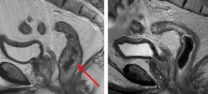
(Press-News.org) PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — First things first. If cancer patients are having trouble tolerating chemotherapy after chemoradiation and surgery, then try administering it beforehand. Reordering the regimen that way enabled all but six of 39 patients to undergo a full course of standard treatment for rectal cancer, according to research to be presented at the American Society for Clinical Oncology annual meeting in Chicago.
Studies have shown that only about 60 percent of rectal cancer patients comply with postoperative chemotherapy, said lead researcher Dr. Kimberly Perez, assistant professor of medicine in the Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University and a cancer physician at Rhode Island Hospital. In the phase II trial, "Complete Neoadjuvant Therapy in Rectal Cancer" (CONTRE), more than 90 percent of the patients were able to complete a regimen of mFOLFOX6 when it was moved to the front of the line.
"The thought was, what can we do to make it more tolerable and get the benefit that we wanted," said Perez, who will speak at 4 p.m. CDT on Saturday, May 31, 2014 at ASCO. "It's encouraging because we were able to get the numbers up of patients who were able to get all the chemotherapy indicated."
All but one patient in the study underwent surgery and 85 percent underwent the middle step of chemoradiation after completing chemotherapy. The vast majority therefore received all three courses of standard treatment, albeit in a new order.
Almost all of the patients came into the study with rectal bleeding, but that symptom abated for all of them during treatment, Perez said.
Regarding the cancer itself, a majority of patients, 32 of whom entered the trial at stage III and seven of whom were less advanced at stage II, responded at least to some degree to the induction chemotherapy and chemoradiation treatments. By the time they got to surgery, 13 patients had no tumor left ("pathologic complete response"), 10 got all they way back to stage I, seven were at stage II, and eight remained at stage III.
The study occurred too recently, however, to provide a measure of overall survival, Perez acknowledged. The last patient finished surgery in January 2014.
The rate of side effects such as neutropenia, an adverse impact on the immune system, was not unusual.
The results of the CONTRE trial are now feeding into the development of a new national rectal cancer trial spearheaded by NRG Oncology, Perez said. That protocol will involve chemo first, then chemoradiation with biological anti-cancer agents, and finally surgery. Brown Univeristy Oncology Group and the Cancer Center of Rhode Island Hospital and associated satellites will be one of the study sites, Perez said.
INFORMATION:
In addition to Perez, the other researchers involved in the study were, Dr. Nishit Shah, Dr. Victor Pricolo, Dr. Matthew Vrees, Dr. Thomas Dipetrillo, Dr. Niklas Oldenburg, Dr. Adam Klipfel, Dr. Steven Schecter, Dr. Timothy Kinsella, Dr. Leslie Roth, Dr. Murray Resnick, Kayla Rosati, Dr. Howard Safran, and Dr. William Sikov.
The Brown University Oncology Research Group funded the research.
Getting chemo first may help in rectal cancer
2014-05-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
MIPT experts reveal the secret of radiation vulnerability
2014-05-15
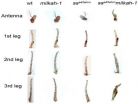
The scientists - Boris Kuzin, Ekaterina Nikitina, Roman Cherezov, Julia Vorontsova, Mikhail Slezinger, Olga Zatsepina, Olga Simonova, Grigori Enikolopov and Elena Savvateeva-Popova - studied Drosophila flies, in whose genome weak mutations of two different genes were combined. The paper is published in the PLoS One. They concluded that these mutations synergistically strengthen their mutual phenotypic expression. In other words, the aggregate effect of these mutations is much greater than that which can be produced by one of them individually.
The mutant flies bred by ...
MIPT scientists develop algorithm for anti-aging remedy search
2014-05-15
The scientists – Alexander Zhavoronkov, Anton Buzdin, Andrey Garazha, Nickolay Borisov and Alexey Moskalev– have based the new research on their previously-developed methods in the study of cancer cells. Each cell uses particular schemes of molecular interaction, which physiologists call intercellular signaling pathways.
A signaling pathway is a chain of sequential events of interaction between certain molecules which make the cell respond to stimulation. For example, hormone molecules first interact with the cell's membrane receptors, then the receptors engage with the ...
Next frontier: How can modern medicine help dying patients achieve a 'good' death?
2014-05-15
(TORONTO, Canada – May, 15, 2014) -- The overall quality of death of cancer patients who die in an urban Canadian setting with ready access to palliative care was found to be good to excellent in the large majority of cases, helping to dispel the myth that marked suffering at the end of life is inevitable.
"Fear of dying is something almost every patient with advanced cancer or other life-threatening illness faces, and helping them, to achieve a "good death" is an important goal of palliative care," says Dr. Sarah Hales, Coordinator of Psychiatry Services, Psychosocial ...
Study shows young men increasingly outnumber young women in rural Great Plains
2014-05-15
Lincoln, Neb., May 15, 2014 -- In many rural communities hard hit by decades of population declines, young men increasingly outnumber young women, a new study of Kansas and Nebraska census data shows.
In places with 800 or fewer residents, the proportion of young men increased by an average of nearly 40 percent as people went from their teens to their 20s.
Those findings suggest leaders should consider the needs of young women in their economic and community development plans, said Robert Shepard, a University of Nebraska-Lincoln doctoral candidate ...
Most NHL players peak by age 29: Study
2014-05-15
A new University of British Columbia study identifies when the clock runs out on an NHL player's peak performance, giving team executives insight into how best to build a roster.
The study by Sauder School of Business professor James Brander found that the performance of forwards peaks between the ages of 27 and 28. Defencemen are best between 28 and 29, and the performance of goaltenders varies little by age.
The forthcoming study to be published in the Journal of Quantitative Analysis in Sports also reveals that players performed close to their peak levels for a ...
Learning from sharks
2014-05-15
This news release is available in German.
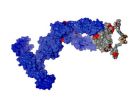
Custom-tailored antibodies are regarded as promising weapons against a multitude of serious illnesses. Since they can accurately recognize specific structures on the surface of viruses, bacteria or cancer cells, they are already being deployed successfully in cancer diagnostics and therapy, as well as against numerous other diseases. The stability of the sensitive antibodies is a decisive factor in every step, from production and storage to therapeutic application.
A team of researchers headed by Dr. Matthias J. Feige and ...
Where have all the mitochondria gone?
2014-05-15
It's common knowledge that all organisms inherit their mitochondria – the cell's "power plants" – from their mothers. But what happens to all the father's mitochondria? Surprisingly, how – and why – paternal mitochondria are prevented from getting passed on to their offspring after fertilization is still shrouded in mystery; the only thing that's certain is that there must be a compelling reason, seeing as this phenomenon has been conserved throughout evolution.
Now, Dr. Eli Arama and a team in the Weizmann Institute's Molecular Genetics Department have discovered special ...
Sugar implicated in cardiovascular disease risk independent of weight gain
2014-05-15
Researchers from New Zealand's University of Otago have uncovered evidence that sugar has a direct effect on risk factors for heart disease, and is likely to impact on blood pressure, independent of weight gain.
Research Fellow with Otago's Department of Human Nutrition Dr Lisa Te Morenga, Professor Jim Mann and colleagues have conducted a review and meta-analysis of all international studies that compared the effects of higher versus lower added sugar consumption on blood pressure and lipids (blood fats or cholesterol) – both of which are important cardiovascular risk-factors.
They ...
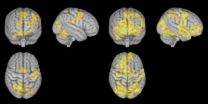
This is your brain on meditation
2014-05-15
Mindfulness. Zen. Acem. Meditation drumming. Chakra. Buddhist and transcendental meditation. There are countless ways of meditating, but the purpose behind them all remains basically the same: more peace, less stress, better concentration, greater self-awareness and better processing of thoughts and feelings.
But which of these techniques should a poor stressed-out wretch choose? What does the research say? Very little – at least until now.
A team of researchers at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU), the University of Oslo and the University ...
HIV patient nutrition more vital than once assumed
2014-05-15
Roughly 25 million Africans live with HIV, many of who now have access to antiretroviral drugs (ARVs). Among their side effects, ARVs can cause patients to put on weight. Subsequently, attention paid to malnutrition among African HIV patients has waned. However, widespread malnutrition has been identified as a reason that up to a quarter of HIV patients in a number of African countries die just months after beginning medical treatment.
A collaborative project between the University of Copenhagen and Jimma University, Ethiopia has demonstrated that daily nutritional supplementation ...