(Press-News.org) TORONTO, June 26, 2014 – Women with chronic physical illnesses are more likely to use mental health services than men with similar illnesses; they also seek out mental health services six months earlier than those same men, according to new study from St. Michael's Hospital and the Institute for Clinical Evaluative Sciences (ICES).
"Chronic physical illness can lead to depression," said Dr. Flora Matheson, a scientist in the hospital's Centre for Research on Inner City Health. "We want to better understand who will seek mental health services when diagnosed with a chronic physical illness so we can best help those who need care."
The findings, published today in the British Medical Journal's Journal of Epidemiology & Community Health, looked at people diagnosed with at least one of four physical illnesses: diabetes, high blood pressure, asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Researchers found that among those with at least one of these four illnesses, women were 10 per cent more likely to use mental health services than men. Furthermore, within any three-year period, women with physical illness used medical services for mental health treatment six months earlier than men.
"Our results don't necessarily mean that more focus should be paid to women, however," said Dr. Matheson, who is also an adjunct scientist at ICES. "We still need more research to understand why this gender divide exists."
The results may imply that women are more comfortable seeking mental health support than men. Alternatively, the gender discrepancy might mean that symptoms are worse among women, requiring more women to seek help and sooner, or that men defer seeking treatment for mental health concerns.
The study used data from the Canadian Community Health Survey, physician claims and inpatient medical records from ICES. Mental illness service use was defined as one visit to a physician or specialist for mental health reasons, such as depression, anxiety, smoking addiction or marital difficulties.
INFORMATION:
This research was funded by the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council of Canada.
About St. Michael's Hospital
St. Michael's Hospital provides compassionate care to all who enter its doors. The hospital also provides outstanding medical education to future health care professionals in 27 academic disciplines. Critical care and trauma, heart disease, neurosurgery, diabetes, cancer care, care of the homeless and global health are among the hospital's recognized areas of expertise. Through the Keenan Research Centre and the Li Ka Shing International Healthcare Education Centre, which make up the Li Ka Shing Knowledge Institute, research and education at St. Michael's Hospital are recognized and make an impact around the world. Founded in 1892, the hospital is fully affiliated with the University of Toronto.
About ICES
ICES is an independent, non-profit organization that uses population-based health information to produce knowledge on a broad range of health care issues. Our unbiased evidence provides measures of health system performance, a clearer understanding of the shifting health care needs of Ontarians, and a stimulus for discussion of practical solutions to optimize scarce resources. ICES knowledge is highly regarded in Canada and abroad, and is widely used by government, hospitals, planners, and practitioners to make decisions about care delivery and to develop policy.
Media Contact
For more information, or to arrange an interview with Dr. Matheson, contact:
Geoff Koehler
Adviser, Media Relations
St. Michael's Hospital
416-864-6060 ext. 6537
koehlerg@smh.ca
Deborah Creatura
Media Advisor, ICES
deborah.creatura@ices.on.ca
(o) 416-480-4780 or (c) 647-406-5996
Please note that Dr. Matheson is available for on-camera interviews on Friday, June 20, 2014 only. She is, however, available by phone throughout the embargo window.
Men and women use mental health services differently
2014-06-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Continued use of low-dose aspirin may lower pancreatic cancer risk
2014-06-26
PHILADELPHIA — The longer a person took low-dose aspirin, the lower his or her risk for developing pancreatic cancer, according to a study published in Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research.
"We found that the use of low-dose aspirin was associated with cutting the risk of pancreatic cancer in half, with some evidence that the longer low-dose aspirin was used, the lower the risk," said Harvey A. Risch, MD, PhD, professor of epidemiology in the Department of Chronic Disease Epidemiology at the Yale School ...
Revisions needed for current IV feeding safeguards against bloodstream infections
2014-06-26
Current guidelines to help prevent bloodstream infections during intravenous feeding may need
revisions to strengthen protections for patients, a new study finds.
Researchers at the United Kingdom's University of Southampton found that current guidelines do not account for other independent factors that can affect the growth of potentially deadly microorganisms. Their study was published today in the OnlineFirst version of the Journal of
Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition (JPEN), the research journal of the American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition (A.S.P.E.N.). ...
Researchers call for patients who receive home nutritional care to have emergency plans
2014-06-26
On the heels of the 2014 hurricane season, researchers are calling for home parenteral and enteral nutrition (HPEN) consumers and their homecare providers to have a comprehensive emergency preparedness plan (EPP) to ensure that special needs are met during the time of a disaster.
In a paper published today in the American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition's (A.S.P.E.N.) Nutrition in Clinical Practice journal, researchers with Coram Specialty Infusion Services outline the experiences of HPEN consumers and homecare providers in New Jersey affected by Hurricane ...
Researchers discover 'Trojan Horse' method of penetrating cellular walls without harm
2014-06-26
COLLEGE STATION – Scientists with Texas A&M AgriLife Research have found a "Trojan horse" way to deliver proteins into live human cells without damaging them.
The finding, published in this month's Nature Methods, is expected to be easily adopted for use in medical research to find cures and treatments for a wide range of diseases, according to the team's lead scientist, Dr. Jean-Philippe Pellois, an associate professor of biochemistry at Texas A&M University.
"This is something that for many years people have tried to do, because proteins are basic components of the ...
Invasive watersnakes introduced to California may pose risk to native species
2014-06-26
Watersnakes, commonly seen in the lakes, rivers and streams of the eastern United States, are invading California waterways and may pose a threat to native and endangered species in the state, according to a University of California, Davis, study.
While scientists do not know exactly how many watersnakes are in California, roughly 300 individuals of two different species –the common watersnake and the southern watersnake -- have been found in the Sacramento area (Roseville and Folsom), and at least 150 were seen in Long Beach. Researchers suspect the nonvenomous snakes ...
Sequencing efforts miss DNA crucial to bacteria's disease causing power
2014-06-26
Genomic sequencing is supposed to reveal the entire genetic makeup of an organism. For infectious disease specialists, the technology can be used to analyze a disease-causing bacterium to determine how much harm it is capable of causing and whether or not it will be resistant to antibiotics. But new research at Rockefeller University suggests that current sequencing protocols overlook crucial bits of information: isolated pieces of DNA floating outside the bacterial chromosome, the core of a cell's genetic material.
"Extensive sequencing of chromosomal DNA has been performed ...
A win-win-win solution for biofuel, climate, and biodiversity
2014-06-25
Fossil fuel emissions release billions of tons of carbon into the atmosphere each year, which is changing the climate and threatening the sustainability of life on planet Earth. In Brazil, the demand for alternative energy sources has led to an increase in biofuel crops. A new "News and Views" paper in Nature Climate Change, co-authored by Woods Hole Research Center scientists Marcia Macedo and Eric Davidson, reviews new research conducted by Brazilian colleagues demonstrating the high carbon costs of converting intact Brazilian savanna compared to the carbon gains obtained ...
Scientists develop a 'nanosubmarine' that delivers complementary molecules inside cells
2014-06-25
VIDEO:
Francisco Raymo discusses his work in this video.
Click here for more information.
CORAL GABLES, Fla. (June 25, 2014) — With the continuing need for very small devices in therapeutic applications, there is a growing demand for the development of nanoparticles that can transport and deliver drugs to target cells in the human body.
Recently, researchers created nanoparticles that under the right conditions, self-assemble – trapping complementary guest molecules within ...
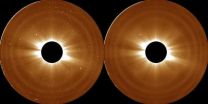
NASA's STEREO maps much larger solar atmosphere than previously observed
2014-06-25
Surrounding the sun is a vast atmosphere of solar particles, through which magnetic fields swarm, solar flares erupt, and gigantic columns of material rise, fall and jostle each other around. Now, using NASA's Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory, scientists have found that this atmosphere, called the corona, is even larger than thought, extending out some 5 million miles above the sun's surface -- the equivalent of 12 solar radii. This information has implications for NASA's upcoming Solar Probe Plus mission, due to launch in 2018 and go closer to the sun than any man-made ...
New NASA model gives glimpse into the invisible world of electric asteroids
2014-06-25
Space may appear empty -- a soundless vacuum, but it's not an absolute void. It flows with electric activity that is not visible to our eyes. NASA is developing plans to send humans to an asteroid, and wants to know more about the electrical environment explorers will encounter there.
A solar wind blown from the surface of the sun at about a million miles per hour flows around all solar system objects, forming swirling eddies and vortices in its wake. Magnetic fields carried by the solar wind warp, twist, and snap as they slam into the magnetic fields around other objects ...