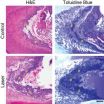
(Press-News.org) Sequenta, Inc. today announced publication of a study done in collaboration with researchers from UCSF and UCLA that used the company's proprietary LymphoSIGHT™ immune repertoire sequencing platform to investigate the effects of anti-CTLA-4 antibody on the number and types of T cells present in a patient's blood. The results, which appear in the May 28 issue of Science Translational Medicine, shed light on the mechanism of action of this type of cancer immunotherapy and suggest that immune repertoire sequencing could be used to predict which patients will have improved survival in response to treatment.
"Immune repertoire sequencing is a new tool that allows us to assess the totality and complexity of immune responses in ways not previously possible," said Lawrence Fong, M.D., Professor, Division of Hematology/Oncology, Department of Medicine, UCSF. "Our analysis of anti-CTLA-4 antibody treated patients using the LymphoSIGHT platform revealed that this therapy induces profound turnover and large-scale remodeling of the entire human T cell repertoire. These findings have implications for understanding how cancer immunotherapy works, which patients will benefit, and the etiology of side effects, such as autoimmune responses."
The researchers used next-generation sequencing to assess the impact of CTLA-4 blockade on changes to the T cell repertoire in 25 metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer patients treated with ipilimumab and GM-CSF, 21 metastatic melanoma patients treated with tremelimumab, and nine untreated control subjects. Results showed that patients with longer survival had significantly lower numbers of T cell clones (sets of T cells that all express the same receptor) that decreased in frequency after treatment compared to patients with shorter survival. This association held for both the prostate cancer patients (p < 0.01) and the melanoma patients (p < 0.05).
"By leveraging the power of Sequenta's LymphoSIGHT platform for immune repertoire profiling, we and our collaborators have uncovered new aspects of the mechanism of action of anti-CTLA-4 monoclonal antibodies in human cancers," said Tom Willis, CEO of Sequenta. "We have also demonstrated the potential of next-generation sequencing analysis of the immune repertoire for identification of patterns that may predict clinical benefit of immunotherapies, which will be crucial for optimal use of currently available treatments and efficient development of new ones."
INFORMATION:
About the LymphoSIGHT™ Platform
Sequenta's LymphoSIGHT platform is a simple and scalable laboratory process that allows each of the several million B and T cells (lymphocytes) in a blood or tissue sample to be characterized and enumerated. Individual cells can be detected at levels as low as one cell per million white blood cells. The LymphoSIGHT platform combines proprietary multiplexed PCR assays for the universal amplification of rearranged immunoglobulin and T-cell receptor genes with powerful algorithms for the analysis of next-generation sequencing data.
Sequenta has commercialized the LymphoSIGHT platform for clinical use in minimal residual disease (MRD) detection in lymphoid cancers as the ClonoSIGHT™ test. The company is also investigating the use of the LymphoSIGHT platform in a diverse set of immune-mediated diseases and as a method for evaluating the efficacy of therapies based on immune system modulation.
About Sequenta
Sequenta is a venture-backed biotechnology company dedicated to improving patient care in diseases mediated by immune cells through the discovery and development of novel clinical diagnostics. The company, located in South San Francisco, was founded in 2008 and has received funding from Mohr Davidow Ventures, Index Ventures and Foresite Capital. For more information, please visit http://www.sequenta.com.
T cell repertoire changes predictive of anti-CTLA-4 cancer immunotherapy outcome revealed
2014-05-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study: Amphetamines can delay exhaustion during exercise in the heat -- at a cost
2014-05-28
Indiana University researchers put male rats to the test to determine the role amphetamines play when used in conjunction with exercise.
When people or animals exercise in the heat, exhaustion is a safety gauge telling the body it is time to stop. Exhaustion occurs when the body's core temperature reaches a potentially dangerous point. The use of amphetamines is banned in many sports because they increase time to exhaustion.
What they found: Amphetamines can delay exhaustion during exercise in the heat by increasing the temperature at which it occurs. This potentially ...
Researchers use light to coax stem cells to repair teeth
2014-05-28
A Harvard-led team is the first to demonstrate the ability to use low-power light to trigger stem cells inside the body to regenerate tissue, an advance they reported in Science Translational Medicine. The research, led by Wyss Institute Core Faculty member David Mooney, Ph.D., lays the foundation for a host of clinical applications in restorative dentistry and regenerative medicine more broadly, such as wound healing, bone regeneration, and more.
The team used a low-power laser to trigger human dental stem cells to form dentin, the hard tissue that is similar to bone ...
EARTH magazine: The history, science and poetry of New England's stone walls
2014-05-28
Alexandria, Va. — When author John-Manuel Andriote returned to his hometown in New England after years away, he noticed something that had been invisible to him while growing up there — the old stone walls tumbling off into the forests. The realization that the crumbling and overgrown walls meant those forests had once been cleared farm lands set Andriote on a years-long journey of discovery that highlights the intersections of geologic and human history.
The story of New England's stone walls begins with the glaciers of the last ice age, meanders through the Colonial ...
Some high blood pressure drugs may be associated with increased risk of vision-threatening disease
2014-05-28
SAN FRANCISCO – May 28, 2014 – There may be a connection between taking vasodilators and developing early-stage age-related macular degeneration (AMD), the leading cause of vision loss and blindness among Americans who are age 65 and older, according to a study published online in Ophthalmology, the journal of the American Academy of Ophthalmology.
AMD – the deterioration of the eye's macula, which is responsible for the ability to see fine details clearly – affects an estimated 11 million people in the United States. In addition to increased age, the cause of AMD ...
NYU researchers pilot educational and behavioral program to reduce lymphedema risk
2014-05-28
Viewed as one of the most unfortunate outcomes of breast cancer treatment, lymphedema is characterized by an accumulation of lymph fluid in the interstitial spaces of the affected limb, leading to chronic ipsilateral limb swelling causing psychosocial distress and physical challenges for patients.
Even conservative estimates suggest that 3% of women who have had sentinel lymph node biopsy and 20% of those who have had axillary lymph node dissection may develop lymphedema a year after breast cancer surgery. Two established risk factors for lymphedema are compromised ...
A cure for dry eye could be a blink away
2014-05-28
A treatment for dry eye—a burning, gritty condition that can impair vision and damage the cornea—could some day result from computer simulations that map the way tears move across the surface of the eye.
Kara Maki, assistant professor in Rochester Institute of Technology's School of Mathematical Sciences, contributed to a recent National Science Foundation study seeking to understand the basic motion of tear film traversing the eye. "Tear Film Dynamic with Evaporation, Wetting and Time Dependent Flux boundary Condition on an Eye-shaped Domain," published in the journal ...
Antarctic ice-sheet less stable than previously assumed
2014-05-28
The first evidence for massive and abrupt iceberg calving in Antarctica, dating back 19,000 to 9,000 years ago, has now been documented by an international team of geologists and climate scientists. Their findings are based on analysis of new, long deep sea sediment cores extracted from the region between the Falkland Islands and the Antarctic Peninsula. The study in the May 28, 2014 issue of Nature bears witness to an unstable Antarctic ice sheet that can abruptly reorganize Southern Hemisphere climate and cause rapid global sea level rise.
"One of the iceberg events ...
Filling in the gaps on the protein map
2014-05-28
By cataloging over 18,000 proteins, researchers from TUM have produced an almost complete inventory of the human proteome. This information is now freely available in the ProteomicsDB database, which is a joint development of TUM and software company SAP. The database includes information for example on the types, distribution, and abundance of proteins in various cells and tissues as well as in body fluids.
The investigations show that, on the one hand, around 10,000 proteins are concerned with housekeeping processes in many different places. On the other hand, it was ...
Zeroing in on the proton's magnetic moment
2014-05-28
As part of a series of experiments designed to resolve one of the deepest mysteries of physics today, researchers from RIKEN, in collaboration with the University of Mainz, GSI Darmstadt and the Max Planck Institute for Physics at Heidelberg, have made the most precise ever direct measurement of the magnetic moment of a proton.
The work, published in Nature today, seeks to answer the fundamental question of why we exist at all. It is believed that the Big Bang some 13 billion years ago generated equal amounts of matter and antimatter-which annihilate when they collide-and ...
Extensive cataloging of human proteins uncovers 193 never known to exist
2014-05-28
Striving for the protein equivalent of the Human Genome Project, an international team of researchers has created an initial catalog of the human "proteome," or all of the proteins in the human body. In total, using 30 different human tissues, the team identified proteins encoded by 17,294 genes, which is about 84 percent of all of the genes in the human genome predicted to encode proteins.
In a summary of the effort, to be published May 29 in the journal Nature, the team also reports the identification of 193 novel proteins that came from regions of the genome not predicted ...