(Press-News.org) Human mortality and survival may have improved in the generations following the Black Death, according to results published May 7, 2014, in the open access journal PLOS ONE by Sharon DeWitte from University of South Carolina.
As one of the most devastating epidemics in human history, the medieval Black Death (c. 1347-1351) killed tens of millions of Europeans. Previous studies have shown that the disease targeted elderly adults and sick or stressed people; however, not much is known about any substantial changes in the population, like overall health and mortality, before and after its occurrence. Following the epidemic, standards of living—particularly diet—improved, and in this study, Dr. DeWitte examined whether the deaths of frail people during the Black Death, combined with consequent rising standards of living, may have resulted in a healthier post-epidemic population in London. Unfortunately, most available data is in historical documentation (e.g., tax records and postmortem analysis), but in this study, Dr. DeWitte sampled nearly 600 skeletons from several pre- and post-Black Death London cemeteries and then analyzed their age and modeled age estimates, mortality hazards, and birth rate data for these samples.
Post-Black Death samples had a higher proportion of older adults, suggesting that survival may have improved following the epidemic. Additionally, results of hazards analysis indicate that overall, mortality risks were lower in the post-Black Death population than before the epidemic. Together, these results may indicate enhanced survival and decreased mortality after the Black Death, and by inference, improved health in some age groups in the post-epidemic population. Although other factors could have influenced these differences, like the migration of people to London after the plague, Dr. DeWitte suggests that this study highlights the power that infectious diseases may have in shaping population-wide patterns of health and demography over both the short- and long-term.
Sharon DeWitte added, "This study suggests that even in the face of major threats to health, such as repeated plague outbreaks, several generations of people who lived after the Black Death were healthier in general than people who lived before the epidemic."
INFORMATION:
Citation: DeWitte SN (2014) Mortality Risk and Survival in the Aftermath of the Medieval Black Death. PLoS ONE 9(5): e96513. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0096513
Financial Disclosure: Data collection was supported by funding from NSF (http://www.nsf.gov; BCS-1261682), the Wenner-Gren Foundation (whttp://www.wennergren.org; grant #8247), and the American Association of Physical Anthropologists (http://www.physanth.org). Preliminary analyses were conducted during a summer fellowship at the
School for Advanced Research, sponsored by the Ethel-Jane Westfeldt Bunting Foundation (http://www.sarweb.org). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Competing Interest Statement: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
PLEASE LINK TO THE SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE IN ONLINE VERSIONS OF YOUR REPORT (URL goes live after the embargo ends): http://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0096513
Study suggests improved survivorship in the aftermath of the medieval Black Death
Skeletal analysis may support increased survival and mortality risk after Black Death
2014-05-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Scientists focus on role of ventilation in preventing tuberculosis transmission
2014-05-08
Scientists studying the role of room ventilation in tuberculosis transmission found that students in Cape Town, South Africa, spend almost 60 percent of their day in poorly ventilated rooms, at risk of transmission, according to results published May 7, 2014, in the open access journal PLOS ONE by Eugene Richardson from Stanford University School of Medicine and colleagues. The researchers propose an increase in low-cost, WHO-compliant natural ventilation to facilitate healthy indoor environments and reduce risks.
Despite biomedical improvements to treat tuberculosis ...
A new tool to measure the speed of aging
2014-05-08
A physical test for measuring age shows wide differences between the rates of aging among different population groups, according to new research by demographers at the International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis.
A strong handshake can say a lot about a person—it can indicate power, confidence, health, or aggression. Now scientists say that the strength of a person's grasp may also be one of the most useful ways to measure people's true age.
In a new study published today in the journal PLOS ONE, IIASA researchers Serguei Scherbov and Warren Sanderson (also at ...
UH Rainbow study finds rising incidence of acute pancreatitis in hospitalized children
2014-05-08
The largest investigation to date has found a significant increase in the number of acute pancreatitis (AP) cases in hospitalized children in the United States.
The new study, in the "PLOS ONE" journal found a 51 percent increase in the primary diagnosis of AP from 2000 to 2009. The number increased from 6,350 in 2000 to 9,561 in 2009.
The study looked at hospitalization records of patients 20 years old and younger using a federal children's inpatient database. From 2000 to 2009, they identified 55,012 cases of AP in hospitalized children ages 1 – 20.
According ...
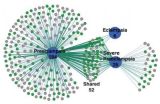
Study finds genetic patterns in preeclampsia
2014-05-08
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — Different manifestations of preeclampsia, such as early vs. late timing or typical vs. high severity, appear to have distinct genetic underpinnings, suggesting that they may need to be studied and treated differently. That and several other insights are described in a newly published comprehensive review of genetic studies of the condition, which produces life-threatening complications such as high-blood pressure in as many as 8 percent of pregnancies in the United States.
"There are probably very different phenotypes of preeclampsia ...
Experts say 'insourcing' innovation may be the best approach to transforming health care
2014-05-08
Philadelphia - A group of health care and policy experts from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania is urging health care institutions to look more to their own in-house personnel, including physicians and nurses, as a source of new ideas for improving how care is delivered. The practice – referred to as insourcing – relies on an organization's existing staff to drive needed transformations. The team also suggests a four-stage design process which, when adopted internally, may help organizations implement more efficient health care delivery solutions. ...
New order of marine creatures discovered among sea anemones
2014-05-08
A deep-water creature once thought to be one of the world's largest sea anemones, with tentacles reaching more than 6.5 feet long, actually belongs to a new order of animals. The finding is part of a new DNA-based study led by the American Museum of Natural History that presents the first tree of life for sea anemones, a group that includes more than 1,200 species. The report, which is published today in the journal PLOS ONE, reshapes scientists' understanding of the relationships among these poorly understood animals.
"The discovery of this new order of Cnidaria—a phylum ...
Recent Ebola outbreak highlights need for better global response
2014-05-08
WHAT:In an invited perspective article on the Ebola outbreak under way in West Africa, Heinz Feldmann, M.D., Ph.D., of the National Institutes of Health (NIH) emphasizes the need for scientists to make their data available to colleagues in real-time to improve the public health response to outbreaks. He cites past responses to influenza and SARS (severe acute respiratory syndrome) outbreaks as successful examples of global information sharing. Rapid diagnoses are key to controlling outbreaks of deadly viruses such as Ebola, for which no therapies are available. The immediate ...
Malaria severity not determined solely by parasite levels in blood
2014-05-08
WHAT:
Although malaria kills some 600,000 African children each year, most cases of the mosquito-borne parasitic disease in children are mild. Repeated infection does generate some immunity, and episodes of severe malaria are unusual once a child reaches age 5. However, the relative contributions of such factors as the level of malaria-causing parasites in a person's blood—parasite density—to disease severity and to development of protective immunity are not well understood.
To clarify these issues, researchers from the United States and Tanzania regularly examined 882 ...
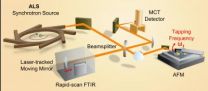
Berkeley Lab develops nanoscope to probe chemistry on the molecular scale
2014-05-08
For years, scientists have had an itch they couldn't scratch. Even with the best microscopes and spectrometers, it's been difficult to study and identify molecules at the so-called mesoscale, a region of matter that ranges from 10 to 1000 nanometers in size. Now, with the help of broadband infrared light from the Advanced Light Source (ALS) synchrotron at the U.S. Department of Energy's Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab), researchers have developed a broadband imaging technique that looks inside this realm with unprecedented sensitivity and range.
By ...
Common drug may help treat effects of muscle disease in boys
2014-05-07
MINNEAPOLIS – A drug typically prescribed for erectile dysfunction or increased pressure in the arteries may help improve blood flow in the muscles of boys with Duchenne muscular dystrophy, according to a study published in the May 7, 2014, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
Duchenne muscular dystrophy is a progressive and fatal muscle disease affecting boys and young men that causes loss of muscle function. There is no specific treatment for the disease, which is genetic. Corticosteroids can slow muscle degeneration ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Reconstructing the world’s ant diversity in 3D
UMD entomologist helps bring the world’s ant diversity to life in 3D imagery
ESA’s Mars orbiters watch solar superstorm hit the Red Planet
The secret lives of catalysts: How microscopic networks power reactions
Molecular ‘catapult’ fires electrons at the limits of physics
Researcher finds evidence supporting sucrose can help manage painful procedures in infants
New study identifies key factors supporting indigenous well-being
Bureaucracy Index 2026: Business sector hit hardest
ECMWF’s portable global forecasting model OpenIFS now available for all
Yale study challenges notion that aging means decline, finds many older adults improve over time
Korean researchers enable early detection of brain disorders with a single drop of saliva!
Swipe right, but safer
Duke-NUS scientists identify more effective way to detect poultry viruses in live markets
Low-intensity treadmill exercise preconditioning mitigates post-stroke injury in mouse models
How moss helped solve a grave-robbing mystery
How much sleep do teens get? Six-seven hours.
Patients regain weight rapidly after stopping weight loss drugs – but still keep off a quarter of weight lost
GLP-1 diabetes drugs linked to reduced risk of addiction and substance-related death
Councils face industry legal threats for campaigns warning against wood burning stoves
GLP-1 medications get at the heart of addiction: study
Global trauma study highlights shared learning as interest in whole blood resurges
Almost a third of Gen Z men agree a wife should obey her husband
Trapping light on thermal photodetectors shatters speed records
New review highlights the future of tubular solid oxide fuel cells for clean energy systems
Pig farm ammonia pollution may indirectly accelerate climate warming, new study finds
Modified biochar helps compost retain nitrogen and build richer soil organic matter
First gene regulation clinical trials for epilepsy show promising results
Life-changing drug identified for children with rare epilepsy
Husker researchers collaborate to explore fear of spiders
Mayo Clinic researchers discover hidden brain map that may improve epilepsy care
[Press-News.org] Study suggests improved survivorship in the aftermath of the medieval Black DeathSkeletal analysis may support increased survival and mortality risk after Black Death