(Press-News.org) Since white-tailed deer serve as the primary host for the adult blacklegged tick (Ixodes scapularis) — the vector for Lyme disease — scientists have wondered whether reducing the number of deer in a given area would also mean fewer cases of Lyme disease. Now, after a 13-year study was conducted, researchers in Connecticut have found that reduced deer populations can indeed lead to a reduction in Lyme disease cases. The results of their study are published in the Journal of Medical Entomology .
The researchers surveyed 90% of all permanent residents in a Connecticut community from 1995 to 2008 to document their exposure to tick-related diseases and the frequency and abundance of deer observations. After hunts were initiated, the number and frequency of deer observations in the community were greatly reduced, as were resident-reported cases of Lyme disease.
The number of resident-reported cases of Lyme disease per 100 households was strongly correlated to deer density in the community, they found. Reducing deer density to 5.1 deer per square kilometer resulted in a 76% reduction in tick abundance, a 70% reduction in the entomological risk index, and an 80% reduction in resident-reported cases of Lyme disease.
"We found that reducing deer density by ≥87% resulted in a significant reduction in tick abundance, nearly a 50% reduction in tick infection rate, and an 80% reduction in resident-reported human cases of Lyme disease," the authors wrote. "Our study demonstrated that deer populations can be manipulated to reduce human interactions with deer, infected nymphal ticks, and human risk of contracting Lyme disease."
"Reducing deer populations to levels that reduce the potential for ticks to successfully breed should be an important component of any long-term strategy seeking to reduce the risk of people contracting Lyme disease," they concluded. "Additionally, good hunter access to deer habitat and a wide variety of management tools (bait, unlimited tags, incentive programs) are important components of a successful deer reduction strategy."
INFORMATION:
The full article is available at http://tinyurl.com/k52xdes.
The Entomological Society of America is the largest organization in the world serving the professional and scientific needs of entomologists and people in related disciplines. Founded in 1889, ESA today has nearly 7,000 members affiliated with educational institutions, health agencies, private industry, and government. Members are researchers, teachers, extension service personnel, administrators, marketing representatives, research technicians, consultants, students, and hobbyists. For more information, visit http://www.entsoc.org.
Reducing deer populations may reduce risk of Lyme disease
2014-07-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Enlightening cancer cells
2014-07-01
This news release is available in German.
Harald Janovjak, Assistant Professor at IST Austria, together with Michael Grusch, Associate Professor at the Institute of Cancer Research of the Medical University of Vienna, "remote-controlled" the behaviour of cancer cells with light, as reported this week in EMBO Journal (DOI: 10.15252/embj.201387695). This work is the first application of the new field of optogenetics to cancer research.
To understand the dynamics of cellular signaling, researchers need to activate and inactivate membrane receptor proteins, which ...
A new method to detect infrared energy using a nanoporous ZnO/n-Si photodetector
2014-07-01
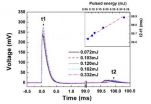
Experiments aimed at devising new types of photodetectors have been triggered by the increasing use of optoelectronic devices in personal electronics, cameras, medical equipment, computers and by the military. Professor Zhao Kun and co-researchers at the State Key Laboratory of Petroleum Resource and Prospecting, part of the China University of Petroleum in Beijing, have proposed a new type of infrared photodetector.
Photodetectors, which can convert photons to electrical signals, are used to observe and measure the wavelength or energy of light, including infrared light, ...
Drink walkers do it because their mates think it's okay: QUT study
2014-07-01
Friends may be the key to stopping their mates drink walking, a risky behaviour that kills on average two Australians every week, a QUT study has found.
Researcher Dr Ioni Lewis, from QUT's Centre for Accident Research & Road Safety - Queensland (CARRS-Q), said in a survey of young people aged 17 to 25, friends were the strongest influence on their intentions to drink walk.
"Drink walking, or walking while intoxicated in a public place, is linked to increased risk of injury and fatality," Dr Lewis said.
In a survey, published in Transportation Research, more than ...
EORTC presents European solution for effective cancer drug development
2014-07-01
Drug developers are facing the perfect storm. They are confronted with major patent expiries, increased payer scrutiny, changing priorities, shifting business models, increased risk averseness, increased clinical trial costs, not to mention issues concerning R&D productivity. There needs to be a better way to identify new candidate drugs. There needs to be a new drug development pathway that is compatible with research aimed at understanding the biology of a cancer and simultaneously able to support the design and conduct of subsequent confirmatory trials, but building ...
Unsuspected aspect of immune regulation revealed
2014-07-01
A discovery by Australian immunologists, uncovering an additional role for antibody-making 'B cells', is considered important enough by the American Association of Immunologists to rank it among the top 10% of articles in the latest issue of The Journal of Immunology, off the press today.
The finding by Senior Research Assistant Stacey Walters and Associate Professor Shane Grey, from Sydney's Garvan Institute of Medical Research, shows that B cells also participate in the development of 'regulatory T cells'.
T cells develop in the thymus gland, a soft triangular organ ...
New analysis of 'swine flu' pandemic conflicts with accepted views on how diseases spread
2014-07-01
The most detailed analysis to date of the spread of the H1N1 2009 pandemic influenza virus, known informally as 'swine flu', has found that short-range travel was likely the primary driver for the 2009 pandemic in the United States, in contrast with popularly accepted views on the way diseases spread.
The study, based on data gathered from health insurance claims made throughout 2009, found that international air travel, which was previously thought to be important in the pandemic, played only a minor role in its spread within the US.
A team of researchers from University ...
Cancer risk: Aspirin and smoking affect aging of genes
2014-07-01
The risk of developing cancer increases with age. Factors like smoking and regular aspirin use also affect the risk of cancer – although in the opposite sense. Researchers from the University of Basel were now able to show that aspirin use and smoking both influence aging processes of the female genome that are connected to colorectal cancer. The Journal of the National Cancer Institute has published their results.
Already in the 1990s, scientists discovered that regular use of aspirin over long periods of time decreases the cancer risk. Since then, numerous studies have ...
Analysis of the Chinese facial profile: Contours of the side face in the Tu & Zang ethnic minorities
2014-07-01
Li Haijun and fellow researchers at Minzu University of China, in Beijing, conducted a series of geometric morphometric analyses of the contours of the side face and variations in the Tu and Zang (Tibetan) ethnic minorities from Qinghai Province, in northwestern China.
Their study, entitled "Morphometric analysis of the Chinese facial profile: Contours of the side face and variations in the Tu and Zang ethnic minorities", was published (in Chinese) in the Chinese Science Bulletin, 2014, Vol 59(16).
The team of researchers used advanced digital cameras and image processing ...
A Spaniard and a Portuguese discover a new species of beetle in the world's deepest cave
2014-07-01
The unusual habitat of the Krubera cave in the Western Caucasus remains a mystery. Researchers from two Spanish universities have discovered a new species of beetle in the depths of this cave.
Cave beetles are one of the most iconic species found in subterranean habitats. They were historically the first living organisms described by science that are adapted to the conditions of hypogean or subterranean life.
Now, a Portuguese scientist and a Spaniard have discovered a new species of beetle in the deepest cave known to man; a cave 2,140 metres deep. It is the Krubera ...
Scientists uncover the key to adaptation limits of ocean dwellers
2014-07-01
The simpler, the more heat-resistant – scientists uncover the key to adaptation limits of ocean dwellers
Bremerhaven, Germany, 1 July 2014. The simpler a marine organism is structured, the better it is suited for survival during climate change. Scientists of the Alfred Wegener Institute, Helmholtz Centre for Polar and Marine Research discovered this in a new meta-study, which appears today in the research journal Global Change Biology. For the first time biologists studied the relationship between the complexity of life forms and the ultimate limits of their adaptation ...