(Press-News.org) Orlando, Fla. — New research finds that cataract surgery dramatically decreases the number of falls individuals suffer due to poor vision. The research is being presented at the 2014 Annual Meeting of the Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology (ARVO) this week in Orlando, Fla.
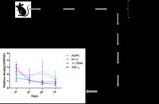
In a study of more than 400 Vietnamese patients who were 50-plus years old with cataracts in both eyes, the number of falls patients suffered before and after cataract surgery was monitored. Researchers found a 78% decrease in the risk of falls the year after patients had cataract surgery on one eye.
A cataract, which develops when the part of the eye known as the lens becomes cloudy, is a common eye condition in senior citizens that leads to dull or blurry vision.
Abstract Title: A Longitudinal Study of the Impact of First and Second Eye Cataract Surgery on Falls in Vietnam
Presentation Start/End Time: Monday, May 5, 11:30 – 11:45am
Location: S 320CD
Session Number: 231
INFORMATION:
The Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology (ARVO) is the largest eye and vision research organization in the world. Members include some 11,500 eye and vision researchers from over 70 countries. ARVO encourages and assists research, training, publication and knowledge-sharing in vision and ophthalmology.
All abstracts accepted for presentation at the ARVO Annual Meeting represent previously unpublished data and conclusions. This research may be proprietary or may have been submitted for journal publication. Embargo policy: Journalists must seek approval from the presenter(s) before reporting data from paper or poster presentations. Press releases or stories on information presented at the ARVO Annual Meeting may not be released or published until the conclusion of the presentation.
Visit us at:
Website: http://www.arvo.org
Twitter: http://www.twitter.com/#!/ARVOinfo
Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/ARVOinfo
Flicker: http://www.flickr.com/photos/ARVOinfo
YouTube: http://www.youtube.com/user/ARVOinfo
Cataract surgery decreases risk of falls in older patients
2014-05-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Simulated model of eye's 3D structure facilitates stem cells transplant
2014-05-06
Orlando, Fla. — Scientists have developed a model that mimics the complex structure of the cornea to enable the transplant of healthy corneal stem cells. The research is being presented at the 2014 Annual Meeting of the Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology (ARVO) this week in Orlando Fla.
Used to restore sight, corneal stem cells live in a specific physical environment. Transplanting these stem cells requires accurate mimicry of their natural surroundings during transport. In this work, vision scientists have recreated the 3D architecture where corneal ...
Astronomers harness the galaxy's biggest telescope
2014-05-06
An international team of astronomers has made a measurement of a distant neutron star that is one million times more precise than the previous world's best.
The researchers were able to use the interstellar medium, the 'empty' space between stars and galaxies that is made up of sparsely spread charged particles, as a giant lens to magnify and look closely at the radio wave emission from a small rotating neutron star.
This technique yielded the highest resolution measurement ever achieved, equivalent to being able to see the double-helix structure of our genes from the ...
A novel transgenic mouse model of Chinese Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 2L
2014-05-06
Dr. Ruxu Zhang and colleagues from Third Xiangya Hospital, Central South University in China previously found that the K141N mutation in heat shock protein B8 (HSPB8) was responsible for Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 2L in a large Chinese family. Therefore, they generated a transgenic mouse model bearing the K141N mutation in the human HSPB8 gene, and to determine whether this K141NHSPB8 transgenic mouse model would manifest the clinical phenotype of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 2L, and consequently be suitable for use in studies of disease pathogenesis. The K141NHSPB8 ...
Regulatory effects of glial cells on retinal synaptic plasticity
2014-05-06
Different types of retinal damage could induce plastic changes of retinal synapses, which might precede the serious damage of neuron soma. These morphological and functional changes to synapses after retinal injury could explain why many intervention measures protected neurons from death but failed to fully recover the damaged visual function. Therefore, it is necessary to investigate both the protection of synapses as well as protecting neurons from death. Dr. Lihong Zhou and co-workers from Central South University in China suggested that retinal glial cell activation ...
The Pael-R gene does not mediate the changes in rotenone-induced PD model cells
2014-05-06
Currently, the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease is not entirely clear, but it has been generally considered to be the result of interactions among various genetic and environmental factors. Ting Zou and coworkers from Second Xiangya Hospital, Central South University in China previously found that Parkin mutation causes Parkin-associated endothelin receptor-like receptor (Pael-R) protein deposition, and the associated cytotoxicity leads to dopaminergic neuronal apoptosis. These researchers speculated that the Pael-R gene is possibly involved in the action of rotenone ...
AMPK and inflammatory mediators are involved in postoperative cognitive dysfunction
2014-05-06
Postoperative cognitive dysfunction is associated with neuronal apoptosis, which may result from post-surgery inflammation, the phosphorylation of tau protein and the accumulation of amyloid in aged people. 5′adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) can be involved in anti-inflammation, neuronal repair and anti-inflammation of the body through different downstream proteins and pathways. In addition, the activation of AMPK regulates tau protein phosphorylation and reduces amyloidogenesis in neurons. Yanlin Bi and co-workers from the Affiliated Qianfoshan ...
Danish social workers have become the moral agents of the state
2014-05-06
"We are turning the professional social workers into moral agents. This development recalls a time before the welfare state, when we had poor relief and when the extent to which the state could help you depended on your own dignity."
This is the assertion by Marie Østergaard Møller, who is associate professor at the Department of Political Science and Government, Aarhus University regarding the labour market policy that has been carried out in Denmark since the 1990s. More specifically, since 1994 the opportunities for citizens to get relief from the state have been reduced. ...
Hotspots of climate change impacts in Africa: Making sense of uncertainties
2014-05-06
Overlapping impacts of climate change such as drought or flooding, declining crop yields or ecosystem damages create hotspots of risk in specific parts of Africa. These are for the first time identified in a study now published by the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research. The uncertainties in assessing the impacts do not necessarily hamper but can inform development strategies, according to the scientists. Likelihood and potential severity of impacts can be weighed to decide on suitable adaptation measures.
"We found three regions to be amongst those most at ...
Nanocellulose sponges to combat oil pollution
2014-05-06
All industrial nations need large volumes of oil which is normally delivered by ocean-going tankers or via inland waterways to its destination. The most environmentally-friendly way of cleaning up nature after an oil spill accident is to absorb and recover the floating film of oil. The Empa researchers Tanja Zimmermann and Philippe Tingaut, in collaboration with Gilles Sèbe from the University of Bordeaux, have now succeeded in developing a highly absorbent material which separates the oil film from the water and can then be easily recovered, "silylated" nanocellulose sponge. ...
Molecular switches age-related memory decline? Genetic variant protect against brain aging
2014-05-06
Philadelphia, PA, May 6, 2014 – Even among the healthiest individuals, memory and cognitive abilities decline with age. This aspect of normal aging can affect an individual's quality of life and capability to live independently but the rate of decline is variable across individuals. There are many factors that can influence this trajectory, but perhaps none more importantly than genetics.
Scientists are seeking to identify key molecular switches that control age-related memory impairment. When new molecules are identified as critical to the process of memory consolidation, ...