(Press-News.org) Scientists from North Carolina State University and the University of Florida have combined cookies, citizen science and robust research methods to track the diversity of ant species across the United States, and are now collaborating with international partners to get a global perspective on how ants are moving and surviving in the modern world.
"We think our School of Ants project serves as a good model for how citizen science can be used to collect more data, more quickly, from more places than a research team could do otherwise," says Dr. Andrea Lucky, a researcher at the University of Florida who started work on the School of Ants while a postdoctoral researcher at NC State and now heads the project. Lucky is co-lead author of a paper describing the work and its early findings. "And our protocols help ensure that the data we are collecting are high quality."
The School of Ants project was developed at NC State to help researchers get a handle on the diversity of ant species across the United States, with a particular focus on Chicago, Raleigh and New York City. In short, to discover which ant species are living where.
"But we also wanted to launch a citizen science project that both increased the public's ecological literacy and addressed criticisms that public involvement made citizen science data unreliable," says Dr. Amy Savage , a postdoctoral biological sciences researcher at NC State and the other co-lead author of the paper.
The researchers developed a simple protocol involving Pecan Sandies cookies and sealable plastic bags, detailing precisely how the public should collect and label ant samples before shipping them to NC State or UF. This process was designed to engage the public in the aspect of the research that was easiest for non-scientists to enjoy and participate in, while also limiting the chances that the public could make mistakes that would skew the findings.
Once the samples arrive at NC State or UF, they are sorted, identified by a team of national experts and entered into a database. That information is then made publicly available in a user-friendly format on the project's schoolofants.org site, allowing study participants to track the survey.
"This information is helping us tackle a variety of ecological and evolutionary questions, such as how ants may be evolving in urban environments, and how invasive species are spreading in the U.S.," Savage says.
More than 1,000 participants, with samples from all 50 states, have taken part in the project since its 2011 launch – and there have already been some surprising findings.
For example, the researchers learned that a venomous invasive species, the Asian needle ant (Pachycondyla chinensis), had spread thousands of miles farther than anyone expected. Researchers knew the species had established itself in the Southeast, but study participants sent in Asian needle ant samples from as far afield as Wisconsin and Washington state.
To build on the School of Ants model, the researchers have launched collaborations with counterparts in Italy and Australia.
"We're optimistic that this project will give us a broader view of ant diversity and how these species intersect with us, where we live and work around the world," Lucky says.
The researchers are also working with teachers to incorporate the project into K-12 instruction modules that incorporate key elements of common core education standards. One early teacher collaboration has led to a research paper co-written by 4th and 5th graders.
"We also collaborated with a science writer to produce a free series of iBooks featuring natural history stories about the most common ants that our citizen science partners are collecting in their backyards and sidewalks," Savage says.
"One of our big goals now is to move from collecting data and finding patterns to identifying ways that we can work with the public to figure out what is driving those patterns," says Dr. Rob Dunn, an associate professor of biological sciences at NC State and co-author of the paper.
INFORMATION:
The paper, "Ecologists, educators, and writers collaborate with the public to assess backyard diversity in The School of Ants Project," was published online July 7 in the open-access journal Ecosphere. Co-authors include Lauren Nichols and Leonora Shell of NC State; and Drs. Cristina Castracani, Donato Grasso and Alessandra Mori of the Università degli Studi di Parma. The research was funded National Science Foundation grant 551819-0654, with support from the Burroughs Wellcome Fund.
Science and cookies: Researchers tap into citizen science to shed light on ant diversity
2014-07-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Concern at lack of teenage patients in cancer trials
2014-07-07
Age limits on clinical trials need to be more flexible to allow more teenage cancer patients the chance to access new treatments, according to a report from the National Cancer Research Institute (NCRI), published in the Lancet Oncology.
The study, funded by the National Institute for Health Research and Teenage Cancer Trust, found that trials designed with broader age limits resulted in more teenagers and young adults going on clinical trials.
The study showed this recommendation led to a 13 per cent rise in 15-19 year old cancer patients taking part in clinical trials ...
Sutures or staples? The best choice for closing a C-section
2014-07-07
(PHILADELPHIA) -- In the largest study to date comparing sutures (stitches) versus surgical staples for closing a C-section, researchers found a 57 percent decrease in wound complications in women who were sutured versus those who received staples. By carefully addressing the concerns that previous studies had raised, the research shows a clear benefit of suture for women.
"There has been ongoing debate in the field about the use of sutures versus staples," says senior author Vincenzo Berghella, M.D., director of Maternal Fetal Medicine in the Department of Obstetrics ...
Low-cost TB test means quicker, more reliable diagnosis for patients
2014-07-07
(BRYAN, Texas) — A new test for tuberculosis (TB) could dramatically improve the speed and accuracy of diagnosis for one of the world's deadliest diseases, enabling health care providers to report results to patients within minutes, according to a study published this week in the journal Angewandte Chemie.
Jeffrey Cirillo, Ph.D., professor at the Texas A&M Health Science Center College of Medicine, in collaboration with GBDbio, a Texas A&M spinoff company, and investigators at Stanford University, have identified a new chemical compound to spot the bacteria that cause ...
Platonic solids generate their 4-dimensional analogues
2014-07-07
Alicia Boole Stott, the third daughter of mathematician George Boole, is probably best known for establishing the term "polytope" for a convex solid in four dimensions. Alicia was also a long time collaborator of HSM Coxeter, one of the greatest geometers of the 20th Century.
Platonic solids are regular bodies in three dimensions, such as the cube and icosahedron, and have been known for millennia. They feature prominently in the natural world wherever geometry and symmetry are important, for instance in lattices and quasi-crystals, as well as fullerenes and viruses (see ...
Scientists find important piece in the brain tumor puzzle
2014-07-07
This news release is available in French. Scientists at the Montreal Neurological Institute and Hospital, McGill University and McGill University Health Centre have shown that a member of the protein family known as SUMO (small ubiquitin-like modifier) is a key to why tumour cells multiply uncontrollably, especially in the case of glioblastoma. The SUMO family proteins modify other proteins and the SUMOylation of proteins are critical for many cellular processes. Identifying SUMO's role in the cancer cell growth will lead to a new strategy for glioblastoma treatment. ...
NASA sees Hurricane Arthur's July fourth fireworks on US East Coast
2014-07-07
VIDEO:
On July 3, NASA's TRMM satellite passed over Arthur and saw intense bands of thunderstorms north of Arthur's well defined eye dropping rainfall at a rate of over 98.4 mm...
Click here for more information.
Hurricane Arthur made landfall in North Carolina on July 3, and today, July 4, it is bringing its own fireworks along the Mid-Atlantic and New England states. Those fireworks were in the form of "hot towers," powerful, high thunderstorms with heavy rainfall that indicate ...
Conclusion of the Lindau Nobel Laureate meeting
2014-07-07
The 64th Lindau Nobel Laureate Meeting ended with a panel discussion entitled "Science for the benefit of mankind" on Mainau Island, Lake Constance, Germany, today." 37 Nobel laureates and more than 600 selected young scientists from 80 countries had participated in the week-long meeting in the Bavarian city of Lindau since last Sunday. A boat trip to Mainau at the invitation of the State of Baden-Württemberg marked the finish of the programme which was devoted to medicine and physiology. In 1895 Alfred Nobel determined in his will that the Nobel Prizes shall be awarded ...
New optogenetic tool for controlling neuronal signalling by blue light
2014-07-07
Institute for Basic Science (IBS), the main organization of the International Science and Business Belt project in South Korea, has announced that a group of researchers, led by professor Won Do Heo, have developed a new technology in the field of optogenetics that can remotely control specific receptors by light. They have named this new technology "OptoTrk" and it has succeeded with neuronal differentiation inducement.
The most significant feature of OptoTrk technology is that it requires only light to activate neuronal functions without the need of other substances. ...
Perspective of the PandaX dark matter experiment
2014-07-07
The PandaX experiment of China, which is located in the deepest underground laboratory, has released its technical design report recently. The full article will appear in SCIENCE CHINA Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy, 2014, 57(8): 1476-1494.
The Particle and Astrophysical Xenon (PandaX) collaboration was established in 2009 and mainly supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology, the Ministry of Education in China, the Natural Science Foundation of China,and Shanghai Jiao Tong University. The experiment is suitable for both direct dark matter detection ...
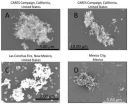
New type of soot particle discovered from wildfire emissions
2014-07-07
RENO – Every year, wildfires clear millions of hectares of land and emit around 34-percent of global soot mass into the atmosphere. In certain regions, such as Southeast Asia and Russia, these fires can contribute as much as 63-percent of regional soot mass.
In a paper published in Nature Scientific Reports, a team of scientists led by Rajan Chakrabarty from Nevada's Desert Research Institute report the observation of a previously unrecognized form of soot particle, identified by the authors as "superaggregates," from wildfire emissions. These newly identified particles ...