(Press-News.org) Millions of microbial species populate the world, but so far only a few have been identified due to the inability of most microbes to grow in the laboratory. Edgar Goluch, an engineer, and Slava Epstein, a biologist, aim to change this. The pair, both researchers at Northeastern University, has developed a device that allows scientists to cultivate a single species of bacteria that can then be studied and identified.
Goluch's previous research devices incorporated permeable membranes that allow sequestered bacteria to be exposed to the nutrients and molecules of their native environment. But natural competition between species, even in the wild, has so far limited the number of species of bacteria that biologists have been able to isolate with these methods and in traditional lab settings.
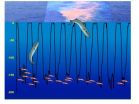
Goluch and Epstein's device, detailed in a paper released July 1 in the journal PLOS ONE, solves this problem. This new device permits just a single bacterial cell to enter an inner chamber containing a food source, to which the only access is a microscopic passageway just slightly narrower than a single cell. The passageway is so small that the first cell to enter it gets stuck, blocking entry by any other cell or species. Once inside, this cell pro-liferates as in previous devices, and when it does it fills up the inner chamber with a pure, single-species sample, since it is isolated from competition from other species.
In the paper, the team demonstrates the device's ability to separate mixtures of cell types in a laboratory setting. In one experiment, the researchers separated two different bacterial species whose cells are slightly different sizes—E. coli and P. aueruginosa. In a second experiment, they isolated a combination of similarly sized but differently shaped species that commonly show up together in the marine environment—Roseobacter sp. and Pscyhoserpens sp. Finally, they used the device to separate cells of the same species that had been differentially tagged to glow either red or green. This final experiment validates the hypothesis that the cells grown inside the food chamber are daughters of the single cell caught in the entryway. Epstein will test the devices in the biological setting beginning this month during a research trip to Greenland.
Going forward, funding from an Instrument Development Biological Research Grant from the National Science Foundation will enable Goluch and his team of engineers to begin optimizing the device and its manufacture on a larger scale.
INFORMATION:
Identifying microbial species
New device will help identify the millions of bacteria that populate the world
2014-07-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Women veterans want options, follow up support when dealing with intimate partner violence
2014-07-03
(Boston)--Intimate partner violence (IPV) is a significant health issue faced by women veterans, but little has been known up until now about their preferences for IPV-related care. A new study has found that most of these women support routine screening for IPV and want options, follow-up support, transparent documentation and Veterans Health Administration (VHA) and community resources. These findings appear in the journal Research in Nursing and Health.
Although women of all socio-demographic groups are at risk for IPV, population-based research suggests that women ...
Hot Pot with chicken causes campylobacter infections in Switzerland
2014-07-03
This news release is available in German and French. In Switzerland, between 7000 and 8000 persons fall ill with a campylobacter infection annually. This makes it the most frequent bacterial disease transmitted through food. Contamination of chicken meat with campylobacter bacteria during the slaughtering process is one of the known causes of the infection. An increase of campylobacteriosis case numbers is being observed throughout Europe. Human cases of campylobacteriosis must be reported to the relevant authorities in Switzerland.
In Switzerland, an unusual increase ...
Low brain protein levels associated with neurodegeneration
2014-07-03
Persons with reduced levels of the TREM2 protein could be at greater risk of developing neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease or frontotemporal dementia, according to an international study which included the participation of the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona and the Sant Pau Biomedical Research Institute (IIB Sant Pau).
The study, published in Science Translational Medicine, reveals the molecular mechanism by which the mutated forms of this protein prevent the amyloid waste cleaning process from functioning correctly and detects a lower level of ...
Whales as ecosystem engineers
2014-07-03
"Consider the subtleness of the sea; how its most dreaded creatures glide under water, unapparent for the most part," wrote Herman Melville in Moby Dick. Today, we no longer dread whales, but their subtlety remains. "For a long time, whales have been considered too rare to make much of a difference in the oceans," notes University of Vermont conservation biologist Joe Roman. That was a mistake.
In a new paper, Roman and a team of biologists have tallied several decades of research on whales from around the world; it shows that whales, in fact, make a huge difference—they ...
No two lark sparrows are alike (at least when it comes to migration habits)
2014-07-03
A new paper by Dr. Jeremy Ross from the University of Oklahoma describes the use of tiny devices strapped to birds' backs called geolocators, which capture the individual migration routes of lark sparrows in North America. By sensing the light levels, these backpacks can pinpoint the location of a bird anywhere in the world, even if retrieving the data-logger can sometimes pose a major problem.
This study, published in the online journal Animal Migration, mapped for the first time the routes traveled by three lark sparrows after they left their breeding grounds in Ohio. ...
Consider water use in climate change policies, advise Australian researchers
2014-07-03
There's more to trying to slow down climate change than just cutting greenhouse gas emissions. Technology, policies or plans that aim to do so should also take environmental factors such as water usage into account. A more integrated approach might make some options considerably more attractive than others, especially when implemented in arid countries such as Australia, advise Philip Wallis of Monash University in Australia and colleagues, in an article in Springer's journal Climatic Change.
The researchers considered the example of Australia to show how water usage ...
Jump to it! A frog's leaping style depends on the environment
2014-07-03
VIDEO:
Tree frogs reach great heights with their jumps, but do not cover much distance.
Click here for more information.
A frog's jump is not as simple as it seems....Australian scientists have discovered that different species adopt different jumping styles depending on their environment.
Lead researcher, Miss Marta Vidal-Garcia ( PhD candidate, Australian National University ), found that tree dwelling frogs reached great heights but didn't cover much distance with their ...
Study finds higher risk for celiac disease in some children
2014-07-03
AURORA, Colo. (July 3, 2014) – Physicians from the University of Colorado School of Medicine in collaboration with an international team of researchers have demonstrated that screening of genetically susceptible infants can lead to the diagnosis of celiac disease at a very early age.
The collaborative group studied 6,403 children with specific genetic markers from birth to identify the factors involved in the development of both celiac disease and type 1 diabetes. The children are from the United States, Finland, Germany and Sweden and are part of The Environmental Determinants ...
Biological signal processing: Body cells -- instrumentalists in a symphony orchestra
2014-07-03
Every organism has one aim: to survive. Its body cells all work in concert to keep it alive. They do so through finely tuned means of communication. Together with cooperation partners from Berlin and Cambridge, scientists at the Luxembourg Centre for Systems Biomedicine (LCSB) of the University of Luxembourg have now successfully revealed for the first time the laws by which cells translate signals from their surroundings into internal signals. Like an isolated note in a symphony orchestra, an isolated signal in the cell is of subordinate importance. "What is important ...
A CNIO team reduces the size of the human genome to 19,000 genes
2014-07-03
How nutrients are metabolised and how neurons communicate in the brain are just some of the messages coded by the 3 billion letters that make up the human genome. The detection and characterisation of the genes present in this mass of information is a complex task that has been a source of ongoing debate since the first systematic attempts by the Human Genome Project more than ten years ago.
A study led by Alfonso Valencia, Vice-Director of Basic Research at the Spanish National Cancer Research Centre (CNIO) and head of the Structural Computational Biology Group, and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Globe-trotting ancient ‘sea-salamander’ fossils rediscovered from Australia’s dawn of the Age of Dinosaurs
Roadmap for Europe’s biodiversity monitoring system
Novel camel antimicrobial peptides show promise against drug-resistant bacteria
Scientists discover why we know when to stop scratching an itch
A hidden reason inner ear cells die – and what it means for preventing hearing loss
Researchers discover how tuberculosis bacteria use a “stealth” mechanism to evade the immune system
New microscopy technique lets scientists see cells in unprecedented detail and color
Sometimes less is more: Scientists rethink how to pack medicine into tiny delivery capsules
Scientists build low-cost microscope to study living cells in zero gravity
The Biophysical Journal names Denis V. Titov the 2025 Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator awardee
Scientists show how your body senses cold—and why menthol feels cool
Scientists deliver new molecule for getting DNA into cells
Study reveals insights about brain regions linked to OCD, informing potential treatments
Does ocean saltiness influence El Niño?
2026 Young Investigators: ONR celebrates new talent tackling warfighter challenges
Genetics help explain who gets the ‘telltale tingle’ from music, art and literature
Many Americans misunderstand medical aid in dying laws
Researchers publish landmark infectious disease study in ‘Science’
New NSF award supports innovative role-playing game approach to strengthening research security in academia
Kumar named to ACMA Emerging Leaders Program for 2026
AI language models could transform aquatic environmental risk assessment
New isotope tools reveal hidden pathways reshaping the global nitrogen cycle
Study reveals how antibiotic structure controls removal from water using biochar
Why chronic pain lasts longer in women: Immune cells offer clues
Toxic exposure creates epigenetic disease risk over 20 generations
More time spent on social media linked to steroid use intentions among boys and men
New study suggests a “kick it while it’s down” approach to cancer treatment could improve cure rates
Milken Institute, Ann Theodore Foundation launch new grant to support clinical trial for potential sarcoidosis treatment
New strategies boost effectiveness of CAR-NK therapy against cancer
Study: Adolescent cannabis use linked to doubling risk of psychotic and bipolar disorders
[Press-News.org] Identifying microbial speciesNew device will help identify the millions of bacteria that populate the world