(Press-News.org) EAST LANSING, Mich. — Helping farmers around the globe apply more-precise amounts of nitrogen-based fertilizer can help combat climate change.
In a new study published in this week's Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Michigan State University researchers provide an improved prediction of nitrogen fertilizer's contribution to greenhouse gas emissions from agricultural fields.
The study uses data from around the world to show that emissions of nitrous oxide, a greenhouse gas produced in the soil following nitrogen addition, rise faster than previously expected when fertilizer rates exceed crop needs.
Nitrogen-based fertilizers spur greenhouse gas emissions by stimulating microbes in the soil to produce more nitrous oxide. Nitrous oxide is the third most important greenhouse gas, behind only carbon dioxide and methane, and also destroys stratospheric ozone. Agriculture accounts for around 80 percent of human-caused nitrous oxide emissions worldwide, which have increased substantially in recent years, primarily due to increased nitrogen fertilizer use.
"Our specific motivation is to learn where to best target agricultural efforts to slow global warming," said Phil Robertson, director of MSU's Kellogg Biological Station Long-term Ecological Research Program and senior author of the paper. "Agriculture accounts for 8 to 14 percent of all greenhouse gas production globally. We're showing how farmers can help to reduce this number by applying nitrogen fertilizer more precisely."
The production of nitrous oxide can be greatly reduced if the amount of fertilizer crops need is exactly the amount that's applied to farmers' fields. Simply put, when plant nitrogen needs are matched with the nitrogen that's supplied, fertilizer has substantially less effect on greenhouse gas emission, Robertson said.
Iurii Shcherbak, lead author and MSU researcher, noted that the research also informs fertilizer practices in underfertilized areas such as sub-Saharan Africa.
"Because nitrous oxide emissions won't be accelerated by fertilizers until crop nitrogen needs are met, more nitrogen fertilizer can be added to underfertilized crops with little impact on emissions," she said.
Adding less nitrogen to overfertilized crops elsewhere, however, would deliver major reductions to greenhouse gas emissions in those regions.
This study provides support for expanding the use of carbon credits to pay farmers for better fertilizer management. Carbon credits for fertilizer management are now available to U.S. corn farmers. This paper provides a framework for using this system around the world.
The research was funded by the National Science Foundation, the Department of Energy's Great Lakes Bioenergy Research Center and the Electric Power Research Institute. Robertson's work also is funded in part by MSU AgBioresearch.
INFORMATION:
Michigan State University has been working to advance the common good in uncommon ways for more than 150 years. One of the top research universities in the world, MSU focuses its vast resources on creating solutions to some of the world's most pressing challenges, while providing life-changing opportunities to a diverse and inclusive academic community through more than 200 programs of study in 17 degree-granting colleges.
For MSU news on the Web, go to MSUToday. Follow MSU News on Twitter at twitter.com/MSUnews.
How much fertilizer is too much for the climate?
2014-06-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Coral, human cells linked in death
2014-06-09
SAN DIEGO (June 6, 2014) — Humans and corals are about as different from one another as living creatures get, but a new finding reveals that in one important way, they are more similar than anyone ever realized.
A biologist at San Diego State University has discovered they share the same biomechanical pathway responsible for triggering cellular self-destruction. That might sound scary, but killing off defective cells is essential to keeping an organism healthy.
The finding will help biologists advance their understanding of the early evolution of multicellular life, ...
Researchers recast addiction as a manageable disease
2014-06-09
Neuroscientists agree that abuse of drugs hijacks circuits in the brain that are crucial for decision-making, but society as a whole tends to stigmatize addicted people for lacking self-control. Slowly but steadily, scientists say, they are making important progress in changing the perception of addiction as they identify new therapeutic interventions that could render addiction into the equivalent of a manageable disease like diabetes.
A group of addiction researchers, for one, recently recommended to the Commission on Narcotic Drugs, part of the United Nations Office ...
Protein could put antibiotic-resistant bugs in handcuffs
2014-06-09
DURHAM, N.C. -- Staph infections that become resistant to multiple antibiotics don't happen because the bacteria themselves adapt to the drugs, but because of a kind of genetic parasite they carry called a plasmid that helps its host survive the antibiotics.
Plasmids are rings of bare DNA containing a handful of genes that are essentially freeloaders, borrowing most of what they need to live from their bacterial host. The plasmids copy themselves and go along for the ride when the bacteria divide to copy themselves.
A team from Duke and the University of Sydney in ...
Parent and child must get enough sleep to protect against child obesity
2014-06-09
URBANA, Ill. – Is sleep one of your most important family values? A new University of Illinois study suggests that it should be, reporting that more parental sleep is related to more child sleep, which is related to decreased child obesity.
"Parents should make being well rested a family value and a priority. Sleep routines in a family affect all the members of the household, not just children; we know that parents won't get a good night's sleep unless and until their preschool children are sleeping," said Barbara H. Fiese, director of the U of I's Family Resiliency Center ...
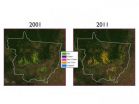
Land quality and deforestation in Mato Grosso, Brazil
2014-06-09
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — The state of Mato Grosso is the epicenter of an agricultural revolution in Brazil. During the last 15 years, expansion of agriculture in the state has helped Brazil become one of the world's top producers of soy, corn, cotton, and other staple crops. Despite the increase in production, the rate at which Amazon forestland in the state was cleared to make room for new farmland slowed significantly in the second half of the last decade.
Much of the credit for slowing deforestation has been given to government policies and intervention, ...
Does 'free will' stem from brain noise?
2014-06-09
VIDEO:
UC Davis researchers found that the pattern of electrical activity in the brain immediately before making a decision can predict the choice made. This video shows how these experiments are...
Click here for more information.
Our ability to make choices — and sometimes mistakes — might arise from random fluctuations in the brain's background electrical noise, according to a recent study from the Center for Mind and Brain at the University of California, Davis.
"How ...
Humanitarian liking on Facebook
2014-06-09
"Liking" a page on the social networking site Facebook is a new form of civic engagement and humanitarian support, so concludes research published in the International Journal of Web Based Communities. According to the paper's authors social motives and an emotional response underpinned users' inclination to like, or follow, a page, rather than their simply seeking information and news.
Petter Bae Brandtzaeg and Ida Maria Haugstveit of Scandinavian research organization SINTEF in Oslo, Norway, surveyed more than 400 Facebook users about their habits on the site and their ...
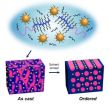
Berkeley Lab researchers create nanoparticle thin films that self-assemble in 1 minute
2014-06-09
The days of self-assembling nanoparticles taking hours to form a film over a microscopic-sized wafer are over. Researchers with the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE)'s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) have devised a technique whereby self-assembling nanoparticle arrays can form a highly ordered thin film over macroscopic distances in one minute.
Ting Xu, a polymer scientist with Berkeley Lab's Materials Sciences Division, led a study in which supramolecules based on block copolymers were combined with gold nanoparticles to create nanocomposites that ...
'Hello, world!' NASA beams video from space station via laser
2014-06-09
"Hello, World!" came the message from the International Space Station as NASA successfully beamed high-definition video via laser from space to ground on Thursday, June 5. The 175-megabit video transmission was the first of its kind for the Optical Payload for Lasercomm Science (OPALS) with the goal of improving the way we receive data from orbit and beyond. In fact, this emerging technology of optical communications--or lasercomm--is likened to an upgrade from dial-up to DSL.
"It's incredible to see this magnificent beam of light arriving from our tiny payload on the ...
African-American women more likely to be diagnosed with higher risk breast cancer
2014-06-09
Washington, D.C., June 9, 2014 - A research study led by cancer specialists at MedStar Washington Hospital Center found that African-American women frequently present with biologically less favorable subtypes of breast cancer.
Researchers at the Hospital Center's Washington Cancer Institute analyzed the biology of breast cancer in 100 African-American women, using a method of genomic profiling. These genomic tests look at the expression of genes associated with the risk of recurrence in the population and further characterizes the biology of the tumor. The 70-gene MammaPrint ...