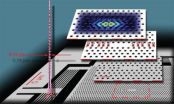
(Press-News.org) Due to their previously discovered fractal nature, financial data patterns are self-similar when scaling up. New research shows that the most extreme events in financial data dynamics—reflected in very large price moves—are incompatible with multi-fractal scaling. These findings have been published in EPJ B by physicist Elena Green from the National University of Ireland in Maynooth and colleagues. Understanding the multi-fractal structure of financially sound markets could, ultimately, help in identifying structural signs of impending extreme events.
The concept of multi-fractality—referring to the intertwining of many fractals—was first introduced in the context of physical turbulence studies. But it was subsequently applied to finance because of the two common features found in financial data, namely an underlying structure of heavy tails distribution and long-term dependence.
The authors performed multi-fractal testing on two sets of financial data: daily data from the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) index and minute-by-minute data from the Euro Stoxx 50 index. Where multi-fractal scaling occurs, the authors calculated the spectrum of fractal scaling factors using a method called Multi-fractal Detrended Fluctuation Analysis. This approach is used for determining the statistical self-affinity, or fractal nature, of a set of data, particularly relevant for data with long-memory characteristics.
The authors then performed further investigations of both data sets. This revealed that the temporal correlations within the data are a more significant source of the multi-fractal scaling than the distribution of the financial returns.
They also demonstrated that the extreme events which make up the heavy tails of the distribution of the Euro Stoxx 50 logarithmic graph of financial returns distort the scaling in the data set. This means that most extreme events adversely affect fractal scaling. Green and colleagues conclude that these results contrast with previous findings that extreme events contribute to multi-fractality.
INFORMATION:
Reference: E. Green, W. Hanan, and D. Heffernan (2014), The origins of multifractality in financial time series and the effect of extreme events, European Physical Journal B, DOI 10.1140/epjb/e2014-50064-x
For more information visit: http://www.epj.org
The full-text article is available to journalists on request.
Market crashes are anomalous features in the financial data fractal landscape
Analysing the adequation of financial data structure with its expected fractal scaling could help early detection of extreme financial events
2014-06-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
US housing policies increase carbon output, Georgia State University research finds
2014-06-16
Land use policies and preferential tax treatment for housing – in the form of federal income tax deductions for mortgage interest and property taxes – have increased carbon emissions in the United States by about 2.7 percent, almost 6 percent annually in new home construction, according to a new Georgia State University study.
Economist Kyle Mangum, an assistant professor in the Andrew Young School of Policy Studies, measures the effect of various housing policies on energy use and carbon output in "The Global Effects of Housing Policy," which he recently presented at ...
New advance allows gels to wiggle through water
2014-06-16
Using a worm's contracting and expanding motion, researchers have designed a way for gels to swim in water. The advance, which is described in a Journal of Applied Polymer Science paper, involves the use of a hand-held laser to shrink and swell polymer gels comprised mostly of water.
"This new method of mobility may allow such hydrogels to be used as environmental and biotechnological tools by allowing them to explore surface waters to combat toxic elements or travel within cavities inside the human body," said co-author Dr. Lilit Yeghiazarian.
INFORMATION:
...
A satellite view: Former Hurricane Cristina now a ghost of its former self
2014-06-16
An infrared image from NOAA's GOES-West satellite showed what appeared to be a ghostly ring of clouds and no convection in former Hurricane Cristina on Monday, June 16 as the system weakened to a remnant low pressure area.
Convection is rising air that forms the thunderstorms that make up a tropical cyclone and when there is none, there are no thunderstorms to keep it going. That's exactly what happened to Cristina in the Eastern Pacific Ocean on Sunday, June 15.
At 11 a.m. EDT (8 a.m. PDT) on Sunday, June 15, Cristina had weakened to a tropical depression near latitude ...
Trapping light: A long lifetime in a very small place
2014-06-16
Physicists at the University of Rochester have created a silicon nanocavity that allows light to be trapped longer than in other similarly-sized optical cavities. An innovative design approach, which mimics evolutionary biology, allowed them to achieve a 10-fold improvement on the performance of previous nanocavities.
In a paper published in Applied Physics Letters today and featured on the cover, the scientists demonstrate they have confined light in a nanocavity – a nanostructured region of a silicon wafer – for nanoseconds. Typically light would travel several meters ...
Broccoli sprout drink enhances detoxification of air pollutants in clinical trial in China
2014-06-16
A clinical trial involving nearly 300 Chinese men and women residing in one of China's most polluted regions found that daily consumption of a half cup of broccoli sprout beverage produced rapid, significant and sustained higher levels of excretion of benzene, a known human carcinogen, and acrolein, a lung irritant. Researchers from the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, working with colleagues at several U.S. and Chinese institutions, used the broccoli sprout beverage to provide sulforaphane, a plant compound already demonstrated to have cancer preventive ...
Genetic influence on pulmonary function: Six further genes identified
2014-06-16
In their investigations or so-called genome-wide association studies, the team of researchers compared the genetic profile of study participants to the forced vital capacity (FVC), a volume parameter of lung function. Six gene loci here displayed a clear association with the FVC values. Involvement in lung development or certain pulmonary diseases is furthermore suspected for these genes.
Better understanding of the association between genes, lung function and lung diseases
The identified genes open up new molecular biological approaches for a better understanding of ...
Children in low-income homes do better in kindergarten if moms work when they are babies
2014-06-16
WASHINGTON - Kindergarteners from lower-income families who were babies when their mothers went to work outside the home fare as well as or even better than children who had stay-at-home moms, according to new research published by the American Psychological Association.
This finding, in a study published in APA's journal Developmental Psychology, is contrary to the findings of previous studies of children born two to three decades ago. Family income is apparently a key factor, with the new research finding children from low-income families had slightly higher cognitive ...
E-cigarettes far less harmful than cigarettes, says Lancet researcher at INFORMS Conference
2014-06-16
A London School of Economics researcher examining the public and private dangers of drugs argues against demonizing e-cigarettes in a presentation being given at a conference of the Institute for Operations Research and the Management Sciences (INFORMS). He also calls on public officials to recognize that alcohol causes greater harm than other recreational drugs and more public attention should be paid to controlling its harmful effects.
Lawrence D. Phillips, an emeritus professor at the London School of Economics, will present his research group's findings about the relative ...
Lipids help to fight leukemia
2014-06-16
T cells use a novel mechanism to fight leukemia. They may recognize unique lipids produced by cancer cells and kill tumor cells expressing these lipid molecules. A study conducted by researchers at the University of Basel shows that a tumor-associated lipid stimulates specific T cells, which efficiently kill leukemia cells both in vitro and in animal models. The results have been published in the Journal of Experimental Medicine.
Leukemias are cancer diseases affecting blood cells . Acute leukemias prevent development of normal bold cells and thereby are severe life-threatening ...
Cellular force that drives allergy and asthma can be blocked by interferon
2014-06-16
DALLAS – June 16, 2014 – A mechanism that could underlie the development of cells that drive asthma and allergies has been uncovered by immunology researchers at UT Southwestern Medical Center.
Asthma and allergies are both driven by an inappropriate activation of the immune system, primarily a subtype of white blood cells known as T helper 2 cells, or Th2 cells. These cells are normally responsible for defense against parasites, but are also the main culprits behind the symptoms of asthma and allergies.
Dr. David Farrar, Associate Professor of Immunology and Molecular ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Study finds Earth may have twice as many vertebrate species as previously thought
NYU Langone orthopedic surgeons present latest clinical findings and research at AAOS 2026
New journal highlights how artificial intelligence can help solve global environmental crises
Study identifies three diverging global AI pathways shaping the future of technology and governance
Machine learning advances non targeted detection of environmental pollutants
ACP advises all adults 75 or older get a protein subunit RSV vaccine
New study finds earliest evidence of big land predators hunting plant-eaters
Newer groundwater associated with higher risk of Parkinson’s disease
New study identifies growth hormone receptor as possible target to improve lung cancer treatment
Routine helps children adjust to school, but harsh parenting may undo benefits
IEEE honors Pitt’s Fang Peng with medal in power engineering
SwRI and the NPSS Consortium release new version of NPSS® software with improved functionality
Study identifies molecular cause of taste loss after COVID
Accounting for soil saturation enhances atmospheric river flood warnings
The research that got sick veterans treatment
Study finds that on-demand wage access boosts savings and financial engagement for low-wage workers
Antarctica has lost 10 times the size of Greater Los Angeles in ice over 30 years
Scared of spiders? The real horror story is a world without them
New study moves nanomedicine one step closer to better and safer drug delivery
Illinois team tests the costs, benefits of agrivoltaics across the Midwest
Highly stable self-rectifying memristor arrays: Enabling reliable neuromorphic computing via multi-state regulation
Composite superionic electrolytes for pressure-less solid-state batteries achieved by continuously perpendicularly aligned 2D pathways
Exploring why some people may prefer alcohol over other rewards
How expectations about artificial sweeteners may affect their taste
Ultrasound AI receives FDA De Novo clearance for delivery date AI technology
Amino acid residue-driven nanoparticle targeting of protein cavities beyond size complementarity
New AI algorithm enables scientific monitoring of "blue tears"
Insufficient sleep among US adolescents across behavioral risk groups
Long COVID and recovery among US adults
Trends in poverty and birth outcomes in the US
[Press-News.org] Market crashes are anomalous features in the financial data fractal landscapeAnalysing the adequation of financial data structure with its expected fractal scaling could help early detection of extreme financial events