(Press-News.org) Barriers to obtaining gene expression profiling test heightened perceived value among patients, new study says
TORONTO, June 17, 2014—Barriers to obtaining gene expression profiling tests heightened their perceived importance among patients with early breast cancer who were deciding whether to have chemotherapy, a new study says.
Gene expression profiling tests, such as Oncotype Dx, analyze the patterns of 21 different genes within cancer cells to help predict how likely it is that a women's cancer will recur within 10 years after initial treatment and how beneficial chemotherapy will be to her.
Dr. Yvonne Bombard, a genomics and health services researcher in the Li Ka Shing Knowledge Institute of St. Michael's Hospital, found that access to this newly available and expensive technology is subject to careful administration and oversight.
However, she said that has created unintended consequences such as making oncologists gatekeepers for determining when it was medically appropriate for someone to have the test, leading to perceived inequalities in access by patients. Moreover, media attention made patients more aware of the gene expression profiling tests and led them to specifically ask for them, but that complicated physicians' gatekeeping efforts, sometimes hurting the doctor-patient relationship.
"There was a sense that the test was scarce or difficult to obtain, which heightened patients' desire for it and led them to perceive gene expression profiling tests as the deciding factor in their chemotherapy decisions, over and above other clinical tests and indicators," she said.
Dr. Bombard interviewed 14 oncologists and 28 breast cancer patients in Ontario for a study published today in Current Oncology. Ontario was the first province in Canada to fund gene expression profiling tests.
She said the careful oversight required of oncologists to the test created perceived inequities in access among patients. This often occurred in how oncologists discussed the test with their patients. Some oncologists offered the test to all their patients; others only to those who were eligible or where they felt there was uncertainty about the potential value of chemotherapy. Some raised it early in their consultations with patients, others late in the process, leading some patients to feel their doctors had already made the decision to recommend chemotherapy. Dr. Bombard said some patients felt information about the test was not offered to them because of its high cost, $4,000.
"Such delays or omissions in mentioning the test often left patients confused or feeling that something of great value was being withheld," she said.
Some patients said they learned about the tests from media reports describing a lack of funding in Canada that framed the issue as one of inequitable access to a highly effective, game-changing technology. Several of the oncologists said they felt pressured by the media coverage to offer the test to women for whom they knew it would not provide useful information for their decision-making about chemotherapy.
Another barrier was the extra paperwork around the test, which is not performed in Canada. Patients and oncologists must fill out forms to establish eligibility for OHIP reimbursement. Oncologists were then required to obtain government approval before sending tumour samples out of the country for testing. Results usually take about three weeks. This extra paperwork was cumbersome, increased anxieties about missing the window to start treatment and also reinforced the impression that the test was special, because it warranted special attention.
INFORMATION:
This study was funded by Cancer Care Ontario and the Ontario Institute for Cancer Research and the Canadian Centre for Applied Research in Cancer Control.
About St. Michael's Hospital
St Michael's Hospital provides compassionate care to all who enter its doors. The hospital also provides outstanding medical education to future health care professionals in 27 academic disciplines. Critical care and trauma, heart disease, neurosurgery, diabetes, cancer care, care of the homeless and global health are among the Hospital's recognized areas of expertise. Through the Keenan Research Centre and the Li Ka Shing International Healthcare Education Centre, which make up the Li Ka Shing Knowledge Institute, research and education at St. Michael's Hospital are recognized and make an impact around the world. Founded in 1892, the hospital is fully affiliated with the University of Toronto.
Media contacts
For more information, or to arrange an interview with Dr. Bombard, contact:
Leslie Shepherd
Manager, Media Strategy
St. Michael's Hospital
416-864-6094
shepherdl@smh.ca
Barriers to obtaining gene expression profiling test heightened perceived value
Access to newly available and expensive technology is subject to careful administration and oversight
2014-06-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
TRMM eyes rainfall in dissipating former Hurricane Cristina
2014-06-17
VIDEO:
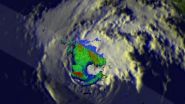
On June 14, NASA's TRMM satellite found rain falling at a rate of almost 97 mm (about 3.8 inches) per hour in the northwestern side of Cristina's eye wall where...
Click here for more information.
NASA and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission or TRMM satellite passed over a dissipating former Hurricane Cristina and found it still contained heavy rain as it rapidly weakened.
Hurricane Cristina had sustained winds of over 130 ...
Tropical depression Hagibis gets a second chance
2014-06-17
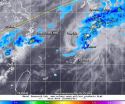
Tropical Depression Hagibis appeared out for the count when it made landfall along southeastern China on June 16, but moved back into the South China Sea where it regenerated and sped northeast through the East China Sea. The next day, the TRMM satellite noticed power had come back to Hagibis in the form of some moderate rainfall in the depression's northeastern quadrant.
On June 17 at 10:30 UTC (6:30 a.m. EDT) the Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission or TRMM satellite passed over the regenerated Hagibis and the Precipitation Radar instrument gathered data on the storm's ...
Sleep education program spurs preschoolers to snooze 30 minutes longer at night
2014-06-17
Ann Arbor, Mich. — Taking part in an educational sleep program resulted in a 30-minute average increase in sleep duration at a one-month follow-up for preschoolers, according to a new study from the University of Michigan.
In the study, published in the journal SLEEP, families in two Head Start programs participated in the Sweet Dreamzzz Early Childhood Sleep Education Program™. The Detroit-area nonprofit organization, Sweet Dreamzzz, Inc. developed the program and offers it for free when funding allows. Head Start programs aim to give preschool opportunities to low-income ...
Dynamic spectroscopy duo
2014-06-17
From allowing our eyes to see, to enabling green plants to harvest energy from the sun, photochemical reactions – reactions triggered by light – are both ubiquitous and critical to nature. Photochemical reactions also play essential roles in high technology, from the creation of new nanomaterials to the development of more efficient solar energy systems. Using photochemical reactions to our best advantage requires a deep understanding of the interplay between the electrons and atomic nuclei within a molecular system after that system has been excited by light.
A major ...
Why species matter
2014-06-17
UC Santa Barbara doctoral candidate Caitlin Fong travels to French Polynesia often but not for vacation. She goes there to study a coral reef ecosystem influenced by human impacts such as overfishing and nutrient pollution.
Her work focuses not only on biological changes but also methods scientists use to determine within-group group responses to ecological processes. The findings are published in ESA Ecology, a journal of the Ecological Society of America.
Fong and Peggy Fong, a professor in UCLA's Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology, conducted a study assessing ...
Not so fast -- our fishy friends can also feel pain
2014-06-17
Do you still believe that fish are dumb and cannot feel pain? That we do not have to worry much about how they are cared for or caught? Think again, says Culum Brown of Macquarie University in Australia, in a review article in Springer's journal Animal Cognition. The research notes that fish cognition and their sensory perception are generally on par with that of other animals. Brown therefore argues that more consideration should be given to fish welfare and anti-cruelty issues.
The Australian researcher says that most people rarely think about fish other than as food, ...
$2.4 million NIH center grant to develop a cleaner, healthier environment in Detroit
2014-06-17
DETROIT — With over $2.4 million in new federal funding, Wayne State University researchers, regional collaborators at Henry Ford Health System, the University of Michigan and Michigan State University, and community partners will study how exposures to stressors that are prevalent in the urban industrialized environment — both chemical and non-chemical — impact human health in Detroit and beyond.
The grant, Center for Urban Responses to Environmental Stressors (CURES), is one of approximately 20 select P30 Core Centers funded by the National Institute of Environmental ...
Do 'walkable' neighborhoods reduce obesity, diabetes?
2014-06-17
June 17, 2014 (San Francisco) – People who live in neighborhoods that are conducive to walking experienced a substantially lower rate of obesity, overweight and diabetes than those who lived in more auto-dependent neighborhoods, according to a pair of studies presented at the American Diabetes Association's 74th Scientific Sessions®.
Researchers in Canada compared adults living in the most and least "walkable" metropolitan areas in southern Ontario and found a lower risk of developing diabetes over a 10-year period for those who lived in neighborhoods with less sprawl, ...
Heparin derivative suppresses neuroblastoma tumor growth
2014-06-17
DURHAM, N.C. -- Researchers at Duke Medicine have identified a new strategy for treating neuroblastoma using a modified version of heparin, a century-old injectable drug that thins the blood to prevent clots from forming.
The study, conducted in mice and published June 17, 2014, in the Journal of Clinical Investigation, found that when heparin is altered to remove its blood-thinning properties, it can suppress and shrink neuroblastoma tumors without causing severe bleeding.
"Our research translates mechanistic insights about heparin into a potential new therapy for ...
Urban Water Management Workshop stresses more collaboration and innovation
2014-06-17
RIVERSIDE, Calif. — Where sustainability of water management is concerned, we must pay more attention to long-term solutions. Efficient water management and policy ought to be promoted at the local level. And a "portfolio approach" to water management is encouraged, one that includes information campaigns, different types of pricing, supply and reuse options, and technology-based rebate programs.
These are some of the key messages that emerged from the first Urban Water Management Workshop that took place earlier this month at the University of California, Riverside.
Sponsored ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Brain activity reveals how well we mentally size up others
Taiwanese and UK scientists identify FOXJ3 gene linked to drug-resistant focal epilepsy
Pregnancy complications impact women’s stress levels and cardiovascular risk long after delivery
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
[Press-News.org] Barriers to obtaining gene expression profiling test heightened perceived valueAccess to newly available and expensive technology is subject to careful administration and oversight