(Press-News.org) Old Westbury, N.Y. (June 25, 2014) –Administering low doses of a thyroid hormone to rats with diabetes helps restore hormone levels in their hearts and prevented deterioration of heart function and pathology, according to a new study by NYIT College of Osteopathic Medicine professor A. Martin Gerdes.
The study, published in the online edition of Molecular Medicine provides the first clear indication that low thyroid hormone levels in cardiac tissue of diabetic individuals may be the major cause of their associated heart disease, says Gerdes.
The study finds that diabetes triggers low thyroid levels that contribute to heart failure. In animal models, Gerdes and colleagues found that administering low doses of the active form of thyroid hormone, T3, prevented the progression of heart disease.
"This treatment prevented the abnormal changes in gene expression, tissue pathology, and heart function," said Gerdes.
The most recent study builds on a growing body of research by Gerdes and others that links low thyroid hormone levels in heart tissue to heart failure. The research was funded by the National Institutes of Health and the American Diabetes Association. Previous studies have demonstrated that hypertension and heart attacks also trigger low cardiac thyroid hormone levels and contribute to heart disease.
"The clinical implications are profound and far-reaching because it suggests that the heart disease associated with diabetes may be easily preventable," Gerdes says of his recent research. "And importantly, the dose we gave of T3 hormone did not significantly change the serum (blood) thyroid hormone levels but it was enough to make all the difference in the heart tissue."
An individual's thyroid levels are usually measured by blood tests. But Gerdes has noted that thyroid hormone levels in cardiac tissue do not necessarily correspond with blood test readings of thyroid levels. An individual with heart disease and low cardiac tissue thyroid hormone levels may have normal blood test results, in part because the blood is diluted about 20 fold once it leaves the heart and joins the rest of circulating blood in the body. Yet, his research has consistently found that low-dose thyroid hormone replacement may be a safe and effective therapy to help humans suffering from heart disease.
"A low thyroid condition can cause heart failure by itself," says Gerdes. "The fundamental question we should be asking about patients with heart failure is: how much is due to the diagnosed disease and how much is due to low thyroid levels in the heart? There clearly needs to be more awareness with regard to research examining the impact of low thyroid hormone levels in the heart and the role this condition plays in acceleration of heart failure."
In his animal study, Gerdes and colleagues induced a mild form of diabetes in rats and waited a month for the condition to develop. They then administered low doses of T3 hormone for two months.
Gerdes says more research is needed to identify peripheral serum bio-markers that track with low thyroid hormone levels in the heart. He also says human clinical studies are necessary.
"There's so much fear of overtreatment (with hormones) and inducing arrhythmias that physicians in general completely avoid treating heart patients with thyroid hormones," he says. But we have established a clear treatment and monitoring program in this study that is safe and can be used in people."
Gerdes conducted the research over three years at NYIT. His colleagues include researchers from the University of South Dakota, the Center for Heart and Lung Research at The Feinstein Institute for Medical Research, and the University of Pisa, Italy.
INFORMATION:
About NYIT
New York Institute of Technology (NYIT) offers 90 degree programs, including undergraduate, graduate, and professional degrees, in more than 50 fields of study, including architecture and design; arts and sciences; education; engineering and computing sciences; health professions; management; and osteopathic medicine. A non-profit independent, private institution of higher education, NYIT has 13,000 students attending campuses on Long Island and Manhattan, online, and at its global campuses. NYIT sponsors 11 NCAA Division II programs and one Division I team.
Led by President Edward Guiliano, NYIT is guided by its mission to provide career-oriented professional education, offer access to opportunity to all qualified students, and support applications-oriented research that benefits the larger world. To date, nearly 100,000 graduates have received degrees from NYIT. For more information, visit nyit.edu.
Contact:
Elaine Iandoli
Office of Communications
516.686.4013
Restoring thyroid hormones in heart may prevent heart disease from diabetes
2014-06-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Neural sweet talk: Taste metaphors emotionally engage the brain
2014-06-25
So accustomed are we to metaphors related to taste that when we hear a kind smile described as "sweet," or a resentful comment as "bitter," we most likely don't even think of those words as metaphors. But while it may seem to our ears that "sweet" by any other name means the same thing, new research shows that taste-related words actually engage the emotional centers of the brain more than literal words with the same meaning.
Researchers from Princeton University and the Free University of Berlin report in the Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience the first study to experimentally ...
Special edition of the Red Journal highlights the need for radiation oncology services in LMICs
2014-06-25
Fairfax, Va., June 25, 2014—The July 1, 2014 edition of the International Journal of Radiation Oncology ● Biology ● Physics (Red Journal), the official scientific journal of the American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO), features a special section of 10 articles focusing on global health and radiation oncology in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs.)
Three papers examine the overall need for more and the current opportunities to provide radiation oncology in LMICs, C. Norman Coleman, MD, FASTRO, highlights the work and the four main principles of ...
Study highlights carbon monoxide hazards on houseboats
2014-06-25
FALLS CHURCH, Va. (June 25, 2014) — Boaters and marina workers should exercise caution this summer before taking to the seas. A study published online in the Journal of Occupational and Environmental Hygiene (JOEH) outlines hazards posed by carbon monoxide levels on houseboats that use gasoline-powered generators without emission controls, along with controls that are available to reduce exposure to carbon monoxide from the generators.
The study, conducted by researchers at the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH), found that uncontrolled generators ...
New treatment option in development for individuals with food allergy
2014-06-25
New Rochelle, NY, June 25, 2014—For some children an allergic reaction to common foods such as milk, eggs, or peanuts can cause an anaphylactic reaction. At present no effective treatment for food allergy exists, and strict dietary avoidance of known food triggers is the only preventive option available. Ongoing trials are exploring options for oral immunotherapy (OIT) for desensitization in the treatment of Immunoglobulin E (IgE)-mediated food allergy, as described in a Review article in Pediatric Allergy, Immunology, and Pulmonology, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary ...
Deploying midwives in poorest nations could avert millions of maternal and newborn deaths
2014-06-25
A modest increase in the number of skilled midwives in the world's poorest nations could save the lives of a substantial number of women and their babies, according to new analyses by researchers from the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
Maternal mortality is a leading cause of death for women in many developing countries and public health efforts to avert it have only made headway in a few countries. Elsewhere, progress has either never started or has stalled in recent years. Poor nations also have troubling rates of infant and fetal deaths. Midwives ...
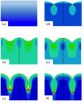
Mathematical models explain how a wrinkle becomes a crease
2014-06-25
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — Wrinkles, creases and folds are everywhere in nature, from the surface of human skin to the buckled crust of the Earth. They can also be useful structures for engineers. Wrinkles in thin films, for example, can help make durable circuit boards for flexible electronics.
A new mathematical model developed by researchers from Brown University could help engineers control the formation of wrinkle, crease, and fold structures in a wide variety of materials. It may also help scientists understand how these structures form in nature. The ...
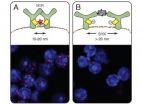
Nanoscale ruler reveals organization of the cell membrane
2014-06-25
This news release is available in German.
After a ten-year effort, Prof. Dr. Michael Reth from the Institute of Biology III of the University of Freiburg and the Max Planck Institute of Immunobiology and Epigenetics has developed a method to investigate the cell surface's organization on a nanometer scale. This allows him to monitor how the antigen receptor, which B cells of the immune system use to recognize foreign substances, changes after activation. This study shows that the receptor components dissociate from each other– rather than assemble, as previously ...
New study quantifies the effects of climate change in Europe
2014-06-25
If no further action is taken and global temperature increases by 3.5°C, climate damages in the EU could amount to at least €190 billion, a net welfare loss of 1.8% of its current GDP. Several weather-related extremes could roughly double their average frequency. As a consequence, heat-related deaths could reach about 200 000, the cost of river flood damages could exceed €10 billion and 8000 km2 of forest could burn in southern Europe. The number of people affected by droughts could increase by a factor of seven and coastal damage, due to sea-level rise, could more than ...
Using math to analyze movement of cells, organisms, and disease
2014-06-25
Traveling waves model tumor invasion
Cell migration, which is involved in wound healing, cancer and tumor growth, and embryonic growth and development, has been a topic of interest to mathematicians and biologists for decades.
In a paper published recently in the SIAM Journal on Applied Dynamical Systems, authors Kristen Harley, Peter van Heijster, Robert Marangell, Graeme Pettet, and Martin Wechselberger study a model describing cell invasion through directional outgrowth or movement in the context of malignant tumors, in particular, melanoma or skin cancer. Tumor ...
Freedom of choice: When rejection and discrimination hinder minority entrepreneurs
2014-06-25
When it comes to The American Dream, freedom of choice is a central value for entrepreneurs. According to a new study in the Journal of Consumer Research, when a person's choices are limited due to rejection and discrimination, they are more likely to fail at business and in their personal lives.
"Not only does restricting a person's choices threaten the success of a new business, it also has swift and damaging effects on the individual's self-esteem and their personal sense of control and power in the world," write authors Sterling A. Bone (Utah State University), Glenn ...