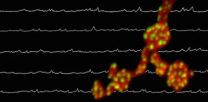
(Press-News.org) Move over, Matrix - astronomers have done you one better. They have created the first realistic virtual universe using a computer simulation called "Illustris." Illustris can recreate 13 billion years of cosmic evolution in a cube 350 million light-years on a side with unprecedented resolution.
"Until now, no single simulation was able to reproduce the universe on both large and small scales simultaneously," says lead author Mark Vogelsberger (MIT/Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics), who conducted the work in collaboration with researchers at several institutions, including the Heidelberg Institute for Theoretical Studies in Germany.
These results are being reported in the May 8th issue of the journal Nature.
Previous attempts to simulate the universe were hampered by lack of computing power and the complexities of the underlying physics. As a result those programs either were limited in resolution, or forced to focus on a small portion of the universe. Earlier simulations also had trouble modeling complex feedback from star formation, supernova explosions, and supermassive black holes.
Illustris employs a sophisticated computer program to recreate the evolution of the universe in high fidelity. It includes both normal matter and dark matter using 12 billion 3-D "pixels," or resolution elements.
The team dedicated five years to developing the Illustris program. The actual calculations took 3 months of "run time," using a total of 8,000 CPUs running in parallel. If they had used an average desktop computer, the calculations would have taken more than 2,000 years to complete.
The computer simulation began a mere 12 million years after the Big Bang. When it reached the present day, astronomers counted more than 41,000 galaxies in the cube of simulated space. Importantly, Illustris yielded a realistic mix of spiral galaxies like the Milky Way and football-shaped elliptical galaxies. It also recreated large-scale structures like galaxy clusters and the bubbles and voids of the cosmic web. On the small scale, it accurately recreated the chemistries of individual galaxies.
Since light travels at a fixed speed, the farther away astronomers look, the farther back in time they can see. A galaxy one billion light-years away is seen as it was a billion years ago. Telescopes like Hubble can give us views of the early universe by looking to greater distances. However, astronomers can't use Hubble to follow the evolution of a single galaxy over time.
"Illustris is like a time machine. We can go forward and backward in time. We can pause the simulation and zoom into a single galaxy or galaxy cluster to see what's really going on," says co-author Shy Genel of the CfA.
INFORMATION:
The team is releasing a high-definition video, which morphs between different components of the simulation to highlight various layers (e.g. dark matter density, gas temperature, or chemistry). They also are releasing several smaller videos and associated imagery online at http://www.illustris-project.org/
Astronomers create first realistic virtual universe
2014-05-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Brain noise found to nurture synapses
2014-05-07
NEW YORK, NY (May 7, 2014) — A study has shown that a long-overlooked form of neuron-to-neuron communication called miniature neurotransmission plays an essential role in the development of synapses, the regions where nerve impulses are transmitted and received. The findings, made in fruit flies, raise the possibility that abnormalities in miniature neurotransmission may contribute to neurodevelopmental diseases. The findings, by researchers at Columbia University Medical Center (CUMC), were published today in the online edition of the journal Neuron.
The primary way ...
Native algae species to blame for 'rock snot' blooms in rivers worldwide
2014-05-07
VIDEO:
The recent appearance of the freshwater algae known as "rock snot " on river bottoms worldwide is caused by a native species responding to changing environmental conditions rather than by accidental...
Click here for more information.
The recent blooms of the freshwater algae known as "rock snot" on river bottoms worldwide are caused by a native species responding to changing environmental conditions rather than by accidental introductions by fishermen or the ...
Early depression, anger may taint love life even 20 years later, study shows
2014-05-07
A University of Alberta study is helping crack the code to happiness by exploring the long reach of depression and anger over more than two decades.
The study, published recently in the Journal of Family Psychology, followed 341 people for 25 years, and found that negative emotions they may have suffered as young adults can have a lasting grip on their couple relationships, well into middle age.
The fact that depression and anger experienced during the teen years clung to people, even through major life events such as child-rearing, marriages and careers was surprising, ...
Community doulas can be a big help for mother-baby relationships
2014-05-07
Young mothers are more likely to breastfeed and have positive relationships with their babies when they have another woman "mothering" them in the delivery room, according to new research at the University of Chicago on the value of doulas—women who help with deliveries and early care for mothers and babies.
The assistance from doulas is particularly valuable to young mothers from disadvantaged backgrounds. Those mothers sometimes receive help from women known as community doulas, who are from similar backgrounds as the young women and who visit them weekly for several ...
Emerald ash borers were in US long before first detection
2014-05-07
EAST LANSING, Mich. — New research at Michigan State University shows that the uber-destructive emerald ash borer arrived at least 10 years before it was first identified in North America.
The study, published in the current issue of journal Diversity and Distributions, shows that EABs were feasting on ash trees in southeast Michigan by the early 1990s, well before this pest was discovered in 2002, said Deb McCullough, MSU professor of forest entomology.
"We suspect they arrived inside wood crating or pallets imported from Asia where the beetle is native," she said. ...
Clues about black hole formation
2014-05-07
This news release is available in Spanish.
The work, which has had the participation of the Ikerbasque researcher Javier Gorosabal, co-director of the Associated Unit with the Institute of Astrophysics of Andalusia/CSIC-UPV/EHU, has been published in the prestigious journal Nature.
There is no other event in the cosmos that can compete in terms of energy and intensity with stellar explosions on the outer reaches of the universe and which are known as LGRBs (Long Gamma-Ray Bursts): in just one second a single GRB can emit as many as hundreds of stars like the Sun ...
How businesses can maximize revenue when introducing new products
2014-05-07
BUFFALO, N.Y. — Companies should use existing brand names and add new, sub-brand names to maximize revenue when introducing new products to market, according to a new study from the University at Buffalo School of Management.
Forthcoming in Management Science, the study notes a proliferation of new products in the consumer packaged-goods market each year. For example, U.S. manufacturers introduced more than 150,000 new products in 2010 alone. Of these, more than 90 percent were extensions of existing brand-name products.
"These new products can be line extensions, like ...
Regular doctor visits may greatly diminish skin cancer deaths
2014-05-07
VIDEO:
Melody Eide, M.D., M.P.H., a Henry Ford Hospital dermatologist and the study's lead author, says regular visits to the doctor may lead to significant reductions in melanoma mortality....
Click here for more information.
DETROIT – The risk of dying from the most dangerous type of skin cancer is significantly reduced with regular doctor visits, according to a Henry Ford Hospital study.
This is believed to be the first study of its kind to link melanoma mortality with ...
For slumbering diabetics, a way to detect low blood sugar and stop insulin delivery
2014-05-07
STANFORD, Calif. — New research could soon make it easier for people with type-1 diabetes to get a safe night's sleep, says a Stanford University School of Medicine scientist who led the study.
In a large trial conducted in patients' homes in the United States and Canada, scientists demonstrated that they could predict and prevent dangerously low overnight blood sugars in adolescents and adults with type-1 diabetes.
Very low blood-sugar levels can cause seizures or even, in rare cases, death. People with type-1 diabetes often sense warning signs of low blood sugar when ...
Ancient crater points to massive meteorite strike
2014-05-07
EDMONTON—The discovery of an ancient ring-like structure in southern Alberta suggests the area was struck by a meteorite large enough to leave an eight-kilometre-wide crater, producing an explosion strong enough to destroy present-day Calgary, say researchers from the Alberta Geological Survey and University of Alberta.
The first hints about the impact site near the southern Alberta hamlet of Bow City were discovered by a geologist with the Alberta Geological Survey and studied by a U of A team led by Doug Schmitt, Canada Research Chair in Rock Physics.
Time and glaciers ...