(Press-News.org) Surface catalysts are notoriously difficult to study mechanistically, but scientists at the University of South Carolina and Rice University have shown how to get real-time reaction information from Ag nanocatalysts that have long frustrated attempts to describe their kinetic behavior in detail.
The key to the team's success was bridging a size gap that had represented a wide chasm to researchers in the past. To be effective as nanocatalysts, noble metals such as Au, Pt, Pd and Ag typically must be nanoparticles smaller than 5 nm, says Hui Wang, an assistant professor of chemistry and biochemistry at South Carolina who led the team in collaboration with Peter Nordlander of Rice University.
Unfortunately, 5 nm is below the size threshold at which plasmon resonance can be effectively harnessed. Plasmon resonance is a phenomenon giving rise to a dramatic enhancement of impinging electromagnetic signals, which is the basis of analytical techniques such as surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS).
The ability to utilize the analytical power of plasmon resonance in a nanomaterial requires larger nanoparticles, "at least tens of nanometers in diameter," says Wang. The incompatibility of the two size regimes had long precluded the use of a range of spectral techniques based on plasmon resonance—SERS is just one—on noble metal nanocatalysts under 5 nm.
But as they just reported in Nano Letters, Wang and his team managed to combine the best of both size worlds.
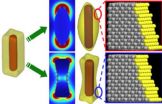
Starting with cuboidal nanoparticles about 50 nm wide and 120 nm long, they chemically etched flat surfaces in a way that generated curved surfaces, creating nanoparticles that successfully catalyzed a model surface hydrogenation reaction. According to the team, the catalysis is the result of replacing low-energy atoms on the flat surface with exposed atoms after etching.
"If you have a flat surface, the coordination number of every single surface atom is either eight or nine," says Wang of their nanoparticles, which had a surface of pure Ag before etching. "But if you have some atomic steps on a surface, the coordination number will decrease. These exposed atoms are more active."
The stepped surface of the etched nanomaterial thus mimics the environment of a sub-5-nm nanoparticle: more exposed, active surface atoms can participate in catalysis.
And the catalysis is on a nanoparticle with plasmonic activity, which the researchers showed can be "tuned" by varying the shape and size of the nanoparticles. The team demonstrated the ability to convert cuboids (something like a short rod but with square rather than round sides) into what they termed "nanorice" and "nanodumbbells" through two different kinds of chemical etching. The two shapes had distinct plasmonic properties that could be varied by stopping the etching at different stages to create different sizes and shapes of nanoscale rice and dumbbells.
That plasmonic activity can be harnessed for SERS and other analytical techniques to study catalytic reactions in great detail as they occur.
"Raman spectroscopy is extremely powerful, with information about molecular fingerprints—you can see the structures, you can tell how the molecules are oriented on the surface," Wang says. "If you want to use GC, HPLC, or mass spec, you have to damage a sample, but here you can actually monitor the reaction in real time.
"And there is much more information with this approach. For example, we identified the intermediate along the reaction pathway. With those other approaches, it's really hard to do that."
INFORMATION: END
Opening a wide window on the nano-world of surface catalysis
Bridging size gap makes real-time SERS data available from the surface of Ag nanocatalysts
2014-06-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Exotic particle confirmed
2014-06-06
This news release is available in French. For decades, physicists have searched in vain for exotic bound states comprising more than three quarks. Experiments performed at Jülich's accelerator COSY have now shown that, in fact, such complex particles do exist in nature. This discovery by the WASA-at-COSY collaboration has been published in the journal Physical Review Letters. The measurements confirm results from 2011, when the more than 120 scientists from eight countries discovered for the first time strong indications for the existence of an exotic dibaryon made ...
Early exposure to certain bacteria may protect toddlers from wheezing
2014-06-06
WHAT: Research funded by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) suggests that exposure to specific combinations of allergens and bacteria within the first year of life may protect children from wheezing and allergic disease. These observations come from the Urban Environment and Childhood Asthma (URECA) study, which aims to identify factors responsible for asthma development in children from inner-city settings, where the disease is more prevalent and severe. Since 2005, the URECA study has enrolled 560 children from four cities—Baltimore, Boston, New York and St. Louis. ...
New report: Local public grants for art varies across US
2014-06-06
Local direct public funding provided through grants for the arts in Chicago is low compared to peer regions in both total dollar and per capita terms, according to a new report from the Cultural Policy Center at the University of Chicago.
The study tracks direct public funding for the arts in 13 regions from 2002-2012. It provides a nuanced look at how much money comes to the nonprofit arts from national, state and local arts agencies, with an emphasis on the important role of local arts agencies. While most studies of public funding for the arts use appropriations made ...
HIV transmission networks mapped to reduce infection rate
2014-06-06
Researchers at the University of California, San Diego School of Medicine have mapped the transmission network of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) in San Diego. The mapping of HIV infections, which used genetic sequencing, allowed researchers to predictively model the likelihood of new HIV transmissions and identify persons at greatest risk for transmitting the virus.
The findings are published online in the June 5 issue of the journal PLOS ONE.
"The more we understand the structure and dynamics of an HIV transmission network, the better we can identify 'hot spots' ...
Alcohol may protect trauma patients from later complications
2014-06-06
Injured patients who have alcohol in their blood have a reduced risk for developing cardiac and renal complications, according to a study from the University of Illinois at Chicago School of Public Health. Among patients who did develop complications, those with alcohol in their blood were less likely to die.
The study is published in the June issue of the journal Alcohol.
"After an injury, if you are intoxicated there seems to be a substantial protective effect," says UIC injury epidemiologist Lee Friedman, author of the study. "But we don't fully understand why this ...
Is glaucoma a brain disease?
2014-06-06
Rockville, Md. — Findings from a new study published in Translational Vision Science & Technology (TVST) show the brain, not the eye, controls the cellular process that leads to glaucoma. The results may help develop treatments for one of the world's leading causes of irreversible blindness, as well as contribute to the development of future therapies for preserving brain function in other age-related disorders like Alzheimer's.
In the TVST paper, Refined Data Analysis Provides Clinical Evidence for Central Nervous System Control of Chronic Glaucomatous Neurodegeneration, ...
Clinical review published in JAMA
2014-06-06
Many women experience bothersome urine loss with laughing, coughing and sneezing (stress urinary incontinence) AND on their way to the bathroom (urge urinary incontinence). When women experience both types of urine leakage, their condition is called mixed urinary incontinence. It is estimated that 20 to 36 percent of women suffer from mixed urinary incontinence, which is challenging to diagnose and treat because symptoms vary and guidelines for treatment are not clear.
A clinical review entitled "Clinical Crossroads – Female Mixed Urinary Incontinence" by Deborah L. ...
Prostate cancer biomarkers identified in seminal fluid
2014-06-06
Improved diagnosis and management of one of the most common cancers in men – prostate cancer – could result from research at the University of Adelaide, which has discovered that seminal fluid (semen) contains biomarkers for the disease.
Results of a study now published in the journal Endocrine-Related Cancer have shown that the presence of certain molecules in seminal fluid indicates not only whether a man has prostate cancer, but also the severity of the cancer.
Speaking in the lead-up to Men's Health Week (9-15 June), University of Adelaide research fellow and lead ...
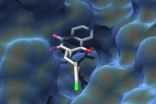
Toward a better drug against malaria
2014-06-06
This news release is available in German.
A research team led by Prof. Dr. Carola Hunte of the University of Freiburg/ Germany has succeeded in describing how the antimalarial drug atovaquone binds to its target protein. The scientists used x-ray crystallography to determine the three-dimensional structure of the protein with the active substance bound. The drug combination atovaquone-proguanil (Malarone®) is a medication used worldwide for the prevention and treatment of malaria. The data and the resulting findings concerning the mode of action of atovaquone could ...
Football for untrained 70-year-old men
2014-06-06
Research carried out by the Copenhagen Centre for Team Sport and Health in Denmark shows that untrained elderly men get markedly fitter and healthier as a result of playing football (soccer). After only 4 months of twice-weekly 1-hour training sessions, the men achieved marked improvements in maximum oxygen uptake, muscle function and bone mineralization.
Later today, three scientific articles will be published in the Scandinavian Journal of Medicine & Science in Sports describing the fitness and health effects of football training for 63‒75-year-old untrained men. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
JMIR Publications partners with the University of Turku for unlimited OA publishing
Strange cosmic burst from colliding galaxies shines light on heavy elements
Press program now available for the world's largest physics meeting
New release: Wiley’s Mass Spectra of Designer Drugs 2026 expands coverage of emerging novel psychoactive substances
[Press-News.org] Opening a wide window on the nano-world of surface catalysisBridging size gap makes real-time SERS data available from the surface of Ag nanocatalysts