(Press-News.org) This news release is available in Spanish.
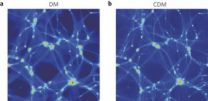
In cosmology, cold dark matter is a form of matter the particles of which move slowly in comparison with light, and interact weakly with electromagnetic radiation. It is estimated that only a minute fraction of the matter in the Universe is baryonic matter, which forms stars, planets and living organisms. The rest, comprising over 80%, is dark matter and energy.
The theory of cold dark matter helps to explain how the universe evolved from its initial state to the current distribution of galaxies and clusters, the structure of the Universe on a large scale. In any case, the theory was unable to satisfactorily explain certain observations, but the new research by Broadhurst and his colleagues sheds new light in this respect.
As the Ikerbasque researcher explained, "guided by the initial simulations of the formation of galaxies in this context, we have reinterpreted cold dark matter as a Bose-Einstein condensate". So, "the ultra-light bosons forming the condensate share the same quantum wave function, so disturbance patterns are formed on astronomic scales in the form of large-scale waves".
This theory can be used to suggest that all the galaxies in this context should have at their centre large stationary waves of dark matter called solitons, which would explain the puzzling cores observed in common dwarf galaxies.
The research also makes it possible to predict that galaxies are formed relatively late in this context in comparison with the interpretation of standard particles of cold dark matter. The team is comparing these new predictions with observations by the Hubble space telescope.
The results are very promising as they open up the possibility that dark matter could be regarded as a very cold quantum fluid that governs the formation of the structure across the whole Universe.
This is not Thomas Broadhurst's first publication in the prestigious journal Nature. In 2012, he participated in a piece of research on a galaxy of the epoch of the reionization, a stage in the early universe not explored previously and which could be the oldest galaxy discovered. This research opened up fresh possibilities to conduct research into the first galaxies to emerge after the Big Bang.
INFORMATION:
Tom Broadhurst has a PhD in Physics from the University of Durham (United Kingdom); until joining Ikerbasque he did his research at top research centres in the United Kingdom, United States, Germany, Israel, Japan and Taiwan. He has had 184 papers published in leading scientific journals, and so far has received 11,800 citations. In 2010, he was recruited by Ikerbasque and carries out his work in the UPV/EHU's department of Theoretical Physics. His line of research focusses on observational cosmology, dark matter and the formation of galaxies.
Reference
H-Y. Schive, T. Chiueh & T. Broadhurst. Cosmic structure as the quantum interference of a coherent dark wave. Nature Physics, 2014. DOI 10.1038/nphys2996
Reinterpreting dark matter
Research published in Nature Physics opens up the possibility that it could be regarded as a very cold quantum fluid governing the formation of the structure across the whole universe
2014-07-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Weekend emergency surgeries deadlier for children
2014-07-02
Children who undergo simple emergency surgeries, such as hernia repairs or appendix removals, on weekends are more likely to suffer complications and even die than children getting the same kind of treatment during the week, according to results of a Johns Hopkins Children's Center study.
The Johns Hopkins team says that although the number of deaths was small, the marked difference in death and risk of other complications points to a worrisome "weekend effect" observed across hospitals nationwide that calls for an in-depth examination of possible after-hours safety lapses ...
One in six adolescents in the ER has experienced dating violence
2014-07-02
WASHINGTON — Of adolescents visiting the emergency department for any reason, one in five girls and one in eight boys reported dating violence in the past year. According to a study published online Monday in Annals of Emergency Medicine, dating violence among adolescents was also strongly associated with alcohol, illicit drug use and depression ("Dating Violence Among Male and Female Youth Seeking Emergency Department Care") http://tinyurl.com/oakk4aq.
"An enormous number of youth and adolescents have already experienced violence in their dating lives," said lead ...
A stellar womb shaped and destroyed by its ungrateful offspring
2014-07-02
This image was taken as part of the ESO Cosmic Gems programme [1] using the Wide Field Imager on the MPG/ESO 2.2-metre telescope at the La Silla Observatory in Chile. It shows Gum 15, located in the constellation of Vela (The Sails), some 3000 light-years from Earth [2]. This glowing cloud is a striking example of an HII region [3]. Such clouds form some of the most spectacular astronomical objects we can see; for example the Eagle Nebula (which includes the feature nicknamed "The Pillars of Creation"), the great Orion Nebula , and this less famous example, Gum 15.
Hydrogen ...
'Deep learning' makes search for exotic particles easier
2014-07-02
Irvine, Calif. — Fully automated "deep learning" by computers greatly improves the odds of discovering particles such as the Higgs boson, beating even veteran physicists' abilities, according to findings by UC Irvine researchers published today in the journal Nature Communications.
"We are thrilled with the publication of our work," said co-author Pierre Baldi, Chancellor's Professor of computer science, "and even more so with the hope that deep learning may help solve fundamental open questions about the nature of matter, gravity and the origin of the universe."
Baldi, ...
Superconducting-silicon qubits
2014-07-02
Theorists propose a way to make superconducting quantum devices such as Josephson junctions and qubits, atom-by-atom, inside a silicon crystal. Such systems could combine the most promising aspects of silicon spin qubits with the flexibility of superconducting circuits. The researcher's results have now been published in Nature Communications (1).
High quality silicon is one of the historical foundations of modern computing. But it is also promising for quantum information technology. In particular, electron and nuclear spins in pure silicon crystals have been measured ...
From despair to repair: Dramatic decline of Caribbean corals can be reversed
2014-07-02
Gland, Switzerland – With only about one-sixth of the original coral cover left, most Caribbean coral reefs may disappear in the next 20 years, primarily due to the loss of grazers in the region, according to the latest report by the Global Coral Reef Monitoring Network (GCRMN), the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) and the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP).
The report, Status and Trends of Caribbean Coral Reefs: 1970-2012, is the most detailed and comprehensive study of its kind published to date – the result of the work of 90 experts over ...
License plate readers are important police tool, but hurdles remain, study finds
2014-07-02
Systems that automatically read automobile license plates have the potential to save police investigative time and increase safety, but law enforcement officials must address issues related to staffing, compatibility and privacy before the technology can reach its full potential, according to a new RAND Corporation report.
As part of efforts to promote innovation in law enforcement, many of the first generation license plate reader systems were purchased with federal and state grants. As these funding streams can be inconsistent, law enforcement agencies are – or will ...
A 'magic moment' for unwed parents
2014-07-02
DURHAM, N.C. -- If unwed parents are going to get married, the best window of opportunity for that union seems to be before their child turns 3, says a new study from Duke University.
But patterns vary greatly by race, with more African-American mothers marrying much later than mothers of other races or ethnicities.
Federal policies have often presumed that unmarried parents will be most receptive to marriage right after a baby's birth, a period that has been dubbed the "magic moment." The new study is the first to test that assumption, said author Christina Gibson-Davis. ...
How do ants get around? Ultra-sensitive machines measure their every step…
2014-07-02
How do ants manage to move so nimbly whilst coordinating three pairs of legs and a behind that weighs up to 60% of their body mass? German scientists have recently developed a device that may reveal the answer.
Measuring the forces generated by single limbs is vital to understanding the energetics of animal locomotion. However, with very small animals such as insects, this becomes problematic. Dr Reinhardt (Friedrich-Schiller University) used an elastic polycarbonate material to produce a miniature force plate. Springs arranged at right angles to each other enabled forces ...
Locusts harness the sun to get their optimum diet
2014-07-02
If you are a locust, the most nutritious plant to eat depends on the ambient temperature. Scientists at the University of Sydney, Australia, have discovered that locusts choose their food and then where they digest it according to how hot it is.
Dr Fiona Clissold, who led the study, explains why temperature has such a large influence on insect diets. "Whilst an insect's metabolic rate increases exponentially with temperature, the rate at which locusts absorb protein and carbohydrate from different plants does not increase in step with temperature. As a result, nutrient ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
SKKU research team unravels the origin of stochasticity, a key to next-generation data security and computing
Flexible polymer‑based electronics for human health monitoring: A safety‑level‑oriented review of materials and applications
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
[Press-News.org] Reinterpreting dark matterResearch published in Nature Physics opens up the possibility that it could be regarded as a very cold quantum fluid governing the formation of the structure across the whole universe