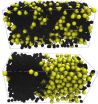
(Press-News.org) Systems containing self-propelling particles, such as bacteria or artificial colloidal particles, are always out of equilibrium but may show interesting transitions between different states, reminiscent of phase transitions in equilibrium. However, application of analytical and computational methodologies from equilibrium statistical mechanics is questionable to study properties of such active systems. An international team of researchers – including Dr. Peter Virnau and Professor Kurt Binder of Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU), Benjamin Trefz of the JGU Graduate School of Excellence "Materials Science in Mainz" (MAINZ), and scientists from India and the U.S. – has studied the phase separation of a mixture of active and passive particles via molecular dynamics simulations and integral equation theoretical calculations. The distinctive feature of the model used is that the "activity" of the particles is tunable, containing passive particles as a limiting case for which already phase separation occurs.
"Our research results demonstrate that the introduction of activity may not only hamper phase separation as shown previously, but can enhance it as well, based on the coordination among the active particles," explained Dr. Peter Virnau of the Institute of Physics at Mainz University. Moreover, the researchers provided an approximate mapping of the phase behavior and structural properties of this nonequilibrium problem onto an equilibrium problem. A general validity of this mapping is subject to further careful testing. The confirmation of such validity would be an important step forward in understanding properties of active matter.
INFORMATION:
Publication:
Subir K. Das et al.
Phase Behavior of Active Swimmers in Depletants: Molecular Dynamics and Integral Equation Theory
Physical Review Letters, 15 May 2014
DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.112.198301
http://journals.aps.org/prl/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevLett.112.198301
Active particles may enhance phase separation
Model system used to illustrate phase transition of a mixture of active and passive particles
2014-06-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Immune response affects sleep and memory -- new study
2014-06-12
Fighting off illness- rather than the illness itself- causes sleep deprivation and affects memory, a new study has found.
University of Leicester biologist Dr Eamonn Mallon said a common perception is that if you are sick, you sleep more.
But the study, carried out in flies, found that sickness induced insomnia is quite common.
The research has been published in the journal PeerJ at: http://peerj.com/articles/434
Dr Mallon said: "Think about when you are sick. Your sleep is disturbed and you're generally not feeling at your sharpest. Previously work has been ...
Twelve minutes of exercise improves attention, reading comprehension in low-income adolescents
2014-06-12
HANOVER, N.H. – June 12, 2014 – A new Dartmouth study shows 12 minutes of exercise can improve attention and reading comprehension in low-income adolescents, suggesting that schools serving low-income populations should work brief bouts of exercise into their daily schedules.
The study, published as part of the June volume of Frontiers in Psychology, compared low-income adolescents with their high-income peers. While both groups saw improvement in selective visual attention up to 45 minutes after exercising, the low-income group experienced a bigger jump. (Selective visual ...
Potential new treatment may protect celiac patients from gluten-induced injury
2014-06-12
Bethesda, MD (June 12, 2014) — The gluten-specific enzyme ALV003 reduces a patient's exposure to gluten and its potential harm, according to a new phase 2 study appearing in Gastroenterology1, the official journal of the American Gastroenterological Association. This study is the first to find that a non-dietary intervention can potentially benefit celiac disease patients.
Study participants were put on an everyday gluten-free diet, challenged with up to 2 grams of gluten daily (equivalent to approximately one half of a standard slice of bread in the U.S.). Researchers ...
First articles published in new Journal of Medical Imaging
2014-06-12
BELLINGHAM, Washington (USA) — The Journal of Medical Imaging (JMI) has launched, with freely accessible articles on new research on earlier and more accurate diagnosis and monitoring of cancer and other diseases, image quality assessment, 3D imaging, and other topics. Published by SPIE, the international society for optics and photonics, the quarterly journal is available online in the SPIE Digital Library, with each peer-reviewed article published as it is approved. JMI will also be issued in print.
JMI covers fundamental and translational research and applications ...
Climate change winners and losers
2014-06-12
The Antarctic Peninsula, the northern most region of Antarctica, is experiencing some of the most dramatic changes due to climate warming, including population declines of some penguin species.
This is not the first time that region has felt the effects of climate warming. How did penguins respond to the melting of snow and ice cover 11,000 years ago at the end of the last Ice Age?
Today, scientists have traced the genetics of modern penguin populations back to their early ancestors from the last Ice Age to better understand how three Antarctic penguin species – gentoo, ...
Rise and fall of prehistoric penguin populations charted
2014-06-12
A study of how penguin populations have changed over the last 30,000 years has shown that between the last ice age and up to around 1,000 years ago penguin populations benefitted from climate warming and retreating ice. This suggests that recent declines in penguins may be because ice is now retreating too far or too fast.
An international team, led by scientists from the Universities of Southampton and Oxford, has used a genetic technique to estimate when current genetic diversity arose in penguins and to recreate past population sizes. Looking at the 30,000 years before ...
A picture's worth a thousand words
2014-06-12
For nearly 100 years, we have known that type 1 diabetes (T1D) is a disease fundamentally about the progressive loss of insulin-producing beta cells, but measuring that loss has continued to elude researchers—at least until now.
In a recent scientific publication, JDRF-funded researchers used a radiotracer or marker and PET (Positron Emission Tomography) scanning as a non-invasive technique to follow changes in how many active beta cells a person has. Dr. Olle Korsgren and his colleagues at the University of Uppsala in Sweden used the technique in a clinical study ...
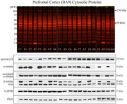
Alcohol abuse damage in neurones at a molecular scale identified for first time
2014-06-12
This news release is available in Spanish.
Joint research between the University of the Basque Country (UPV/EHU) and the University of Nottingham has identified, for the first time, the structural damage caused at a molecular level to the brain by the chronic excessive abuse of alcohol. In concrete, the research team has determined the alterations produced in the neurones of the prefrontal zone of the brain (the most advanced zone in terms of evolution and that which controls executive functions such as planning, designing strategies, working memory, selective ...
David and Goliath: How a tiny spider catches much larger prey
2014-06-12
In nature, it is very rare to find a proverbial much smaller David able to overpower and kill a Goliath for supper. This is exactly the modus operandi of a solitary tiny spider from the Negev desert in Israel that routinely kills ants up to almost four times its own size. Details about how it attacks and kills its prey with a venomous bite is published in Springer's journal Naturwissenschaften – The Science of Nature. The study was led by Stano Pekár of Masaryk University in the Czech Republic.
Pekár's team observed the natural prey and predatory behavior of the minute ...
Survivors of childhood liver transplant at risk of becoming 'skinny fat'
2014-06-12
New research reports that survivors of childhood liver transplant remain nutritionally compromised over the long-term. Findings published in Liver Transplantation, a journal of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the International Liver Transplantation Society, indicate that the recipients' return to normal weight post-transplant was due to an increase in fat mass as body cell mass remained low, indicating a slim body composition with little lean muscle mass or "skinny fat."
Children with end-stage liver disease may be malnourished due to inadequate ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
SKKU research team unravels the origin of stochasticity, a key to next-generation data security and computing
Flexible polymer‑based electronics for human health monitoring: A safety‑level‑oriented review of materials and applications
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
[Press-News.org] Active particles may enhance phase separationModel system used to illustrate phase transition of a mixture of active and passive particles