(Press-News.org) A working group evaluating sexual orientation-related disorders listed in the International Classification of Diseases (ICD), a publication of the World Health Organization (WHO), has recommended the disorders be deleted, a move that will make getting health care easier for gays and others who may have gender atypicality.
The WHO is the world body charged with deciding what is a disease and more than 170 countries, including the United States, follow their recommendations. The organization is currently revising the 10th edition of the ICD for release of the 11th edition in 2017.
Susan D. Cochran, a professor at the UCLA Fielding School of Public Health and a member of the working group, said the recommendation, if adopted, resolves "a human rights issue."
"In California, gay people may have the right to marry, but in most of the world, being gay can be dangerous. There are at least six countries that criminalize homosexuality with a possible death sentence," said Cochran, who is a clinical psychologist and epidemiologist. "This recommendation, to remove diagnoses that have no scientific basis, is a way of cleansing our public health apparatus of the social animus directed at a group of people for reasons that have no health justification."
The recommendation must survive several layers of approval, the final being a vote by the member countries.
In 1974, the American Psychiatric Association decreed that homosexuality would no longer be considered a mental illness, though it created a new disorder, ego-dystonic homosexuality, as a political compromise. That disorder was later dropped as a diagnosis, and in the last iteration of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, the last reference to sexual orientation being associated with a mental disorder was eliminated.
In 1990, the ICD made the same declaration, but retained several purported disorders, Cochran said. For example, if a person was married and woke one day and decided that they were gay and wanted a divorce, the current ICD considers that a mental disorder. Or if a teenager was unsure if they were gay, straight or bisexual and were distressed about that, that also is considered mental disorder. Or if a person were gay, and for whatever reason wished not to be, that also is a disorder.
"It doesn't make any sense. If a person were short and wished they weren't, that is not a disorder. Or if someone was a lousy singer and wished they weren't, that is not a disorder," Cochran said. "In other words, the ICD takes content that is sexual orientation–related and attaches a diagnosis to it in ways that it does not do for other aspects of people."
If the recommendation is adopted it will have an immediate and important impact on access to health care, she said. Every health care event and every doctor visit has an ICD code attached to it. These codes that are used for insurance billing, for public health surveillance and for medical records.
By removing these codes related to sexual orientation, the health care that gay people receive will be improved, Cochran said. For example, if a gay man is depressed and seeks care he is vulnerable to being mistreated by the health system. Currently, he could be diagnosed with ego-dystonic homosexuality if he says he is upset about how he is being treated as a gay man and wishes he were straight. There are discredited treatments, such as conversion therapy, that have been deemed unethical but sometimes are justified by this diagnosis. With the codes removed, it will be more likely that his complaints will result in a proper diagnosis of depression and treatments for that depression.
"This means that gay people can feel free to seek care, to share their concerns and not fear that they will diagnosed with a mental illness simply because the content is about homosexuality or gender atypicality," Cochran said. "It would mean an end to the medicalization of homosexuality."
An article published in the latest issue of the Bulletin of World Health Organization outlined the scientific basis for the recommendation to delete the sexual orientation-related disorders from the ICD.
"It is not justifiable from a clinical, public health or research perspective for a diagnostic classification to be based on sexual orientation," the article states.
INFORMATION:
Group recommends removing sexual orientation-related disorders from the ICD
2014-06-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
UMMS scientists show that monarch butterflies employ a magnetic compass during migration
2014-06-24
WORCESTER, MA – Each fall millions of monarch butterflies use a sophisticated navigation system to transverse 2,000 miles from breeding sites across the eastern United States to an overwintering habitat in specific groves of fir trees in central Mexico. Scientists at the University of Massachusetts Medical School and Worcester Polytechnic Institute have identified a new component of this complex system. They reported in Nature Communications that monarchs use a light-dependent, inclination magnetic compass to help them orient southward during migration.
"Taken as a whole, ...
Cancer risks increase with complex heart tests
2014-06-24
Complex heart imaging can increase cancer risks for children throughout their lifetime, according to a new study co-authored by Le Bonheur Cardiologist Jason Johnson, MD, MHS. The study, which appears in the June 9, 2014 issue of the American Heart Association's journal Circulation, is the first in which researchers quantified cumulative radiation doses in pediatric heart patients and predicted lifetime cancer risks based on the types of exposures.
In the study, Johnson and fellow researchers found that radiation from standard X-rays don't significantly raise cancer risks ...
Those with episodic amnesia are not 'stuck in time,' says philosopher Carl Craver
2014-06-24
In 1981, a motorcycle accident left Toronto native Kent Cochrane with severe brain damage and dramatically impaired episodic memory. Following the accident, Cochrane could no longer remember events from his past. Nor could he predict specific events that might happen in the future.
When neuroscientist Endel Tulving, PhD, asked him to describe what he would do tomorrow, Cochrane could not answer and described his state of mind as "blank."
Psychologists and neuroscientists came to know Cochrane, who passed away earlier this year, simply as "KC." Many scientists have described ...
Mining mountains of data for medical insights
2014-06-24
Epidemiologists know that an important piece of evidence is often staring you in the face – but it's not always easy to see the forest for the trees.
Danish scientists recently teamed up with University of New Mexico researchers to test a powerful new method for predicting the progress of common diseases through time by teasing out previously undetected patterns from a very large data set – in this case, the health records of Denmark's entire population.
This approach maps out surprising correlations: a disease like gout – a form of arthritis – is strongly linked to ...
Research explains action of drug that may slow aging, related disease
2014-06-24
Dietary restriction is one of the most-researched methods for slowing the aging process. Now, a new article published in The Journals of Gerontology, Series A: Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences helps explain the action of a drug that appears to mimic that method — rapamycin.
Rapamycin, an antibiotic and immunosuppressant approved for use about 15 years ago, has drawn extensive interest for its apparent ability — at least in laboratory animal tests — to emulate the ability of dietary restriction in helping animals to live both longer and healthier.
However, this ...
Hormones affect voting behavior, Nebraska researchers find
2014-06-24
OMAHA, Neb. – Researchers from the University of Nebraska at Omaha (UNO), the University of Nebraska-Lincoln (UNL) and Rice University have released a study that shows hormone levels can affect voter turnout.
As witnessed by recent voter turnout in primary elections, participation in U.S. national elections is low, relative to other western democracies. In fact, voter turnout in biennial national elections ranges includes only 40 to 60 percent of eligible voters.
The study, published June 22 in Physiology and Behavior, reports that while participation in electoral ...
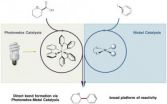
A collaboration of minds and metal
2014-06-24
This past January, Derek Ahneman, a graduate student in the lab of Abigail Doyle, a Princeton University associate professor of chemistry, began work on an ambitious new project: he proposed the merger of two areas of research to enable a powerful reaction that neither could broadly achieve on its own.
One field, which is the Doyle research group's domain, was nickel catalysis, wherein nickel squeezes in and out of chemical bonds to bring molecules together. The other field was photoredox catalysis, which uses light to initiate a series of unique bond-breaking and bond-making ...
Researchers publish one of the longest longitudinal studies of cognition in MS
2014-06-24
Researchers at Kessler Foundation and the Cleveland Clinic have published one of the longest longitudinal studies of cognition in multiple sclerosis (MS). The article, "Cognitive impairment in multiple sclerosis: An 18-year follow-up study," (DOI: 10.1016/j.msard.2014.03.004) was epublished by Multiple Sclerosis and Related Disorders on April 13, 2014. Results provide insight into the natural evolution of cognitive changes over time, an important consideration for researchers and clinicians. Authors are Lauren B. Strober, PhD, of Kessler Foundation and Stephen M. Rao, ...
3-D printer for the world's largest delta?
2014-06-24
Boulder, Colo., USA - Three main rivers -- the Ganges, Brahmaputra, and Meghna -- meet in the Bengal basin to form the world's largest delta system, which serves as a gateway between the Himalayan mountains and the vast, deep-ocean Bengal Fan. This GSA BULLETIN paper by Stephen Goodbred and colleagues presents a new understanding of how this mega-delta, the Ganges-Brahmaputra-Meghna delta, came together over the past 10,000 years.
To determine the delta's construction during the Holocene, Goodbred and colleagues followed geochemical fingerprints to trace the paths and ...
NOAA GOES-R satellite black wing ready for flight
2014-06-24
The solar array that will provide power to NOAA's GOES-R satellite has been tested, approved and shipped to a facility where it will be incorporated on the spacecraft. The five sections of the solar array come together as one to resemble a giant black wing.
On May 13, 2014, the GOES-R satellite solar array panels were successful deployed in a Lockheed Martin clean room in Sunnyvale, California. The completed solar array was then delivered to Lockheed Martin's facility near Denver.
"The GOES-R solar array generates more than 4,000 watts of power, twice as much as that ...