(Press-News.org) VIDEO:
This animation of visible and infrared imagery from NOAA's GOES-West satellite shows the weakening of Hurricane Amanda from May 28 to its dissipation on May 30.
Click here for more information.
A new animation of visible and infrared imagery from NOAA's GOES-West satellite shows the weakening and dissipation of the Eastern Pacific Ocean's Hurricane Amanda. The animation that runs from from May 28 to May 30 was created at NASA/NOAA's GOES Project at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland.
On satellite imagery, Amanda last resembled a tropical cyclone on May 28 around 21:45 UTC (5:45 p.m. EDT) when it still had a comma shape to it. On May 29, Amanda ceased to qualify as a tropical cyclone, according to the National Hurricane Center (NHC).
The 45 second animation shows how Amanda's circulation weakened as the thunderstorm development waned and the circulation center became harder to identify. To create the video and imagery, NASA/NOAA's GOES Project used cloud data from NOAA's GOES-West satellite and overlayed it on a true-color image of ocean and land created by data from the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer, or MODIS, instrument that flies aboard NASA's Aqua and Terra satellites. Together, those data created the entire picture of Amanda's last days.
NHC issued their final warning on post-tropical cyclone Amanda on May 29 at 21:00 UTC (5:00 p.m. EDT). At that time, Amanda's maximum sustained winds were near 25 knots and weakening. It was located near 16.2 north latitude and 109.0 west longitude, about 465 nautical miles south of Cabo San Lucas, Mexico.
By May 29 at 23:15 UTC (5:45 p.m. EDT), the circulation was barely identifiable on GOES-West satellite imagery as the post-tropical cyclone moved east toward mainland Mexico.
On May 30, the remnant low pressure area formerly known as Amanda was located near 17.0 north latitude and 109 west longitude. The minimum central pressure of the remnant low was near 1008 millibars. The NHC noted "Although this low is currently Embedded within a broad area of deep moisture...upper level drier air is starting to approach from the northwest."
GOES satellites provide the kind of continuous monitoring necessary for intensive data analysis. Geostationary describes an orbit in which a satellite is always in the same position with respect to the rotating Earth. This allows GOES to hover continuously over one position on Earth's surface, appearing stationary. As a result, GOES provide a constant vigil for the atmospheric "triggers" for severe weather conditions such as tornadoes, flash floods, hail storms and hurricanes.
Now that Amanda has faded into hurricane history as the strongest May hurricane on record in the Eastern Pacific, forecasters and satellites are now keeping an eye on a developing area of disturbed weather several hundred miles south of southeastern Mexico.
INFORMATION:
For more information about GOES satellites, visit: http://www.goes.noaa.gov or goes.gsfc.nasa.gov
Text credit: Rob Gutro
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
New satellite animation shows the end of Hurricane Amanda
2014-05-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Hepatitis C reactivation doesn't worsen survival for HIV+ patients diagnosed with lymphoma
2014-05-30
CHICAGO, IL (May 30, 2014)—More than a quarter of HIV+ patients are also infected with the Hepatitis C virus (HCV), which may complicate treatment and care decisions after a cancer diagnosis. The specifics of those complications haven't been well-researched in the past. Results from a new Fox Chase Cancer Center study on this patient population may start filling in that gap.
Fox Chase Hematologist and Medical Oncologist Stefan K. Barta, MD, MS, MRCP – who led the study – analyzed data from HIV+ patients diagnosed with lymphoma, collected over 17 years, to better understand ...
Identification of central nervous system involvement for patients with AIDS-related lymphomas
2014-05-30
CHICAGO, IL (May 30, 2014)—Patients with AIDS-related lymphomas (ARL) may face an increased risk of central nervous system involvement (CNSi) compared to other lymphomas. The effect of CNSi on survival outcomes, however, hasn't been thoroughly examined until now.
In a new study led by Fox Chase Cancer Center Hematologist and Oncologist Stefan K. Barta, MD, MS, MRCP, researchers report that CNSi – identified at the time of an ARL diagnosis – does not appear to have an impact on overall survival. Dr. Barta's collaborators will present the findings at the 50th Annual Meeting ...
Moffitt Cancer Center instrumental in new clinical guidelines for cancer-related fatigue
2014-05-30
TAMPA, Fla. (May 30, 2014) – Fatigue is a debilitating problem for cancer patients undergoing treatment; however, it also poses a huge detriment after treatment and can significantly affect quality of life. Approximately 30 percent of cancer patients endure persistent fatigue for several years after treatment, according to an American Society of Clinical Oncology Expert Panel co-chaired by Paul Jacobsen, Ph.D., associate center director of Population Sciences at Moffitt Cancer Center.
ASCO created the panel to develop assessment, screening, and treatment guidelines for ...
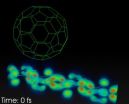
First real time movies of the light-to-current conversion in an organic solar cell
2014-05-30
VIDEO:
Real time quantum simulation of the conversion of light into current in an organic solar cell composed of a polymer chain, and a Fullerene buckyball. The movie lasts for about...
Click here for more information.
Photovoltaic cells directly convert sun light into electricity and hence are key technological devices to meet one of the challenges that mankind has to face in this century: a sustainable and clean production of renewable energy. Organic solar cells, using polymeric ...
Research details how developing neurons sense a chemical cue
2014-05-30
Symmetry is an inherent part of development. As an embryo, an organism's brain and spinal cord, like the rest of its body, organize themselves into left and right halves as they grow. But a certain set of nerve cells do something unusual: they cross from one side to the other. New research in mice delves into the details of the molecular interactions that help guide these neurons toward this anatomical boundary.
In an embryo, a neuron's branches, or axons, have special structures on their tips that sense chemical cues telling them where to grow. The new findings, by ...
Study highlights side effects felt by BRCA mutation carriers after cancer risk-reducing procedure
2014-05-30
PHILADELPHIA — The majority of women with cancer causing BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations experience sexual dysfunction, menopausal symptoms, cognitive and stress issues, and poor sleep following prophylactic removal of their Fallopian tubes and ovaries - a procedure known as risk-reducing salpingo-oophorectomy (RRSO) - according to results of a new study from the Abramson Cancer Center and the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. The team's findings, which reaffirm the need for a better understanding of how to manage long-term effects of the risk-reducing ...
Can narcissists be moved to show empathy?
2014-05-30
Researchers at the University of Surrey and the University of Southampton have investigated whether narcissists can elicit empathy for another person's suffering. It has been well documented that narcissists lack empathy, but why is that the case, and do they have the capacity to change that behavior? The research is published in Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin.
Characterizing narcissism
When we think of narcissism most of us can all think of a colleague, friend, or former significant other that would fit the description; "A bit full of themselves, self-centered, ...
Narcissists can feel empathy, research finds
2014-05-30
Narcissists tend to lack empathy, which can cause problems for themselves, the people around them and society in general. However, new research published today from the University of Surrey, suggests that with the right focus, people with narcissistic tendencies can feel empathy for another person's suffering. This may be important in helping to prevent the often violent or anti-social behaviours that some narcissists are prone to and the crimes that are committed as a result.
The research, published in Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, studied participants ...
Eating prunes can help weight loss
2014-05-30
Research by the University of Liverpool has found that eating prunes as part of a weight control diet can improve weight loss.
Consumption of dried fruit is not readily recommended during weight loss despite evidence it enhances feelings of fullness.
However, a study by the University's Institute of Psychology, Health and Society of 100 overweight and obese low fibre consumers tested whether eating prunes as part of a weight loss diet helped or hindered weight control over a 12-week period.
It also examined if low fibre consumers could tolerate eating substantial ...
Cochrane review on use of rectal artesunate for severe malaria
2014-05-30
Researchers from the Cochrane Infectious Diseases Group, hosted at LSTM, conducted an independent review of the effects of pre-referral rectal artesunate for people with severe malaria, published in the Cochrane Library today. The review follows a large trial of rectal artesunate in 2009 which led the World Health Organization to recommend its use.
Severe malaria is a serious medical condition caused by infection with the Plasmodium parasite. It is treated by giving injections of antimalarial drugs, which need to be started as quickly as possible to reduce the risk of ...