(Press-News.org) The winds have shifted and the Slide Fire smoke that once hung heavy and gray over Flagstaff is now covering the city of Sedona in Arizona. Over 20,000 acres have burned in the Coconino Forest in Arizona. Inciweb.org reports that during Memorial Day crews completed the final perimeter burnout around the fire. This perimeter created by the fire crews is approximately 40 miles of line to form a containment perimeter around the fire. The fire is considered 35 percent contained at this point.
Today (Tuesday May 27) crews will work on holding the containment line along the west edge of the fire and burn out patches of unburned land within the fire line. Crews will burn land in a more controlled manner in an effort to able to influence the ultimate outcome. No threats to the fire line are anticipated today.
Weather conditions continue to warm and dry out as the high pressure ridge intensifies into Wednesday. Two Remote Automated Weather Stations were installed to provide additional weather data for fire managers to help them understand weather conditions and their impact on the fire itself.
INFORMATION:
NASA's Terra satellite collected this natural-color image with the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer, MODIS, instrument on May 27, 2014. Actively burning areas, detected by MODIS's thermal bands, are outlined in red. NASA image courtesy Jeff Schmaltz LANCE/EOSDIS MODIS Rapid Response Team, GSFC. Caption by Lynn Jenner with information from Inciweb.org.
May 27 update on Slide Fire, Arizona
2014-05-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Agricultural fires light up central Africa
2014-05-27
It is currently the dry season in the Democratic Republic of the Congo and the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on NASA's Aqua satellite captured this image on May 24, 2014. MODIS detected hundreds of active fires (location marked in red) in the Democratic Republic of the Congo and northeastern Angola, a sign that the agricultural burning season is underway.
Agriculture is responsible for more than half of the products produced by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, and fire is a central feature in agriculture across most of Africa. Places where ...
UCI researchers identify new functional roles on cell surfaces for estrogen
2014-05-27
Irvine, Calif., May 27, 2014 — A discovery by UC Irvine endocrinologists about the importance of cell surface receptors for estrogen has the potential to change how researchers view the hormone's role in normal organ development and function.
To date, scientists in the field focused on receptors in the cell's nucleus as the primary site for estrogen's effect on gene activity and organ development and function. There has been acknowledgement of similar estrogen receptors outside of the nucleus but much debate as to whether they are important.
To investigate this, Dr. ...
New method discovered to protect against chemical weapons
2014-05-27
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Researchers at Oregon State University have discovered that some compounds called polyoxoniobates can degrade and decontaminate nerve agents such as the deadly sarin gas, and have other characteristics that may make them ideal for protective suits, masks or other clothing.
The use of polyoxoniobates for this purpose had never before been demonstrated, scientists said, and the discovery could have important implications for both military and civilian protection. A United Nations report last year concluded that sarin gas was used in the conflict in Syria.
The ...
Moving 'natural capital' from metaphor to reality
2014-05-27
Economists have long touted the importance of quantifying nature's value — from the natural treatment of pollution by wetlands to the carbon storage capacity of forests — and including it in measures of national wealth.
But so far, achieving an actual measurable value for this "natural capital" has remained elusive, says Eli Fenichel, an assistant professor of bioeconomics and ecosystems management at the Yale School of Forestry & Environmental Studies.
In a new paper, Fenichel and co-author Joshua Abbott of Arizona State University report developing an approach to ...
Eastern Pacific season off with a bang: Amanda is first major hurricane
2014-05-27
The first tropical cyclone of the Eastern Pacific hurricane season grew into a major hurricane as Hurricane Amanda reached Category 4 status on the Saffir-Simpson scale over the Memorial Day holiday weekend. NASA and NOAA satellites watched as Amanda developed an eye while strengthening.
Fortunately, Amanda is far enough away from coastal Mexico that no watches or warnings are in effect today, May 27.
On Sunday, May 25, Amanda strengthened into the first Major Hurricane in the Eastern Pacific Ocean. Maximum sustained winds were near 155 mph (250 kph). Amanda was centered ...
Precision-guided epidurals and better blood monitors
2014-05-27
WASHINGTON, May 27, 2014—The march of modern medicine is often driven by revolutions in medical imaging. When technology advances, doctors are better able to peer deeply into human tissues, and thus able to detect, diagnose and treat human diseases more effectively.
Now, researchers have taken an established imaging technology called "optical coherence tomography," or OCT, and integrated it with other instruments to bring about the next revolution in imaging by helping doctors provide safer, less painful and more effective care for women in labor and people with diabetic ...
Update on Funny River Fire, southern Alaska
2014-05-27
NASA's Terra satellite passed over the central Alaska and the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument that flies aboard captured an image of smoke and hot spots from the Funny River Fire in southern Alaska on May 26 at 21:45 UTC (5:45 p.m. EDT). The heat from the fire appears red in the imagery and the smoke appears light brown.
On May 26 at 9:30 a.m. local time, the Alaska Interagency Incident Management Type 2 Team reported on the status of the fire through the multi-agency Incident Information System known as Inciweb. At that time the fire ...
More access to health care may lead to unnecessary mammograms
2014-05-27
GALVESTON —Researchers have concluded that providing better access to health care may lead to the overuse of mammograms for women who regularly see a primary care physician and who have a limited life expectancy.
The cautionary note from researchers at the University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston is that screening women in this category could subject them "to greater risks of physical, emotional and economic suffering."
Dr. Alai Tan, a senior biostatistician in UTMB's Sealy Center on Aging and lead author of the study, said that "there has been little systematic ...
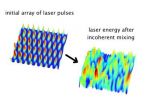
Smaller accelerators for particle physics?
2014-05-27
WASHINGTON D.C., May 27, 2014 -- It took every inch of the Large Hadron Collider's 17-mile length to accelerate particles to energies high enough to discover the Higgs boson. Now, imagine an accelerator that could do the same thing in, say, the length of a football field. Or less.
That is the promise of laser-plasma accelerators, which use lasers instead of high-power radio-frequency waves to energize electrons in very short distances. Scientists have grappled with building these devices for two decades, and a new theoretical study predicts that this may be easier than ...
New epilepsy treatment offers 'on demand' seizure suppression
2014-05-27
A new treatment for drug-resistant epilepsy with the potential to suppress seizures 'on demand' with a pill, similar to how you might take painkillers when you feel a headache coming on, has been developed by UCL (University College London) researchers funded by the Wellcome Trust.
The treatment, described in Nature Communications, combines genetic and chemical approaches to suppress seizures without disrupting normal brain function. The technique was demonstrated in rodents but in future we could see people controlling seizures on-demand with a simple pill.
Epilepsy ...