(Press-News.org) COLUMBIA, Mo. – In 2011, the United States Military repealed its "don't ask, don't tell" policy that prevented gay and lesbian service members from disclosing their sexual orientation. Current estimates indicate that more than 1 million veterans identify as lesbian, gay or bisexual (LGB). Now, a University of Missouri researcher says these service members and veterans often are marginalized and may benefit from mental health professionals, including social workers, who are informed about the needs of individuals who identify as LGB.
"Identifying as LGB and serving in the military can provide a distinct set of experiences and challenges for individuals," said Michael Pelts, a doctoral student at the School of Social Work in the MU College of Human Environmental Sciences. "Within the U.S., identifying as a service member or veteran can marginalize individuals. This is also true for people who identify as LGB. The impact may be compounding. For example, suicide has a high occurrence rate among veterans and even more so among veterans who identify as LGB."
Pelts said studies show that the majority of LGB service members and veterans who seek mental health care services do so outside of Veterans Affairs.
"Social workers in the public and private sectors make up the largest group of mental health service providers to veterans and their families," Pelts said. "It is likely that social workers will continue to see current and new generations of veterans struggling with their sexual identity and with the impact of internal and societal stigmas related to identifying as LGB. Therefore, mental health professionals need to be equipped to care for members of this population."
Social workers and other mental health providers should challenge their cultural assumptions when treating clients who are veterans or service members, Pelts said.
"It's not ethically sound practice to assume that all service members and veterans are heterosexual," Pelts said. "Assuming individuals are heterosexual can compound stress for LGB individuals and make them less likely to share information, which can make it more difficult for health professionals and mental health providers to provide adequate care."
Pelts said health providers should adopt practices to be more inclusive to veterans who identify as LGB. Part of increasing inclusivity includes simple changes such as modifying medical history forms and in-take documents. By using more inclusive terminology, individuals who identify as LGB may feel less alienated, Pelts said.
"It is essential for mental health professionals to create culturally competent practice approaches," Pelts said. "Social workers have a tremendous opportunity, if not ethical responsibility, to be leaders in the provision of mental health services for LGB service members, veterans and their families."
Pelts recently wrote, "Veterans Mental Health: Implication for Services With Gay Men and Lesbians Who Have Served," which was published in Social Work in Mental Health.
INFORMATION: END
Veterans who identify as LGB could benefit from informed mental health services
Social workers and other mental health providers should adopt more inclusive policies
2014-06-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Penn study shows changing roles of physicians with MBAs
2014-06-26
Philadelphia - According to a new study from researchers at the Perelman School of Medicine and the Wharton School at the University of Pennsylvania, physician graduates from the MBA program in heath care management at Penn's Wharton School report that their dual training had a positive effect on their individual careers and professional lives. Study respondents reported such benefits as career acceleration, professional flexibility, and credibility in multidisciplinary domains. Aside from clinical practice, the MD was more often cited as providing professional credibility, ...
Controlling movement with light
2014-06-26
For the first time, MIT neuroscientists have shown they can control muscle movement by applying optogenetics — a technique that allows scientists to control neurons' electrical impulses with light — to the spinal cords of animals that are awake and alert.
Led by MIT Institute Professor Emilio Bizzi, the researchers studied mice in which a light-sensitive protein that promotes neural activity was inserted into a subset of spinal neurons. When the researchers shone blue light on the animals' spinal cords, their hind legs were completely but reversibly immobilized. The ...
Why tech transfer brings universities 'more than money'
2014-06-26
Tampa, Fla. (June 26, 2014) – Academic technology transfer – the process of moving research from the lab to the market – provides intrinsic benefits to universities that go far beyond any potential revenues from licenses and royalties.
So say the authors, from five universities across the country and the Association of University Technology Managers (AUTM), in a new article from the National Academy of Inventors (NAI) that appears in the current issue of Technology and Innovation and is available Open Access.
"More than Money: The Exponential Impact of Academic Technology ...
Chimps like listening to music with a different beat, research finds
2014-06-26
WASHINGTON – While preferring silence to music from the West, chimpanzees apparently like to listen to the different rhythms of music from Africa and India, according to new research published by the American Psychological Association.
"Our objective was not to find a preference for different cultures' music. We used cultural music from Africa, India and Japan to pinpoint specific acoustic properties," said study coauthor Frans de Waal, PhD, of Emory University. "Past research has focused only on Western music and has not addressed the very different acoustic features ...
Traffic light labels can give a false sense of security
2014-06-26
This news release is available in German. Sugar: red; fat: yellow; salt: green. The so-called 'food traffic lights' used in Great Britain indicate the volume of certain nutrients contained in a product by means of color-coded information on the packaging. The intention is to enable consumers to identify the advantages and disadvantages associated with a food product at a glance. The traffic light labeling system is a controversial topic throughout Europe. Since the financial crisis, it is also discussed for investment products.
Scientists from the Technische Universität ...
Tofu ingredient could revolutionize solar panel manufacture
2014-06-26
The chemical used to make tofu and bath salts could also replace a highly toxic and expensive substance used to make solar cells, a University study published in the journal Nature has revealed.
Cadmium chloride is currently a key ingredient in solar cell technology used in millions of solar panels around the world. This soluble compound is highly toxic and expensive to produce, requiring elaborate safety measures to protect workers during manufacture and then specialist disposal when panels are no longer needed.
Now, a University of Liverpool researcher has found ...
Deeper insights into protein folding
2014-06-26
Investigating the structure and dynamics of so-called Meso-Bio-Nano (MBN) systems—micron-sized biological or nanotechnology entities—is a rapidly expanding field of science. Now, scientists Alexander Yakubovich and Andrey Solov'yov from MBN Research Centre in Frankfurt, Germany, have produced a new theoretical study of a protein macromolecule changing from a coil structural conformation to a globular one. Their statistic mechanics model, just published in EPJ D, describes the thermodynamic properties of real proteins in an aqueous environment, using a minimal number of ...
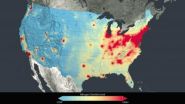
New NASA images highlight US air quality improvement
2014-06-26
Anyone living in a major U.S. city for the past decade may have noticed a change in the air. The change is apparent in new NASA satellite images unveiled this week that demonstrate the reduction of air pollution across the country.
After ten years in orbit, the Ozone Monitoring Instrument (OMI) on NASA's Aura satellite has been in orbit sufficiently long to show that people in major U.S. cities are breathing less nitrogen dioxide – a yellow-brown gas that can cause respiratory problems.
Nitrogen dioxide is one of the six common pollutants regulated by the U.S. Environmental ...
Blocking key enzyme minimizes stroke injury, UT Southwestern research finds
2014-06-26
DALLAS – June 26, 2014 – A drug that blocks the action of the enzyme Cdk5 could substantially reduce brain damage if administered shortly after a stroke, UT Southwestern Medical Center research suggests.
The findings, reported in the June 11 issue of the Journal of Neuroscience, determined in rodent models that aberrant Cdk5 activity causes nerve cell death during stroke.
"If you inhibit Cdk5, then the vast majority of brain tissue stays alive without oxygen for up to one hour," said Dr. James Bibb, Associate Professor of Neurology and Neurotherapeutics at UT Southwestern ...
Study: Foreign-trained physicians frustrated at lack of residency positions
2014-06-26
TORONTO, June 26, 2014—Foreign-trained physicians feel there are not enough residency positions for them in countries such as Canada and the United States and this information was not communicated to them before they emigrated, a new study has found.
Researchers at St. Michael's Hospital surveyed international medical graduates to better understand the concepts of "brain drain," the migration of health care workers from low- and middle-income countries to higher-income countries, and "brain waste," where their skills are under-utilized or not utilized in their new country. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Students run ‘bee hotels’ across Canada - DNA reveals who’s checking in
SwRI grows capacity to support manufacture of antidotes to combat nerve agent, pesticide exposure in the U.S.
University of Miami business technology department ranked No. 1 in the nation for research productivity
Researchers build ultra-efficient optical sensors shrinking light to a chip
Why laws named after tragedies win public support
Missing geomagnetic reversals in the geomagnetic reversal history
EPA criminal sanctions align with a county’s wealth, not pollution
“Instead of humans, robots”: fully automated catalyst testing technology developed
Lehigh and Rice universities partner with global industry leaders to revolutionize catastrophe modeling
Engineers sharpen gene-editing tools to target cystic fibrosis
Pets can help older adults’ health & well-being, but may strain budgets too
First evidence of WHO ‘critical priority’ fungal pathogen becoming more deadly when co-infected with tuberculosis
World-first safety guide for public use of AI health chatbots
Women may face heart attack risk with a lower plaque level than men
Proximity to nuclear power plants associated with increased cancer mortality
Women’s risk of major cardiac events emerges at lower coronary plaque burden compared to men
Peatland lakes in the Congo Basin release carbon that is thousands of years old
Breadcrumbs lead to fossil free production of everyday goods
New computation method for climate extremes: Researchers at the University of Graz reveal tenfold increase of heat over Europe
Does mental health affect mortality risk in adults with cancer?
EANM launches new award to accelerate alpha radioligand therapy research
Globe-trotting ancient ‘sea-salamander’ fossils rediscovered from Australia’s dawn of the Age of Dinosaurs
Roadmap for Europe’s biodiversity monitoring system
Novel camel antimicrobial peptides show promise against drug-resistant bacteria
Scientists discover why we know when to stop scratching an itch
A hidden reason inner ear cells die – and what it means for preventing hearing loss
Researchers discover how tuberculosis bacteria use a “stealth” mechanism to evade the immune system
New microscopy technique lets scientists see cells in unprecedented detail and color
Sometimes less is more: Scientists rethink how to pack medicine into tiny delivery capsules
Scientists build low-cost microscope to study living cells in zero gravity
[Press-News.org] Veterans who identify as LGB could benefit from informed mental health servicesSocial workers and other mental health providers should adopt more inclusive policies