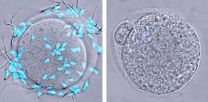
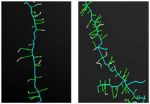
(Press-News.org) Before it can fertilize an egg, a sperm has to bind to and bore through an outer egg layer known as the zona pellucida. Despite decades of research, some of the biological mechanisms behind this process remain unclear. A study in The Journal of Cell Biology now identifies the protein in the zona pellucida that sperm latch onto.
The zona pellucida protects the egg and the early embryo before implantation. Its structure seems simple—in humans it contains four kinds of glycoproteins, and in mice it only contains three. But researchers haven't been able to identify the sperm's binding partner in the layer, although their suspicions have fallen on two of the glycoproteins, ZP2 and ZP3.
To find out more, Jurrien Dean and colleagues from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases engineered mice to produce various combinations of human and mouse zona pellucida glycoproteins. Mouse sperm didn't bind to the zona pellucida if it was missing ZP2, and female mice lacking the protein were sterile. The researchers also found that sperm couldn't latch onto eggs if ZP2 was missing a key region at the beginning of the protein. This result jibes with a previous finding that fertilization triggers the release of an enzyme that severs ZP2 in this region, thus preventing additional sperm from attaching to the zona pellucida.
The team also tested the binding of human sperm to mouse eggs surrounded by a zona pellucida harboring human glycoproteins. Human sperm adhered to the mouse zona pellucida if it contained human ZP2 but not if it carried human ZP3, confirming the importance of ZP2.
INFORMATION:
Avella, M.A., et al. 2014. J. Cell Biol. doi:10.1083/jcb.201404025
The Journal of Cell Biology (JCB) is published by The Rockefeller University Press. All editorial decisions on manuscripts submitted are made by active scientists in conjunction with our in-house scientific editors. JCB content is posted to PubMed Central, where it is available to the public for free six months after publication. Authors retain copyright of their published works, and third parties may reuse the content for non-commercial purposes under a creative commons license. For more information, please visit http://www.jcb.org.
Research reported in the press release was supported by the Intramural Research Program of the National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (ZIA-DK015603).
How sperm get into the zona
Researchers uncover a key biological interaction that occurs during fertilization
2014-06-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
High number of fatalities despite unchanged level of armed conflicts
2014-06-16
At 33, conflicts in the world last year increased by one compared to 2012. This is reported by peace researchers at Uppsala University's Conflict Data Program. The number has remained stable over the past decade. 2012 saw an increase in the number of battle-related deaths with the number of casualties in Syria completely overshadowing any other ongoing conflict. In 2012, two out of five people dying in battles, died in Syria.
The new dataset is described by peace researchers at Uppsala University's Conflict Data Program (UCDP) in an article which will soon be published ...
Anxious children have bigger 'fear centers' in the brain
2014-06-16
Philadelphia, PA, June 16, 2014 – The amygdala is a key "fear center" in the brain. Alterations in the development of the amygdala during childhood may have an important influence on the development of anxiety problems, reports a new study in the current issue of Biological Psychiatry.
Researchers at the Stanford University School of Medicine recruited 76 children, 7 to 9 years of age, a period when anxiety-related traits and symptoms can first be reliably identified. The children's parents completed assessments designed to measure the anxiety levels of the children, ...
Stress early in life can increase the risk of overweight in adulthood
2014-06-16
There are indications that unborn children who are exposed to severe stress levels, have an increased risk of becoming overweight or developing obesity as adults.
This is shown by a new registry study from Aarhus University published in PloS ONE.
The researchers have previously shown that severe stress experienced by pregnant women can lead to weight problems for children between 10 and 13 years; however, a correlation between the mother's level of stress during pregnancy and the risk of developing overweight or obesity as an adult is new:
"Overall our results indicate ...
Wind turbine payback
2014-06-16
US researchers have carried out an environmental lifecycle assessment of 2-megawatt wind turbines mooted for a large wind farm in the US Pacific Northwest. Writing in the International Journal of Sustainable Manufacturing, they conclude that in terms of cumulative energy payback, or the time to produce the amount of energy required of production and installation, a wind turbine with a working life of 20 years will offer a net benefit within five to eight months of being brought online.
Wind turbines are frequently touted as the answer to sustainable electricity production ...
Coalition's deficit reduction has made UK tax base more regressive
2014-06-16
Taxation in the UK has become increasingly regressive since the financial crisis, particularly since the coalition government came to office, according to academics at the Sheffield Political Economy Research Institute (SPERI).
The latest evidence on tax revenue shows that progressive taxes such as income tax and capital gains tax contribute 54 per cent of total tax receipts, down from 58 per cent five years earlier. In contrast, regressive taxes such as VAT contribute 28 per cent of total tax receipts, an increase from 25 per cent.Tax
Research found that of all the ...
Effective drugs for Parkinson's reduce symptoms of Rett syndrome in mice
2014-06-16
IDIBELL researchers, led by the director of the Program for Epigenetics and Cancer Biology, ICREA researcher and Professor of Genetics at the University of Barcelona, Manel Esteller, have shown that a combination of effective drugs for Parkinson's disease in mice that are used as a model of human Rett syndrome reduces some of the symptoms associated with this disease. The results of the study are published in the journal Neurophsycopharmacology
Second leading cause of mental retardation in females
Rett syndrome is the second most common cause of mental retardation in ...
Could politics trump economics as reason for growing income inequality?
2014-06-16
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Most research examining growing income inequality in the United States has focused on economic causes, for seemingly obvious reasons.
But a new study suggests that a different cause – the politically induced decline in the strength of worker unions – may play a much more pivotal role than previously understood.
In fact, the role that union decline has played in growing income inequality may actually be larger than many of the favorite explanations offered by economists, such as the education gap in the United States.
Among their contributions to income ...
Will diabetes patients benefit from the Affordable Care Act?
2014-06-16
New Rochelle, NY, June 14, 2014—The Affordable Care Act (ACA, also known as Obamacare) is dramatically changing health care delivery in the U.S. Specific parts of the new law, which will be phased in through 2020, will have a significant impact on patients with diabetes and prediabetes, as explored in a comprehensive Review article published in Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics (DTT), a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available free on the DTT website at http://online.liebertpub.com/doi/full/10.1089/dia.2014.0171.
In "Diabetes ...
Stem cells in neurodegeneration: challenges and future neurotherapeutic prospects
2014-06-16
Researchers at the University of Florida, USA, led by Dr. K. Wang have demonstrated that inhibition of Rho-associated kinase (ROCK) and subsequent cofilin dephosphorylation is mediating neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells. The lack of axonal regeneration in adult central nervous system (CNS) is one of the main cause of neurodegenerative disorders. Thus ROCK inhibition mediated neurite outgrowth is clinically relevant to treat CNS diseases such as Alzheimer's disease, spinal cord injury, traumatic brain injury and stroke (Zhang et al., 2006).
In a follow up study by Prof. W.S. ...
Nanoscale composites improve MRI
2014-06-16
HOUSTON – (June 16, 2014) – Submicroscopic particles that contain even smaller particles of iron oxide could make magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) a far more powerful tool to detect and fight disease.
Scientists at Rice University and The Methodist Hospital Research Institute (TMHRI) led an international team of researchers in creating composite particles that can be injected into patients and guided by magnetic fields. Once in position, the particles may be heated to kill malignant tissues or trigger the release of drugs at the site.
The "nanoconstructs" should fully ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
[Press-News.org] How sperm get into the zonaResearchers uncover a key biological interaction that occurs during fertilization