(Press-News.org) This news release is available in German.
In the past years, invisibility cloaks were developed for various senses. Objects can be hidden from light, heat or sound. However, hiding of an object from being touched still remained to be accomplished. KIT scientists have now succeeded in creating a volume in which an object can be hidden from touching similar to a pea under the mattress of a princess. The results are now presented in the renowned Nature Communications journal.
Magicians and illusionists make things disappear by means of a skilled use of mental delusions and diversionary tactics. KIT researchers, by contrast, use invisibility cloaks based on the laws of physics. In the past years, various physical invisibility cloaks were developed. Optical invisibility cloaks, for instance, make objects appear invisible, while others appear to let heat or sound pass uninfluenced. A completely new type of invisibility cloak is the mechanical one developed by KIT scientists. It prevents an object from being touched.
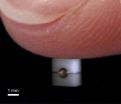
The invisibility cloak is based on a so-called metamaterial that consists of a polymer. Its major properties are determined by the special structure. "We build the structure around the object to be hidden. In this structure, strength depends on the location in a defined way," explains Tiemo Bückmann, KIT, the first author of the article. "The precision of the components combined with the size of the complete arrangement was one of the big obstacles to the development of the mechanical invisibility cloak." The metamaterial is a crystalline material structured with sub-micrometer accuracy. It consists of needle-shaped cones, whose tips meet. The size of the contact points is calculated precisely to reach the mechanical properties desired. In this way, a structure results, through which a finger or a measurement instrument cannot feel its way.
In the invisibility cloak produced, a hard cylinder is inserted into the bottom layer. Any objects to be hidden can be put into its cavity. If a light foam or many layers of cotton would be placed above the hard cylinder, the cylinder would be more difficult to touch, but could still be felt as a form. The metamaterial structure directs the forces of the touching finger such that the cylinder is hidden completely. "It is like in Hans-Christian Andersen's fairy tale about the princess and the pea. The princess feels the pea in spite of the mattresses. When using our new material, however, one mattress would be sufficient for the princess to sleep well," Bückmann explains.
Implementation of such a mechanical invisibility cloak is rather complex. After the definition of the desired mechanical properties, the physical basic equations are inverted mathematically in order to draw conclusions with respect to the structure of the metamaterial. Using this method, materials not encountered in nature can be planned. Examples are solids which are stiff to pressure, but soft to shear. For manufacture from the polymer, the direct laser writing method of the KIT spinoff Nanoscribe is applied. It reaches the required precision over the complete sample length of several millimeters.
The mechanical invisibility cloak represents pure physical fundamental research, but might open up the door to interesting applications in a few years from now, as it allows for producing materials with freely selectable mechanical properties. Examples are very thin, light, and still comfortable camping mattresses or carpets hiding cables and pipelines below.
Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) is a public corporation according to the legislation of the state of Baden-Württemberg. It fulfills the mission of a university and the mission of a national research center of the Helmholtz Association. Research activities focus on energy, the natural and built environment as well as on society and technology and cover the whole range extending from fundamental aspects to application. With about 9400 employees, including more than 6000 staff members in the science and education sector, and 24500 students, KIT is one of the biggest research and education institutions in Europe. Work of KIT is based on the knowledge triangle of research, teaching, and innovation.
INFORMATION:
This press release is available on the internet at http://www.kit.edu.
The photos of printing quality may be downloaded under http://www.kit.edu or requested by mail to presse@kit.edu or phone +49 721 608-4 7414. The photos may be used in the context given above exclusively.
KIT researchers protect the princess from the pea
2014-06-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Citing 'urgent, acute' mental health issues, especially in Africa, experts petition gov'ts to act
2014-06-20
Calling global mental health problems "acute and urgent," 37 leading medical authorities from 11 countries have published a joint declaration calling for basic mental health care in Africa.
The experts also call for global mental health objectives to be included among the United Nations' post-2015 Sustainable Development Goals, for a special UN General Assembly High Level Meeting on Mental Health by 2017, and for efforts to end the stigma and human rights violations inflicted on mental health patients.
Published in the journal Global Health Action, the declaration was ...
Menthol cigarettes linked to increased smoking among teens
2014-06-20
Teens who use menthol cigarettes smoke more cigarettes per day than their peers who smoke non-menthols, says a new study. The findings from the Propel Centre for Population Health Impact at the University of Waterloo mark the first time that menthol cigarettes have been directly linked to elevated nicotine addiction among youth in Canada.
"The appeal of menthol cigarettes among youth stems from the perception that they are less harmful than regular cigarettes. The minty taste helps mask the noxious properties, but the reality is that they are just as dangerous as any ...
UMN research: Nearly 4 percent of US babies born before full-term without medical reason
2014-06-20
New University of Minnesota research out this week is the first of its kind to show who is having early elective deliveries between 37 and 39 weeks gestation, and whether these deliveries happen following labor induction or cesarean.
Labor induction or cesarean delivery without medical reason before a baby is considered full-term at 39 weeks, or an "early elective delivery," is associated with health problems for mothers and babies.
The study, led by University of Minnesota School of Public Health Assistant Professor Katy Kozhimannil, Ph.D., M.P.A., in collaboration ...
Festschrift issue for Hilary Koprowski, MD
2014-06-20
New Rochelle, NY, June 20, 2014—The June issue of Monoclonal Antibodies in Immunodiagnosis and Immunotherapy is a special tribute issue for Hilary Koprowski, MD (1916-2013). The Festschrift papers are available online on the Monoclonal Antibodies in Immunodiagnosis and Immunotherapy website.
An exclusive print copy of the Festschrift will be presented to all speakers at The Wistar Institute Symposium to honor Dr. Koprowski in Philadelphia on June 27, 2014, with support from CASIS™.
"The contributors to this issue are internationally known scientists who were personally ...
Biology of infection: A bacterial ballistic system
2014-06-20
Many pathogenic bacteria use special secretion systems to deliver toxic proteins into host cells. Researchers of Ludwig-Maximilians-Universitaet (LMU) in Munich have determined the structure of a crucial part of one of these systems – which are possible targets for novel antibiotics.
Bacteria secrete a broad range of specific proteins that can affect the behavior or survival of cells in their environment. Among the specialized transport systems responsible for the export of such factors are so-called Type VI secretion systems. In collaboration with Axel Mogk of the Center ...
Triggers and treatment of immediate-type allergic reactions
2014-06-20
Sudden allergic reactions can be fatal. The most common triggers of such reactions, also known as anaphylaxis, are wasp and bee venoms, legumes (pulses), animal proteins, and analgesics (painkillers). The incidence of anaphylaxis is age-dependent. In the current issue of Deutsches Ärzteblatt International, Margitta Worm (Berlin) and her co-authors describe the causes and treatment methods for anaphylaxis, based on data from the anaphylaxis registry of the German-speaking countries (Dtsch Arztebl Int 2014; 111: 367�).
Worm and co-authors analyzed the data from the ...
The pig whipworm genome may aid to treat autoimmune diseases
2014-06-20
Shenzhen, June 15, 2014---An international team, composed of 11 institutions from six countries, including BGI, presented the whole-genome sequence of Trichuris suis, a parasitic worm in pig. Understanding the genetics mechanisms underlying the pig parasite may aid to modify the human immune response that could result in better treatments for autoimmune diseases, including inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and multiple sclerosis. The latest research was published online in Nature Genetics.
The human whipworm (Trichuris) infects around 1 billion people worldwide and causes ...
Cochrane review of RDTs for diagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis
2014-06-20
Researchers from the Cochrane Infectious Disease Group, co-ordinated through the editorial base in LSTM, conducted an independent review into the effectiveness of rapid diagnostic tests in diagnosing patients with visceral leishmaniasis (VL), published in The Cochrane Library today.
VL (or kala-azar) is caused by a parasite and results in fever, a large spleen and other health problems. It occurs in India, Bangladesh and Nepal, east Africa, the Mediterranean region and Brazil. Without treatment it can be fatal, and proper treatment can result in cure, so diagnosis is ...
Creating friendships between African-American and Caucasian couples can reduce prejudice
2014-06-20
DETROIT — Recent research findings from Wayne State University show that the physical presence of romantic partners in intergroup friendships – friendships with different racial and ethnic groups, religious groups, or sexual orientations – positively influences interactions with people who are perceived to be different from themselves.
The study, "Creating positive out-group attitudes through intergroup couple friendships and implications for compassionate love," currently available online in the Journal of Social and Personal Relationships, found that couples that interacted ...
Experimentally testing nonlocality in many-body systems
2014-06-20
Science has recently published a study carried out by researchers at ICFO in collaboration with the Institute for Nuclear Research, Hungarian Academy of Sciences, which demonstrates the capability of detecting non-locality in many-body quantum systems by constructing multipartite Bell inequalities involving only two-body correlations.
In Quantum Theory, interactions among particles create fascinating correlations that cannot be explained by any means known to the Classical World. These correlations, usually known to be nonlocal, prove that the Quantum and Classical Worlds ...