate the sleep-wake cycle. While previous studies have suggested that tart cherry juice has sleep-enhancing benefits, Greenway and colleagues set out to help explain why. They wanted to understand if the benefits were due to the melatonin content or another component in Montmorency tart cherries.
They believe the ruby red pigments in tart cherry juice, known as proanthocyanidins, also play a role. These natural polyphenolic compounds are especially abundant in Montmorency tart cherries. In the study, tart cherry juice helped to increase the availability of tryptophan, an essential amino acid and a precursor to serotonin that helps with sleep. The juice was shown in cells to inhibit an enzyme (indoleamine 2,3 dioxygenase) that degrades tryptophan. Tryptophan degradation is a known predictor of insomnia and is also related to inflammation, said co-authors Jack Losso and John Finley, professors in the School of Nutrition and Food Sciences at Louisiana State University Agricultural Center.
"Even though the amount of tryptophan in tart cherry juice is smaller than a normal dose given to aid sleep, the compounds in tart cherries could prevent the tryptophan from breaking down so it's able to work in the body more effectively," Greenway explained. "These compounds may help to improve tryptophan bioavailability for serotonin synthesis, which could have a positive effect on sleep. Increasing serotonin also helps improve mood and decrease inflammation."
Greenway believes it's the unique combination of melatonin and tryptophan in Montmorency tart cherries that is likely contributing to the sleep benefits. He and his colleagues conclude that drinking a glass of tart cherry juice in the morning and the evening may be a better and a safer way to treat insomnia.
INFORMATION:
Funding for this research was provided by the Cherry Marketing Institute, which had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis or preparation of the abstract or presentation. The study is registered at ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01669317.
Study: Tart cherry juice increases sleep time in adults with insomnia
2014-04-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Decrease in large wildlife drives an increase in rodent-borne disease and risk to humans
2014-04-28
Populations of large wildlife are declining around the world, while zoonotic diseases (those transmitted from animals to humans) are on the rise. A team of Smithsonian scientists and colleagues have discovered a possible link between the two. They found that in East Africa, the loss of large wildlife directly correlated with a significant increase in rodents, which often carry disease-causing bacteria dangerous to humans. The team's research is published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, April 28.
"Our study shows us that ecosystem health, wildlife ...
Smart home programming: Easy as 'if this, then that'
2014-04-28
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — The idea of a smart home sounds promising enough. Who doesn't want a house full of automated gadgets — from light switches to appliances to heating systems — that know exactly when to turn on, turn off, heat up or power down?
But in order for all those devices to do what they're supposed to do, they'll need to be programed — a task the average homeowner might not have the interest or the tech-savvy to perform. And nobody wants to call tech support just to turn on a light.
A group of computer science researchers from Brown and Carnegie ...
Satellite movie shows US tornado outbreak from space
2014-04-28
VIDEO:
This animation of NOAA's GOES-East satellite data shows the development and movement of the weather system that spawned tornadoes affecting seven central and southern US states on Apr. 27-28, 2014....
Click here for more information.
NASA has just released an animation of visible and infrared satellite data from NOAA's GOES-East satellite that shows the development and movement of the weather system that spawned tornadoes affecting seven central and southern U.S. states ...
NIH scientists establish monkey model of hantavirus disease
2014-04-28
WHAT: National Institutes of Health (NIH) researchers have developed an animal model of human hantavirus pulmonary syndrome (HPS) in rhesus macaques, an advance that may lead to treatments, vaccines and improved methods of diagnosing the disease. The study, conducted by researchers at NIH’s National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), is published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
People become infected with hantaviruses by inhaling virus from the urine, droppings or saliva of infected rodents. This infection can progress to HPS, ...
A water test for the world
2014-04-28
HAMILTON, April 28, 2014 – Inspiration can come in many forms, but this one truly was a breath of fresh air.
A group of McMaster researchers has solved the problem of cumbersome, expensive and painfully slow water-testing by turning the process upside-down.
Instead of shipping water to the lab, they have created a way to take the lab to the water, putting potentially life-saving technology into the hands of everyday people.
The team has reduced the sophisticated chemistry required for testing water safety to a simple pill, by adapting technology found in a dissolving ...
Technological advancements extend survival of transplanted hearts across species
2014-04-28
The use of transplant organs from animals (xenotransplantation) could help to compensate for the shortage of human organs available for transplant. NIH researchers have demonstrated that by using hearts from genetically engineered pigs in combination with target-specific immunosuppression of recipient baboons, organ survival can be significantly prolonged. This has potential for paving the way for the use of animal organs for transplantation into humans.
Toronto, ON, Canada, April 28, 2014 – Cardiac transplantation is the treatment of choice for end stage heart failure. ...
Disney Researchers use 3-D printing to produce interactive speakers of any shape
2014-04-28
Forget everything you know about what a loudspeaker should look like. Scientists at Disney Research, Pittsburgh have developed methods using a 3D printer to produce electrostatic loudspeakers that can take the shape of anything, from a rubber ducky to an abstract spiral.
The simple speakers require little assembly, but even those few manual steps might be eliminated in the future, said Yoshio Ishiguro, a Disney Research, Pittsburgh post-doctoral associate. "In five to 10 years, a 3D printer capable of using conductive materials could create the entire piece," he predicted.
The ...
Well-informed patients key to accepting gene-based drug dosing
2014-04-28
A new study out of Western University (London, Canada) illustrates the need for a lot more education around pharmacogenetics (PGx) –the study of how a patient's genes can affect drug reaction and dosage. PGx promises to optimize patient response to therapy, but this is the first study to really investigate how patients perceive this kind of genetic testing, and whether those perceptions differ when it comes to parents and their children. The research, led by Dr. Michael Rieder of Western's Schulich School of Medicine & Dentistry is published in the journal Pediatrics.
"Pharmacogenetic ...
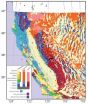
The thin-crusted US Sierra Nevada Mountains: Where did the Earth go?
2014-04-28
Boulder, Colo., USA – In an addition to Geosphere's ongoing themed issue series, "Geodynamics and Consequences of Lithospheric Removal in the Sierra Nevada, California," Craig H. Jones of the University of Colorado Boulder and colleagues examine the seismological study of the entire extent of the U.S. Sierra Nevada range using seismograms collected in the Sierra Nevada EarthScope field experiment from 2005 to 2007.
The southern Sierra Nevada is known to have unusually thin crust for mountains with such high elevations (peaks higher than 4 km/14,000 ft, and average elevations ...
Precise brain mapping can improve response to deep brain stimulation in depression
2014-04-28
Experimental studies have shown that deep brain stimulation (DBS) within the subcallosal cingulate (SCC) white matter of the brain is an effective treatment for many patients with treatment-resistant depression. Response rates are between 41 percent and 64 percent across published studies to date.
One of the proposed mechanisms of action is the modulation of a network of brain regions connected to the SCC. Identifying the critical connections within this network for successful antidepressant response is an important next step.
A new study using MRI analysis of the ...