(Press-News.org) PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — The slopes of a giant Martian volcano, once covered in glacial ice, may have been home to one of the most recent habitable environments yet found on the Red Planet, according to new research led by Brown University geologists.
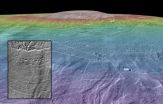
Nearly twice as tall as Mount Everest, Arsia Mons is the third tallest volcano on Mars and one of the largest mountains in the solar system. This new analysis of the landforms surrounding Arsia Mons shows that eruptions along the volcano's northwest flank happened at the same time that a glacier covered the region around 210 million years ago. The heat from those eruptions would have melted massive amounts of ice to form englacial lakes — bodies of water that form within glaciers like liquid bubbles in a half-frozen ice cube.
The ice-covered lakes of Arsia Mons would have held hundreds of cubic kilometers of meltwater, according to calculations by Kat Scanlon, a graduate student at Brown who led the work. And where there's water, there's the possibility of a habitable environment.
"This is interesting because it's a way to get a lot of liquid water very recently on Mars," Scanlon said.
While 210 million years ago might not sound terribly recent, the Arsia Mons site is much younger than the habitable environments turned up by Curiosity and other Mars rovers. Those sites are all likely older than 2.5 billion years. The fact that the Arsia Mons site is relatively young makes it an interesting target for possible future exploration.
"If signs of past life are ever found at those older sites, then Arsia Mons would be the next place I would want to go," Scanlon said.
A paper describing Scanlon's work is published in the journal Icarus.
Scientists have speculated since the 1970s that the northwest flank of Arsia Mons may once have been covered by glacial ice. That view got a big boost in 2003 when Brown geologist Jim Head and Boston University's David Marchant showed that terrain around Arsia Mons looks strikingly similar to landforms left by receding glaciers in the Dry Valleys of Antarctica. Parallel ridges toward the bottom of the mountain appear to be drop moraines — piles of rubble deposited at the edges of a receding glacier. An assemblage of small hills in the region also appears to be debris left behind by slowly flowing glacial ice.
The glacier idea got another boost with recently developed climate models for Mars that take into account changes in the planet's axis tilt. The models suggested that during periods of increased tilt, ice now found at the poles would have migrated toward the equator. That would make Mars's giant mid-latitude mountains — Ascraeus Mons, Pavonis Mons and Arsia Mons — prime locations for glaciation around 210 million years ago.
Fire and ice
Working with Head, Marchant, and Lionel Wilson from the Lancaster Environmental Centre in the U.K., Scanlon looked for evidence that hot volcanic lava may have flowed in the region the same time that the glacier was present. She found plenty.
Using data from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, Scanlon found pillow lava formations, similar to those that form on Earth when lava erupts at the bottom of an ocean. She also found the kinds of ridges and mounds that form on Earth when a lava flow is constrained by glacial ice. The pressure of the ice sheet constrains the lava flow, and glacial meltwater chills the erupting lava into fragments of volcanic glass, forming mounds and ridges with steep sides and flat tops. The analysis also turned up evidence of a river formed in a jökulhlaup, a massive flood that occurs when water trapped in a glacier breaks free.
Based on the sizes of the formations, Scanlon could estimate how much lava would have interacted with the glacier. Using basic thermodynamics, she could then calculate how much meltwater that lava would produce. She found that two of the deposits would have created lakes containing around 40 cubic kilometers of water each. That's almost a third of the volume of Lake Tahoe in each lake. Another of the formations would have created around 20 cubic kilometers of water.
Even in the frigid conditions of Mars, that much ice-covered water would have remained liquid for a substantial period of time. Scanlon's back-of-the-envelope calculation suggests the lakes could have persisted or hundreds or even a few thousand years.
That may have been long enough for the lakes to be colonized by microbial life forms, if in fact such creatures ever inhabited Mars.
"There's been a lot of work on Earth — though not as much as we would like — on the types of microbes that live in these englacial lakes," Scanlon said. "They've been studied mainly as an analog to [Saturn's moon] Europa, where you've got an entire planet that's an ice covered lake."
In light of this research, it seems possible that those same kinds of environs existed on Mars at this site in the relatively recent past.
There's also possibility, Head points out, that some of that glacial ice may still be there. "Remnant craters and ridges strongly suggest that some of the glacial ice remains buried below rock and soil debris," he said. "That's interesting from a scientific point of view because it likely preserves in tiny bubbles a record of the atmosphere of Mars hundreds of millions of years ago. But an existing ice deposit might also be an exploitable water source for future human exploration."
INFORMATION:
A habitable environment on Martian volcano?
2014-05-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Learning early in life may help keep brain cells alive
2014-05-27
Using your brain – particularly during adolescence – may help brain cells survive and could impact how it functions after puberty.
According to a recently published study in Frontiers in Neuroscience, Rutgers University behavioral neuroscientist Tracey Shors, who co-authored the study, found that the newborn brain cells in young rats that were successful at learning survived while the same brain cells in animals that didn't master the task died quickly.
"In those that didn't learn, three weeks after the new brain cells were made, one-half of them were no longer there," ...
Vanderbilt study finds women referred for bladder cancer less often than men
2014-05-27
Women with blood in their urine (hematuria) were less than half as likely as men with the same issue to be referred to a urologist for further tests, according to a new Vanderbilt University study.
The findings may help explain why women with bladder cancer are often diagnosed at a later stage in the disease and have worse mortality than men.
The study, presented by Jeffrey Bassett, M.D., MPH, fellow in Urologic Oncology, and Principal Investigator Daniel Barocas, M.D., MPH, assistant professor of Urologic Surgery, was shared during the American Urological Association ...
Addressing the physician shortage: Recommendations for medical education reform
2014-05-27
Since it started more than 30 years ago, funding the graduate medical education (GME) system has not evolved even as there has been a revolution in GME. The United States contributes almost $10 billion a year from Medicare into funding the GME system. However this system fails to provide the workforce needed for the 21st century and lacks the necessary transparency and accountability.
With an aging population and millions of people newly registered for health insurance because of the Affordable Care Act, there is a pressing need to increase the number of primary care ...
Vines choke a forest's ability to capture carbon, Smithsonian scientists report
2014-05-27
Tropical forests are a sometimes-underappreciated asset in the battle against climate change. They cover seven percent of land surface yet hold more than 30 percent of Earth's terrestrial carbon. As abandoned agricultural land in the tropics is taken over by forests, scientists expect these new forests to mop up industrial quantities of atmospheric carbon. New research by Smithsonian scientists shows increasingly abundant vines could hamper this potential and may even cause tropical forests to lose carbon.
In the first study to experimentally demonstrate that competition ...
Where have all the craters gone?
2014-05-27
Boulder, Colo., USA – Impact craters reveal one of the most spectacular geologic process known to man. During the past 3.5 billion years, it is estimated that more than 80 bodies, larger than the dinosaur-killing asteroid that struck the Yucatan Peninsula 66 million years ago, have bombarded Earth. However, tectonic processes, weathering, and burial quickly obscure or destroy craters. For example, if Earth weren't so dynamic, its surface would be heavily cratered like the Moon or Mercury.
Work by B.C. Johnson and T.J. Bowling predicts that only about four of the craters ...
Cancer, bioelectrical signals and the microbiome connected
2014-05-27
MEDFORD/SOMERVILLE, Mass. (May 27, 2014) -- Developmental biologists at Tufts University, using a tadpole model, have shown that bioelectrical signals from distant cells control the incidence of tumors arising from cancer-causing genes and that this process is impacted by levels of a common fatty acid produced by bacteria found in the tadpole and also in humans.
"Genetic information is often not enough to determine whether a cell will become cancerous; you also have to take into account the physiology of the cell and the bioelectrical signals it receives from other ...
Moderate-intensity physical activity program for older adults reduces mobility problems
2014-05-27
Among older adults at risk of disability, participation in a structured moderate-intensity physical activity program, compared with a health education intervention, significantly reduced the risk of major mobility disability (defined in this trial as loss of ability to walk 400 meters, or about a quarter mile), according to a study published by JAMA. The study is being released early online to coincide with its presentation at the American College of Sports Medicine annual meeting.
Mobility—the ability to walk without assistance—is a critical characteristic for functioning ...
Maintaining mobility in older adults can be as easy as a walk in the park
2014-05-27
With just a daily 20-minute walk, older adults can help stave off major disability and enhance the quality of their later years, according to results of the Lifestyle Interventions and Independence for Elders (LIFE) Study, conducted by researchers at Yale School of Medicine in collaboration with seven other institutions around the country. The study is published in the May 27 issue of the Journal of the American Medical Association.
Mobility, the ability to walk without assistance, is key to functioning independently. Reduced mobility is common in older adults and is ...
Study proves physical activity helps maintain mobility in older adults
2014-05-27
GAINESVILLE, Fla. — It's something we've all heard for years: Exercise can help keep older adults healthy. But now a study, the first of its kind to look at frail, older adults, proves that physical activity can help these people maintain their mobility and dodge physical disability.
A new University of Florida study shows daily moderate physical activity may mean the difference between seniors being able to keep up everyday activities or becoming housebound. In fact, moderate physical activity helped aging adults maintain their ability to walk at a rate 18 percent higher ...
What what role does MSG play in obesity and fatty liver disease?
2014-05-27
New Rochelle, NY, May 27, 2014—The commonly used food additive monosodium glutamate (MSG) has been linked to obesity and disorders associated with the metabolic syndrome including progressive liver disease. A new study that identifies MSG as a critical factor in the initiation of obesity and shows that a restrictive diet cannot counteract this effect but can slow the progression of related liver disease is published in Journal of Medicinal Food, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc.. The paper is available on the Journal of Medicinal Food website.
Makoto ...