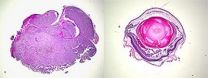
(Press-News.org) Researchers at the University of California, San Diego School of Medicine have identified a therapeutic target for treating the most common form of eye cancer in adults. They have also, in experiments with mice, been able to slow eye tumor growth with an existing FDA-approved drug.
The findings are published online in the May 29 issue of the journal Cancer Cell.
"The beauty of our study is its simplicity," said Kun-Liang Guan, PhD, professor of pharmacology at UC San Diego Moores Cancer Center and co-author of the study. "The genetics of this cancer are very simple and our results have clear implications for therapeutic treatments for the disease."
The researchers looked specifically at uveal melanoma. Uveal collectively refers to parts of the eye, notably the iris, that contain pigment cells. As with melanoma skin cancer, uveal melanoma is a malignancy of these melanin-producing cells.
Approximately 2,000 people in the United States are diagnosed with uveal melanoma each year. If the cancer is restricted to just the eye, the standard treatment is radiation and surgical removal of the eye. But uveal melanoma often spreads to the liver, and determining the metastatic status of the disease can be difficult. In cases of uveal melanoma metastasis, patients typically succumb within two to eight months after diagnosis.
Scientists have long suspected a genetic association with uveal melanoma because one of two gene mutations is present in approximately 70 percent of all tumors. Until this study, however, they had not identified a mechanism that could explain why and how these mutations actually caused tumors.
The work by Guan and colleagues unravels the causal relationship between the genetic mutations and tumor formation, and identifies a molecular pathway along which drugs might counterattack.
The two genes implicated – GNAQ and GNA11 – code for proteins (known as G proteins) that normally function as molecular on-off switches, regulating the passage of information from the outside to the inside of a cell.
In their experiments, the scientists showed that mutations in these genes shift the G proteins to a permanent "on" or active status, which results in over-activation the Yes-associated protein (YAP). The activation of the YAP protein induces uncontrolled cell growth and inhibits cell death, causing malignancies.
Earlier research by other scientists has shown that the drug verteporfin, used to treat abnormal blood vessel formation in the eye, acts on the YAP pathway inhibiting the protein's YAP function.
In experiments with mice, the UC San Diego-led team showed that verteporfin also suppresses the growth of uveal melanoma tumors derived from human tumors.
"We have a cancer that is caused by a very simple genetic mechanism," Guan said. "And we have a drug that works on this mechanism. The clinical applications are very direct."
INFORMATION:
Co-authors include Fa-Xing Yu, Jung-Soon Mo, Guangbo Liu, Young Chul Kim, Zhipeng Meng, Hong Ouyang, Jiagang Zhao and Liangfang Zhang, UC San Diego; Ling Zhao, UC San Diego and Sichuan University, China; Gholam Peyman, Arizona Retinal Specialists; Wei Jiang, Sichuan University; Cun-Yu Wang, UCLA; Boris Bastian and Xu Chen, UC San Francisco; and Kang Zhang, UC San Diego, Veterans Affairs San Diego Healthcare System, Sichuan University and Central South University, China.
Funding for this research came, in part, from the National Institutes of Health (grants EY022611, EY024134 and CA132809) and California Institute for Regenerative Medicine (grant RB2-01547).
Melanoma of the eye caused by 2 gene mutations
2014-05-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
'Free choice' in primates altered through brain stimulation
2014-05-29
When electrical pulses are applied to the ventral tegmental area of their brain, macaques presented with two images change their preference from one image to the other. The study by researchers Wim Vanduffel and John Arsenault, KU Leuven and Massachusetts General Hospital, is the first to confirm a causal link between activity in the ventral tegmental area and choice behavior in primates.
The ventral tegmental area is located in the midbrain and helps regulate learning and reinforcement in the brain's reward system. It produces dopamine, a neurotransmitter that plays an ...
Activation of brain region can change a monkey's choice
2014-05-29
Artificially stimulating a brain region believed to play a key role in learning, reward and motivation induced monkeys to change which of two images they choose to look at. In experiments reported online in the journal Current Biology, researchers from Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) and the University of Leuven in Belgium confirm for the first time that stimulation of the ventral tegmental area (VTA) – a group of neurons at the base of the midbrain – can change behavior through activation of the brain's reward system.
"Previous studies had correlated increased ...
Fertility: Sacrificing eggs for the greater good
2014-05-29
Baltimore, MD— A woman's supply of eggs is a precious commodity because only a few hundred mature eggs can be produced throughout her lifetime and each must be as free as possible from genetic damage. Part of egg production involves a winnowing of the egg supply during fetal development, childhood and into adulthood down from a large starting pool. New research by Carnegie's Alex Bortvin and postdoctoral fellow Safia Malki have gained new insights into the earliest stages of egg selection, which may have broad implications for women's health and fertility. The work is reported ...
NASA missions let scientists see moon's dancing tide from orbit
2014-05-29
Scientists combined observations from two NASA missions to check out the moon's lopsided shape and how it changes under Earth's sway – a response not seen from orbit before.
The team drew on studies by NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, which has been investigating the moon since 2009, and by NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory, or GRAIL, mission. Because orbiting spacecraft gathered the data, the scientists were able to take the entire moon into account, not just the side that can be observed from Earth.
"The deformation of the moon due to Earth's pull ...
UNL team explores new approach to HIV vaccine
2014-05-29
Lincoln, Neb., May 29, 2014 -- Using a genetically modified form of the HIV virus, a team of University of Nebraska-Lincoln scientists has developed a promising new approach that could someday lead to a more effective HIV vaccine.
The team, led by chemist Jiantao Guo, virologist Qingsheng Li and synthetic biologist Wei Niu, has successfully tested the novel approach for vaccine development in vitro and has published findings in the international edition of the German journal Angewandte Chemie.
With the new approach, the UNL team is able to use an attenuated -- or weakened ...
A tool to better screen and treat aneurysm patients
2014-05-29
New research by an international consortium, including a researcher from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, may help physicians better understand the chronological development of a brain aneurysm.
Using radiocarbon dating to date samples of ruptured and unruptured cerebral aneurysm (CA) tissue, the team, led by neurosurgeon Nima Etminan, found that the main structural constituent and protein – collagen type I – in cerebral aneurysms is distinctly younger than once thought.
The new research helps identify patients more likely to suffer from an aneurysm and embark ...
Gender stereotypes keep women in the out-group
2014-05-29
New Rochelle, NY, May 29, 2014—Women have accounted for half the students in U.S. medical schools for nearly two decades, but as professors, deans, and department chairs in medical schools their numbers still lag far behind those of men. Why long-held gender stereotypes are keeping women from achieving career advancement in academic medicine and what can be done to change the institutional culture are explored in an article in Journal of Women's Health, a peer-reviewed publication from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available free on the Journal of Women's ...
Caught by a hair
2014-05-29
Crime fighters could have a new tool at their disposal following promising research by Queen's professor Diane Beauchemin.
Dr. Beauchemin (Chemistry) and student Lily Huang (MSc'15) have developed a cutting-edge technique to identify human hair. Their test is quicker than DNA analysis techniques currently used by law enforcement. Early sample testing at Queen's produced a 100 per cent success rate.
"My first paper and foray into forensic chemistry was developing a method of identifying paint that could help solve hit and run cases," explains Dr. Beauchemin. "Last year, ...
Neural transplant reduces absence epilepsy seizures in mice
2014-05-29
New research from North Carolina State University pinpoints the areas of the cerebral cortex that are affected in mice with absence epilepsy and shows that transplanting embryonic neural cells into these areas can alleviate symptoms of the disease by reducing seizure activity. The work may help identify the areas of the human brain affected in absence epilepsy and lead to new therapies for sufferers.
Absence epilepsy primarily affects children. These seizures differ from "clonic-tonic" seizures in that they don't cause muscle spasms; rather, patients "zone out" or stare ...
Drop in global malnutrition depends on ag productivity, climate change
2014-05-29
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - Global malnutrition could fall 84 percent by the year 2050 as incomes in developing countries grow - but only if agricultural productivity continues to improve and climate change does not severely damage agriculture, Purdue University researchers say.
"The prevalence and severity of global malnutrition could drop significantly by 2050, particularly in the poorest regions of the world," said Thomas Hertel, Distinguished Professor of Agricultural Economics. "But if productivity does not grow, global malnutrition will worsen even if incomes increase. ...