(Press-News.org) About seven days after conception, something remarkable occurs in the clump of cells that will eventually become a new human being. They start to specialize. They take on characteristics that begin to hint at their ultimate fate as part of the skin, brain, muscle or any of the roughly 200 cell types that exist in people, and they start to form distinct layers.
Although scientists have studied this process in animals, and have tried to coax human embryonic stem cells into taking shape by flooding them with chemical signals, until now the process has not been successfully replicated in the lab. But researchers led by Ali Brivanlou, Robert and Harriet Heilbrunn Professor and head of the Laboratory of Stem Cell Biology and Molecular Embryology at The Rockefeller University, have done it, and it turns out that the missing ingredient is geometrical, not chemical.
"Understanding what happens in this moment, when individual members of this mass of embryonic stem cells begin to specialize for the very first time and organize themselves into layers, will be a key to harnessing the promise of regenerative medicine," Brivanlou says. "It brings us closer to the possibility of replacement organs grown in petri dishes and wounds that can be swiftly healed."
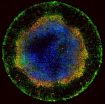
In the uterus, human embryonic stem cells receive chemical cues from the surrounding tissue that signal them to begin forming layers — a process called gastrulation. Cells in the center begin to form ectoderm, the brain and skin of the embryo, while those migrating to the outside become mesoderm and endoderm, destined to become muscle and blood and many of the major organs, respectively.
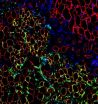
Brivanlou and his colleagues, including postdocs Aryeh Warmflash and Benoit Sorre as well as Eric Siggia, Viola Ward Brinning and Elbert Calhoun Brinning Professor and head of the Laboratory of Theoretical Condensed Matter Physics, confined human embryonic stem cells originally derived at Rockefeller to tiny circular patterns on glass plates that had been chemically treated to form "micropatterns" that prevent the colonies from expanding outside a specific radius. When the researchers introduced chemical signals spurring the cells to begin gastrulation, they found the colonies that were geometrically confined in this way proceeded to form endoderm, mesoderm and ectoderm and began to organize themselves just as they would have under natural conditions. Cells that were not confined did not.
By monitoring specific molecular pathways the human cells use to communicate with one another to form patterns during gastrulation — something that was not previously possible because of the lack of a suitable laboratory model — the researchers also learned how specific inhibitory signals generated in response to the initial chemical cues function to prevent the cells within a colony from all following the same developmental path.
The research was published June 29 in Nature Methods.
"At the fundamental level, what we have developed is a new model to explore how human embryonic stem cells first differentiate into separate populations with a very reproducible spatial order just as in an embryo," says Warmflash. "We can now follow individual cells in real time in order to find out what makes them specialize, and we can begin to ask questions about the underlying genetics of this process."
The research also has direct implications for biologists working to create "pure" populations of specific cells, or engineered tissues consisting of multiple cell types, for use in medical treatments. "These cells have a powerful intrinsic tendency to form patterns as they develop," Warmflash says. "Varying the geometry of the colonies may turn out to be an important tool that can be used to guide stem cells to form specific cell types or tissues."
INFORMATION:
Using geometry, researchers coax human embryonic stem cells to organize themselves
2014-06-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Research team pursues techniques to improve elusive stem cell therapy
2014-06-30
Stem cell scientists had what first appeared to be an easy win for regenerative medicine when they discovered mesenchymal stem cells several decades ago. These cells, found in the bone marrow, can give rise to bone, fat, and muscle tissue, and have been used in hundreds of clinical trials for tissue repair. Unfortunately, the results of these trials have been underwhelming. One problem is that these stem cells don't stick around in the body long enough to benefit the patient.
But Harvard Stem Cell Institute (HSCI) scientists at Boston Children's Hospital aren't ready ...
Oil palm plantations threaten water quality, Stanford scientists say
2014-06-30
If you've gone grocery shopping lately, you've probably bought palm oil.
Found in thousands of products, from peanut butter and packaged bread to shampoo and shaving cream, palm oil is a booming multibillion-dollar industry. While it isn't always clearly labeled in supermarket staples, the unintended consequences of producing this ubiquitous ingredient have been widely publicized.
The clearing of tropical forests to plant oil palm trees releases massive amounts of carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas fueling climate change. Converting diverse forest ecosystems to these ...
New study: Ancient Arctic sharks tolerated brackish water 50 million years ago
2014-06-30
Sharks were a tolerant bunch some 50 million years ago, cruising an Arctic Ocean that contained about the same percentage of freshwater as Louisiana's Lake Ponchatrain does today, says a new study involving the University of Colorado Boulder and the University of Chicago.
The study indicates the Eocene Arctic sand tiger shark, a member of the lamniform group of sharks that includes today's great white, thresher and mako sharks, was thriving in the brackish water of the western Arctic Ocean back then. In contrast, modern sand tiger sharks living today in the Atlantic Ocean ...
First pediatric autism study conducted entirely online
2014-06-30
UC San Francisco researchers have completed the first Internet-based clinical trial for children with autism, establishing it as a viable and cost effective method of conducting high-quality and rapid clinical trials in this population.
In their study, published in the June 2014 issue of the Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, the researchers looked at whether an Internet-based trial was a feasible way to evaluate whether omega-3 fatty acids helped reduce hyperactivity in children with autism. The authors found that not only was it a valuable ...
Research proves shock wave from explosives causes significant eye damage
2014-06-30
Researchers at The University of Texas at San Antonio (UTSA) are discovering that the current protective eyewear used by our U.S. armed forces might not be adequate to protect soldiers exposed to explosive blasts.
According to a recent study, ocular injuries now account for 13 percent of all battlefield injuries and are the fourth most common military deployment-related injury.
With the support of the U.S. Department of Defense, UTSA biomedical engineering assistant professor Matthew Reilly and distinguished senior lecture in geological sciences Walter Gray have been ...
Earth-Kind roses analyzed for salt tolerance
2014-06-30
COLLEGE STATION, TX – Earth-Kind® roses are favorites with gardeners and landscapers. Chosen for their superior tolerance to heat, drought, and pests, as well as their outstanding performance in landscapes, Earth-Kind® roses can thrive in most environments, even with limited care. A new study focused on determining the best Earth-Kind® varieties for withstanding the challenges of salt stress.
As alternative water sources such as reclaimed water are becoming more commonly used as irrigation for urban landscapes and agricultural crops, plants are being subjected to higher ...
New method to grow zebrafish embryonic stem cells can regenerate whole fish
2014-06-30
New Rochelle, NY, June 30, 2014—Zebrafish, a model organism that plays an important role in biological research and the discovery and development of new drugs and cell-based therapies, can form embryonic stem cells (ESCs). For the first time, researchers report the ability to maintain zebrafish-derived ESCs for more than 2 years without the need to grow them on a feeder cell layer, in a study published in Zebrafish, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available free on the Zebrafish website.
Ho Sing Yee and coauthors from the ...
With climate change, heat more than natural disasters will drive people away
2014-06-30
Although scenes of people fleeing from dramatic displays of Mother Nature's power dominate the news, gradual increases in an area's overall temperature — and to a lesser extent precipitation — actually lead more often to permanent population shifts, according to Princeton University research.
The researchers examined 15 years of migration data for more than 7,000 families in Indonesia and found that increases in temperature and, to a lesser extent, rainfall influenced a family's decision to permanently migrate to another of the country's provinces. They report in the ...
Study of animal urination could lead to better-engineered products
2014-06-30
Sir Isaac Newton probably wasn't thinking about how animals urinate when he was developing his laws of gravity. But they are connected – by the urethra, to be specific.
A new Georgia Institute of Technology study investigated how quickly 32 animals urinate. It turns out that it's all about the same. Even though an elephant's bladder is 3,600 times larger than a cat's (18 liters vs. 5 milliliters), both animals relieve themselves in about 20 seconds. In fact, all animals that weigh more than 3 kilograms (6.6 pounds) urinate in that same time span.
"It's possible because ...
Comparison study of planting methods shows drilling favorable for organic farming
2014-06-30
SALINAS, CA – In the fertile growing regions of the central coast of California, scientists are looking for ways to increase organic production of strawberry and other crops. Because cover crops can provide weed and erosion control, determining the best method for establishing a uniform and dense cover crop stand as soon as possible after planting is a critical first step. The authors of a new study say that determining optimal planting strategies that accelerate cover crop emergence and reduce light penetration to weeds should be a primary focus. Eric Brennan and Jim Leap ...