(Press-News.org) The latest version of a bionic pancreas device has been successfully tested in two five-day clinical trials – one in adults, the other in adolescents – that imposed minimal restrictions on
patient activities. A team of investigators from Boston University (BU) and Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) report study results in a New England Journal of Medicine paper being issued online to coincide with a presentation (abstract # 237-OR) at the American Diabetes Association Scientific Sessions. The device controls blood sugar in patients with type 1 diabetes using doses of both insulin and the blood-sugar-raising hormone glucagon.
"In both of these studies this device far exceeded our expectations in terms of its ability to regulate glucose, prevent hypoglycemia and automatically adapt to the very different needs of adults – some of whom were very insulin-sensitive – and adolescents, who typically need higher insulin doses," says Edward Damiano, PhD, of the BU Department of Biomedical Engineering, principal investigator of the project and senior author of the NEJM report. "There's no current standard-of-care therapy that could match the results we saw."
Firas El-Khatib, PhD, of the BU Department of Biomedical Engineering, adds, "One of the key virtues of this device is its ability to start controlling the blood sugar instantly, based only on the patient's weight, and continually adapt its decision making regarding insulin and glucagon dosing to handle a wide range of dosing requirements." El-Khatib co-designed the bionic pancreas device with Damiano and is co-lead author of the NEJM report with Steven Russell, MD, PhD, of the MGH Diabetes Unit,.
Russell – who led the clinical trials reported in the current paper – Damiano, and El-Khatib previously published a 2010 Science Translational Medicine report that described successful use of the first-generation system in controlling the blood sugar of adults for 27 hours. But that study took place in a controlled hospital inpatient environment where participants essentially stayed in bed for the whole period and ate prescribed meals. "The key element with the current version of this device is that it's wearable, allowing participants to stay in something close to their usual environments, exercise and eat whatever they want," says Russell.
Additional inpatient trials conducted after the 2010 paper extended the study period to two days and included adolescents as well as adults. But developing a device that could be tested safely in an outpatient environment presented several challenges, first among which was a control system that could adapt not only to the minute-by-minute changing needs of an individual, but also to the very different needs of adults and adolescents. The rapid growth and hormonal changes of adolescence produces insulin requirements that are two to three times greater than those of adults of the same body weight, Damiano explains. And even though the dosage needs of adults are more predictable, contracting typical a illness like a cold or upset stomach can dramatically change the need for insulin over a period of days to weeks.
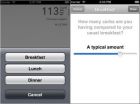
Along with the software improvements that allow the device to adapt to widely varied individual dosage needs, the new version also relies on improved hardware, including a smartphone (iPhone 4S) capable of practical wireless communication with two pumps delivering doses of insulin and glucagon. Every five minutes the smartphone receives a blood sugar reading from an attached continuous glucose monitor, which it uses to calculate and administer a dose of either insulin or glucagon. The smartphone includes an application on which the patient enters information immediately before eating. But instead of the complex calculation patients typically do to estimate their carbohydrate intake, this app only asks whether the meal consumed will be breakfast, lunch, or dinner and whether the carbohydrate content will be typical, larger or smaller than usual.
Both of the studies reported in the NEJM paper compared data reflecting five days on the bionic pancreas system with five days of participants' usual care using their own insulin pumps. The adult trial enrolled 20 participants who lived at home and managed their own care during the usual-care period. While on the bionic pancreas, participants needed to stay within a three-square-mile area of downtown Boston, which enabled constant wireless monitoring of the blood sugar levels by study staff. They were accompanied by a study nurse 24 hours a day and slept in a hotel; but were otherwise free to do as they chose, including exercising at a gym and eating in restaurants.
The adolescent trial enrolled 32 participants, ages 12 to 20, attending a camp for youngsters with type 1 diabetes, who followed the same activity and meal schedule as other campers during both phases of the trial. They were closely monitored by study and camp staff and via wireless monitoring during their time on the bionic pancreas. Participants in both phases of both trials were alerted if blood sugar levels dropped into a range requiring carbohydrate administration, including during nighttime monitoring.
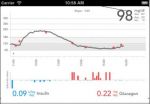
In both studies, the time on the bionic pancreas produced what Russell calls, "two results that almost never go together. Participants' average blood glucose went down while the incidents of low blood sugar also dropped. The fear of hypoglycemia can limit attempts to bring the average blood sugar into the range that dramatically reduces the risk of long-term complications, so it was remarkable that we saw both of these results at once. Both groups had quite good levels in the usual care arms – averages of 159 for both adults and adolescents – but the difference while they were on the bionic pancreas was dramatic, with average blood sugar levels of 133 for the adults and 142 for adolescents." Fewer instances of hypoglycemia on the bionic pancreas also reduced the need for carbohydrate doses to raise blood sugar.
Damiano, whose 15-year-old son was diagnosed with type 1 diabetes at the age of 11 months, explains what having a device like this could mean to patients. "The most practical difference would be not having to think about diabetes 24/7, not having to constantly make decisions about things that those of us without type 1 never have to think about. Another real problem that would be relieved is the fear – fear of going to bed at night and not knowing if your blood sugar level will drop dangerously low while you sleep. Even our study participants, who controlled their blood sugars significantly better than national averages on their usual care, ran high levels overnight but still had significant episodes of hypoglycemia.
"And another extremely frustrating aspect of diabetes that would be completely eliminated by this device is the enormous sense of failure when you stare at that glucose meter and, despite everything you do to control it, your blood sugar is not in or near the normal range," he continues. "But of course you didn't fail; the tools that are available to you failed. The bionic pancreas we are working toward would relieve that sense of failure and provide a bridge to the often-promised but still elusive cure for type 1 diabetes."
Two follow-up trials are in the works, one of which will be a true home study only requiring that participants stay within an hour's drive of the study site. That trial, which will compare 11 days on the bionic pancreas with 11 days of usual care, will be coordinated by Russell's MGH team and conducted at four centers – the MGH, the University of Massachusetts Medical Center in Worcester, the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, and Stanford University – and will begin on June 16 at MGH. The second study, conducted at Camp Clara Barton and Camp Joslin in central Massachusetts, will enroll children ages 6 to 11 and is currently enrolling participants already registered at the camps. Information on both of those trials and on the overall project is available at http://www.bionicpancreas.org/.
INFORMATION:
Damiano is an associate professor of Biomedical Engineering at Boston University, El-Khatib is a senior research scientist of Biomedical Engineering at Boston University, and Russell is an assistant professor of Medicine at Harvard Medical School. Additional co-authors of the NEJM paper are Manasi Sinha, MD, MPH, Kendra Magyar, MSN, NP, Laura Goergen, BSN, RN, Courtney Balliro, BSN, RN, Mallory Hillard and David M. Nathan, MD, MGH Diabetes Unit; and Katherine McKeon, MEng, BU Department of Biomedical Engineering.
Support for the study includes National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases grants R01DK085633 and R01DK097657 and grants from the Helmsley Charitable Trust and the Charlton Fund for Innovative Research in Diabetes. Patents related to the development of the bionic pancreas have been issued to or applied for by several members of the research team.
Founded in 1839, Boston University (http://www.bu.edu) is an internationally recognized institution of higher education and research. With more than 33,000 students, it is the fourth-largest independent university in the United States. BU consists of 16 schools and colleges, along with a number of multi-disciplinary centers and institutes integral to the University's research and teaching mission. In 2012, BU joined the Association of American Universities (AAU), a consortium of 62 leading research universities in the United States and Canada.
Massachusetts General Hospital (http://www.massgeneral.org), founded in 1811, is the original and largest teaching hospital of Harvard Medical School. The MGH conducts the largest hospital-based research program in the United States, with an annual research budget of more than $785 million and major research centers in AIDS, cardiovascular research, cancer, computational and integrative biology, cutaneous biology, human genetics, medical imaging, neurodegenerative disorders, regenerative medicine, reproductive biology, systems biology, transplantation biology and photomedicine.
Bionic pancreas controls blood sugar levels in adults, adolescents with type 1 diabetes
2014-06-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Bionic pancreas outperforms insulin pump in adults, youth
2014-06-16
People with type 1 diabetes who used a bionic pancreas instead of manually monitoring glucose using fingerstick tests and delivering insulin using a pump were more likely to have blood glucose levels consistently within the normal range, with fewer dangerous lows or highs. The full report of the findings, funded by the National Institutes of Health, can be found online June 15 in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The researchers – at Boston University and Massachusetts General Hospital – say the process of blood glucose control could improve dramatically with the ...
Advances in predictive hypoglycemia-minimizing technology from Animas-JDRF collaboration
2014-06-16
CHESTERBROOK, Pennsylvania, June 16, 2014 –Animas Corporation today shared encouraging results from its predictive hypoglycemia-minimizing algorithm in development. Data from a clinical feasibility study demonstrated that the algorithm was capable of helping maintain glucose above hypoglycemic levels an average of 99.1 percent of the time for the 12 participants investigated, all of whom were adults with type 1 diabetes. The study was conducted by Animas in collaboration with industry, academia and JDRF as part of an effort to advance the development of a predictive blood ...
Arctic warming linked to fewer European and US cold weather extremes, new study shows
2014-06-15
Climate change is unlikely to lead to more days of extreme cold, similar to those that gripped the USA in a deep freeze last winter, new research has shown.
The Arctic amplification phenomenon refers to the faster rate of warming in the Arctic compared to places further south. It is this phenomenon that has been linked to a spike in the number of severe cold spells experienced in recent years over Europe and North America.
However, new research by University of Exeter expert Dr James Screen has shown that Arctic amplification has actually reduced the risk of cold extremes ...
Parasitic worms of pigs could provide new treatments of human diseases
2014-06-15
New treatments for inflammatory bowel disease, rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, diabetes and autism could be on the horizon, after a global University of Melbourne – lead study successfully mapped the genes of a parasitic worm in pigs.
Lead researcher, Dr Aaron Jex, Faculty of Veterinary Science, said, "We know that humans infected with the harmless, 'pig whipworm' can have significantly reduced symptoms linked to autoimmune diseases. And now we have the genetic sequence of the worm, it opens the door to future human drug designs and treatment."
Although the ...
Melting and refreezing of deep Greenland ice speeds flow to sea, study says
2014-06-15
Beneath the barren whiteness of Greenland, a mysterious world has popped into view. Using ice-penetrating radar, researchers have discovered ragged blocks of ice as tall as city skyscrapers and as wide as the island of Manhattan at the very bottom of the ice sheet, apparently formed as water beneath the ice refreezes and warps the surrounding ice upwards.
The newly revealed forms may help scientists understand more about how ice sheets behave and how they will respond to a warming climate. The results are published in the latest issue of Nature Geoscience.
"We see ...
Exploring a parasitic tunnel boring machine
2014-06-15
Researchers have deduced essential biological and genetic information from the genome sequence of the whipworm, an intestinal parasitic worm that infects hundreds of millions of people in developing countries.
This information acts as the foundation for the development of new strategies and treatments against this debilitating parasite.
The whipworm is one of three types of soil-transmitted parasitic worms that collectively infect nearly two billion people. While infections often result in mild disease they may also lead to serious and long-term damage such as malnutrition, ...
Understanding the unique nature of children's bodies and brains
2014-06-15
June 15, 2014 (San Francisco) – With the increase in childhood obesity and the associated increase in type 2 diabetes among children and adolescents, there is growing interest in how children's bodies process the foods they eat and how obesity and diabetes begin to develop at early ages. Two studies presented at the American Diabetes Association's 74th Scientific Sessions® help to shed light on this topic.
One study, by researchers at the Yale School of Medicine, compared how the brains of adolescents and adults differed in their response to ingestion of a glucose drink. ...
'Disappointed' researchers find lack of political voices on Twitter
2014-06-15
ITHACA, N.Y. – Social scientists' analysis of 290,119,348 tweets from 193,522 "politically engaged" Twitter users during the 2012 presidential campaign conventions and debates found little creative thinking, and a slavish blitz of retweeting "elites" like @billmaher and @seanhannity, according to a new study.
"Frankly, we're rather disappointed," says Cornell University's Drew Margolin. "Social media has so much potential to improve the diversity of voices and quality of exchanges in political discussion by giving individuals the technological capability to compete with ...
Emotional contagion sweeps Facebook, finds new study
2014-06-15
ITHACA, N.Y. – When it hasn't been your day – your week, your month, or even your year – it might be time to turn to Facebook friends for a little positive reinforcement. According to a new study by social scientists at Cornell University, the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF), and Facebook, emotions can spread among users of online social networks.
The researchers reduced the amount of either positive or negative stories that appeared in the news feed of 689,003 randomly selected Facebook users, and found that the so-called "emotional contagion" effect worked ...
Fasting reduces cholesterol levels in prediabetic people over extended period of time
2014-06-14
For prediabetics, many interventions focus on lifestyle changes and weight loss, but new research on periodic fasting has identified a biological process in the body that converts bad cholesterol in fat cells to energy, thus combating diabetes risk factors.
Researchers at the Intermountain Heart Institute at Intermountain Medical Center in Murray, Utah, noticed that after 10 to 12 hours of time fasting, the body starts scavenging for other sources of energy throughout the body to sustain itself. The body pulls LDL (bad) cholesterol from the fat cells and uses it as energy.
"Fasting ...