(Press-News.org) Premature menopause is associated with long-term negative effects on cognitive function, suggests a new study published today (7 May) in BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology (BJOG).
The average age of menopause is around 50 years in the Western World. Premature menopause refers to menopause at or before 40 years of age, this could be due to a bilateral ovariectomy, (surgically induced menopause)or non-surgical loss of ovarian function (sometimes referred to as 'natural' menopause).
The study, based on a sample of 4868 women, used cognitive tests and clinical dementia diagnosis at baseline and after two, four and seven years and aimed to determine whether premature menopause can have an effect on later-life cognitive function. The effects of the type of menopause, whether natural or surgical, and use of hormone treatment were also examined.
Of the 4,868 women in this study, natural menopause was reported by 79% of the women, 10% as a surgical menopause and 11% of women reported menopause due to other causes, such as radiation or chemotherapy. Around 7.6% of the women in the study had a premature menopause and a further 12.8% an early menopause (between the ages of 41 and 45 years). Over a fifth of the women used hormone treatment during the menopause.
Results show that in comparison to women who experienced menopause after the age of 50, those with a premature menopause had a more than 40% increased risk of poor performance on tasks assessing verbal fluency and visual memory and was associated with a 35% increased risk of decline in psychomotor speed (coordination between the brain and the muscles that brings about movement) and overall cognitive function over 7 years. There was no significant association with the risk of dementia.
Furthermore, both premature ovarian failure and premature surgical menopause were associated with a more than two-fold risk of poor verbal fluency. In terms of visual memory, premature ovarian failure was associated with a significantly increased risk of poor performance, and there was a similar trend for premature surgical menopause.
When the potential modifying effect of using hormone treatment at the time of premature menopause was examined, there was some evidence that it may be beneficial for visual memory, but it could increase the risk of poor verbal fluency.
Dr Joanne Ryan, Postdoctoral Research Fellow, Neuropsychiatry: Epidemiological and Clinical Research, Hospital La Colombiere, Montpellier, said:
"Both premature surgical menopause and premature ovarian failure, were associated with long-term negative effects on cognitive function, which are not entirely offset by menopausal hormone treatment.
"In terms of surgical menopause, our results suggest that the potential long-term effects on cognitive function should form part of the decision-making process when considering ovariectomy in younger women."
Pierre Martin Hirsch, BJOG deputy editor-in-chief added:
"With the ageing population it is important to have a better understanding of the long term effects of a premature menopause on later-life cognitive function and the potential benefit from using menopausal hormone treatment.
"This study adds to the existing evidence base to suggest premature menopause can have a significant impact on cognitive function in later life which healthcare professionals must be aware of."
INFORMATION: END
New study examines premature menopause and effects on later life cognition
2014-05-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Image-guided peritoneal dialysis catheter placement significantly reduces complications
2014-05-07
Leesburg, VA, May 7, 2014— Patients undergoing peritoneal dialysis catheter placement via fluoroscopy and ultrasound-guidance experienced significantly fewer complications at 1 year post-insertion than did patients whose catheters were placed laparoscopically.
The first of two study groups received catheters using fluoroscopy and ultrasound guidance under conscious sedation by interventional radiologists. In the second group, the catheters were inserted using laparoscopy under general anesthesia by surgeons.
"Our results showed that the overall complications at 1 ...
Iterative reconstruction techniques reduce radiation dose for pediatric brain CT
2014-05-07
Leesburg, VA, May 7, 2014—A study conducted at Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School found that estimated radiation doses are substantially lower for pediatric CT exams of the brain that used an adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction technique (ASIR) compared to those that did not use ASIR. The researchers found that the brain and salivary gland doses were much lower for ASIR-enabled exams compared to those without ASIR technique. However, no differences in the estimated organ doses were found for the thyroid gland, skeleton, and eye lenses across ...
Nonscreened patients with breast cancer need more treatment than screened patients
2014-05-07
Leesburg, VA, May 6, 2014—Screening 40- to 49-year-old women for breast cancer has additional benefits beyond the proven decrease in mortality rate. Patients screened with mammography are statistically less likely to undergo chemotherapy, avoiding the associated toxic morbidities. Screening mammography also helps identify a subset of patients at increased risk of breast cancer by diagnosing high-risk lesions.
The majority of high-risk lesions identified in a retrospective chart review were found in screened patients. Identifying patients at high risk may allow for the ...
Overestimation of radiation exposure may keep women from critical screening
2014-05-07
Leesburg, VA, May 5, 2014—Misinformation and misunderstanding about the risks associated with ionizing radiation create heightened public concern and fear, and may result in avoidance of screening mammography that can detect early cancers.
In a study to determine the baseline understanding of the radiation associated with mammography among patients presenting for initial or follow-up imaging, women were asked to rate the amount of radiation received in a single mammogram as being significantly less, slightly less, about the same, slightly more, or significantly more compared ...
EARTH Magazine: Naturally occurring methane found in groundwater in New York
2014-05-07
Alexandria, Va. – Since hydraulic fracturing operations began in the Marcellus Shale region, debate has raged over whether drilling operations are causing high levels of methane in drinking-water wells. But few systematic scientific studies have been published to date, so it's unknown if high methane levels are natural or the result of contamination from nearby gas wells. Now, a new study is adding some much-needed baseline data for methane levels in groundwater in New York. The results suggest that at least in some cases methane occurs at naturally high levels in groundwater.
Read ...
NASA watching year's first tropical low headed for southwestern Mexico
2014-05-07
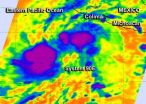
There's a tropical low pressure area in the Eastern Pacific Ocean today, about 8 days before the official Eastern Pacific hurricane season begins. NOAA's National Hurricane Center is giving it a 50 percent chance of becoming a tropical depression in the next two days, and NASA's Aqua satellite passed overhead to gather infrared data on it.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over developing tropical low pressure system 90E on May 8 at 08:41 UTC (4:41 a.m. EDT) and infrared data from the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument aboard, showed that some of the thunderstorms ...
Automated CT dose-tracking software effectively monitors dosage in a clinical setting
2014-05-07
Leesburg, VA, May 5, 2014—Dose-tracking software provides effective and easy monitoring of radiation dose exposure in a busy academic practice, according to research conducted at Massachusetts General Hospital.
For commonly ordered abdominal CT exams, iterative reconstruction techniques enabled approximately 50 percent radiation dose reduction compared to the national averages reported in the Dose Index Registry*.
"A busy practice with diverse CT technology and remote scanner locations encounters challenges in assessing institutional performance in lowering radiation ...
Breast tomosynthesis after screening mammography reduces need for ultrasound, biopsies
2014-05-07
Leesburg, VA, May 5, 2014—Breast tomosynthesis in the diagnostic workup for one- or two-view focal asymmetry detected at screening mammography resulted in less use of ultrasound, fewer biopsies, and higher positive predictive value for cancer than when diagnostic exams involved only 2D mammography, according to a study conducted at the University of Virginia.
"Tomosynthesis has been evaluated in screening populations and been shown to decrease recall rates," said researcher Brandi Nicholson, "but studies in the diagnostic setting are lacking."
Five hundred thirty ...
CT-guided irreversible electroporation safe in unresectable pancreatic carcinoma
2014-05-07
Leesburg, VA, May 6, 2014—A small group of patients with locally advanced unresectable pancreatic carcinoma suffered no major ill effects—pancreatitis or fistula formation—after undergoing percutaneous CT-guided irreversible electroporation (IRE)—a nonthermal ablation technology that is safe near vascular and ductal structures—as a therapy.
"Our findings exceeded our expectations," said Maria Paola Belfiore, a researcher at the Institute of Radiology, Second University of Naples. "In fact, three patients were downstaged, and so had a greater life expectancy. This is a ...
Rising CO2 poses significant threat to human nutrition
2014-05-07
Boston, MA — At the elevated levels of atmospheric CO2 anticipated by around 2050, crops that provide a large share of the global population with most of their dietary zinc and iron will have significantly reduced concentrations of those nutrients, according to a new study led by Harvard School of Public Health (HSPH). Given that an estimated two billion people suffer from zinc and iron deficiencies, resulting in a loss of 63 million life years annually from malnutrition, the reduction in these nutrients represents the most significant health threat ever shown to be associated ...