(Press-News.org) Leesburg, VA, June 18, 2014—Researchers in Saudi Arabia have identified key defining characteristics of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) in CT imaging of patients confirmed as having the disease.
The study found that the most common CT finding in hospitalized patients with MERS infection is suggestive of an organizing pneumonia pattern.
"A few studies have described variable degrees of lung opacities in patients with MERS, but did not clearly address their exact distribution," said Amr M. Ajlan, the corresponding author of the study. "Because we evaluated the CT findings in this laboratory-confirmed group of MERS patients, we had the ability to better characterize the nature and distribution of the abnormalities."
Recognizing this pattern in acutely ill patients living in or traveling from endemic areas may help in the
early diagnosis of MERS.
The study appears ahead of print online in the American Journal of Roentgenology.
INFORMATION:
Founded in 1900, ARRS is the first and oldest radiology society in the United States, and is an international forum for progress in radiology. The Society's mission is to improve health through a community committed to advancing knowledge and skills in radiology. ARRS achieves its mission through an annual scientific and educational meeting, publication of the American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR) and InPractice magazine, topical symposia and webinars, and print and online educational materials. ARRS is located in Leesburg, VA.
New study is first to identify, clarify MERS-related abnormality distribution on CT
2014-06-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study shows cost-effectiveness of smoking cessation counseling during hospitalization
2014-06-18
OTTAWA, June 18, 2014 – In a recent study published in Tobacco Control, researchers at the University of Ottawa Heart Institute have demonstrated the cost-effectiveness of the Ottawa Model for Smoking Cessation (OMSC), an intervention that includes in-hospital counseling, pharmacotherapy and post-hospital follow-up, compared to usual care among smokers hospitalized with acute myocardial infarction, unstable angina, heart failure, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
The study examined patients hospitalized in Ontario, a province with a population of approximately ...
Animals conceal sickness symptoms in certain social situations
2014-06-18
The review's sole author, Dr. Patricia Lopes from the Institute of Evolutionary Biology and Environmental Studies at the University of Zurich, says that animals from a number of different species will eat and drink less, reduce their activity and sleep more when they are sick in order to conserve energy for their recovery. However, this can all change depending on the social situation.
In a paper published this week in the journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B, Lopes reviewed a range of different social situations that affected the behavior of sick animals, including ...
Childhood maltreatment associated with cerebral grey matter abnormalities
2014-06-18
An international study has analysed the association between childhood maltreatment and the volume of cerebral grey matter, responsible for processing information. The results revealed a significant deficit in various late developing regions of the brain after abuse.
According to the World Health Organisation (WHO), child maltreatment is defined as all forms of physical and/or emotional ill-treatment, sexual abuse, neglect or negligent treatment or commercial or other exploitation, resulting in actual or potential harm to the child's health, survival, development or dignity ...
Trap-jaw ants spreading in southeastern United States
2014-06-18
Trap-jaw ant species are active hunters with venomous stings and jaws powerful enough to fling themselves through the air. According to new research, they are also spreading into new territory in the southeastern United States. The research was done by scientists at North Carolina State University, the Mississippi Entomological Museum, the University of California, Davis and Archbold Biological Station.
"The fact that some of these species are spreading is interesting, in part, because these giant ants have managed to expand their territory without anyone noticing," says ...
Scientists about sequencing data: We drown in data but thirst for knowledge
2014-06-18
While more and more genomic information is becoming available at a drastically increasing pace, the knowledge we can gain about how microorganisms interact with their surrounding, infect hosts and alter their molecular programs in accordance to changing environmental conditions remains widely not deducible from genomic data alone, the researchers from University of Southern Denmark claim. This raises questions regarding the value of newly sequenced species.
The researchers have analyzed the genomes that are available from the past 20 years of sequencing bacterial DNA. ...
Horizontal levitation: The ultimate solution to particle separation
2014-06-18
Magnetic separators exploit the difference in magnetic properties between minerals, for example when separating magnetite from quartz. But this exercise becomes considerably more complex when the particles are not magnetic. In the wake of previous particle levitation experiments under high-power magnetic fields, a new study reveals that particles are deflected away from the magnet's round-shaped bore centre in a horizontal direction. Previous studies had observed the vertical levitation of the particles. These findings are presented by Shixiao Liu from the Faculty of Engineering, ...
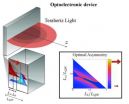
New quantum mechanism to trigger the emission of tunable light at terahertz frequencies
2014-06-18
Scientists have found that two-dimensional (2D) nanostructures with asymmetric design enable a new quantum mechanism, triggering the emission of tunable light at terahertz frequencies—with unprecedented efficiency.
The researchers, from the University of Southampton and Imperial College London, found that quantum wells, 2D nanostructures formed of several layers of semi-conductor alloys placed on top of each other like a sandwich, can enhance light emission in a technological challenging spectral range.
It is hoped that the findings will have an impact on photonic ...
Only 16 percent of Ph.D.s work in the private sector in Spain, half the OECD average
2014-06-18
This news release is available in Spanish.
The report explains that Ph.D.s who work as researchers represent, on average in the OECD, 68.6% of those who are employed. By institutional sectors, the percentages of employees who work as researchers break down as follows: 45.4% in the private sector, 70.8% in public administration and 75.9% in higher education. In Spain, 86% of Ph.D.s employed in higher education are researchers, while for the private sector, this figure is only 26.5%.
According to OECD figures, leading innovative countries like the United States, ...
A noisy world: Crabs can hear
2014-06-18
In new research published in the journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B, Northeastern University professor Randall Hughes and her team at the Marine Science Center in Nahant, Mass. are the first to show that sound plays at least as much of a role in mud crabs' reaction to fish behavior as other widely studied cues—and possibly more.
Fish are not silent creatures. Just like the terrestrial world, there's a veritable symphony of sound echoing under the sea. Indeed, the black drum fish was the subject of many a phone call to the Miami police back in 2005, when their ...
Want to know about vaping? Turn on the TV or go online
2014-06-18
Adults are widely exposed to e-cigarette marketing through the media, but those messages reach different demographic groups in different ways, according to a survey by researchers at the University of Illinois at Chicago's Institute for Health Research and Policy.
The study is published as a special supplement in the July 2014 issue of Tobacco Control.
Eighty-six percent of those surveyed were aware of e-cigarettes, and 47 percent had seen or heard about them on television, on the radio, in print media or online. The survey of 17,522 adults was conducted online last ...