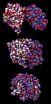
(Press-News.org) For the first time, there is no need to chemically fix, stain or cut cells in order to study them. Instead, whole living cells are fast-frozen and studied in their natural environment. The new method delivers an immediate 3-D image, thereby closing a gap between conventional microscopic techniques.
The new microscope delivers a high-resolution 3-D image of the entire cell in one step. This is an advantage over electron microscopy, in which a 3-D image is assembled out of many thin sections. This can take up to weeks for just one cell. Also, the cell need not be labelled with dyes, unlike in fluorescence microscopy, where only the labelled structures become visible. The new X-ray microscope instead exploits the natural contrast between organic material and water to form an image of all cell structures. Dr. Gerd Schneider and his microscopy team at the Institute for Soft Matter and Functional Materials have published their development in Nature Methods (DOI:10.1038/nmeth.1533).
With the high resolution achieved by their microscope, the researchers, in cooperation with colleagues of the National Cancer Institute in the USA, have reconstructed mouse adenocarcinoma cells in three dimensions. The smallest of details were visible: the double membrane of the cell nucleus, nuclear pores in the nuclear envelope, membrane channels in the nucleus, numerous invaginations of the inner mitochondrial membrane and inclusions in cell organelles such as lysosomes. Such insights will be crucial for shedding light on inner-cellular processes: such as how viruses or nanoparticles penetrate into cells or into the nucleus, for example.
This is the first time the so-called ultrastructure of cells has been imaged with X-rays to such precision, down to 30 nanometres. Ten nanometres are about one ten-thousandth of the width of a human hair. Ultrastructure is the detailed structure of a biological specimen that is too small to be seen with an optical microscope.
Researchers achieved this high 3-D resolution by illuminating the minute structures of the frozen-hydrated object with partially coherent light. This light is generated by BESSY II, the synchrotron source at HZB. Partial coherence is the property of two waves whose relative phase undergoes random fluctuations which are not, however, sufficient to make the wave completely incoherent. Illumination with partial coherent light generates significantly higher contrast for small object details compared to incoherent illumination. Combining this approach with a high-resolution lens, the researchers were able to visualize the ultrastructures of cells at hitherto unattained contrast.
The new X-ray microscope also allows for more space around the sample, which leads to a better spatial view. This space has always been greatly limited by the setup for the sample illumination. The required monochromatic X-ray light was created using a radial grid and then, from this light, a diaphragm would select the desired range of wavelengths. The diaphragm had to be placed so close to the sample that there was almost no space to turn the sample around. The researchers modified this setup: Monochromatic light is collected by a new type of condenser which directly illuminates the object, and the diaphragm is no longer needed. This allows the sample to be turned by up to 158 degrees and observed in three dimensions. These developments provide a new tool in structural biology for the better understanding of the cell structure.
INFORMATION:
New microscope reveals ultrastructure of cells
HZB researchers can take images of small cellular components in their natural environment -- while the cell remains intact
2010-11-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Gene links to anorexia found by Children's Hospital of Philadelphia researchers
2010-11-20
Scientists at The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia have identified both common and rare gene variants associated with the eating disorder anorexia nervosa. In the largest genetic study of this psychiatric disorder, the researchers found intriguing clues to genes they are subjecting to further investigation, including genes active in neuronal signaling and in shaping interconnections among brain cells.
Anorexia nervosa (AN) affects an estimated 9 in 1000 women in the United States. Patients have food refusal, weight loss, an irrational fear of weight gain even when ...
Designing more effective anti-HIV antibodies
2010-11-20
Boston, Mass. – Although people infected with HIV produce many antibodies against the protein encapsulating the virus, most of these antibodies are strangely ineffective at fighting the disease. A new study suggests why some of the most common of these antibodies don't work: they target the protein in a form it takes after the virus has already invaded the cell, when it's too late, report researchers at Children's Hospital Boston and their colleagues.
The findings, published online Nov. 14 in the journal Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, refocus attention on the ...
Professor Zvi Ram presents phase III recurrent glioblastoma survival and quality of life data from the first pivotal study of the NovoTTF-100A at 15th Annual Society for Neuro-Oncology Scientific Meet
2010-11-20
MONTREAL, CANADA - November 19, 2010 - Data presented today from a pivotal, phase III randomized clinical trial for patients with recurrent glioblastoma tumors suggest that Tumor Treating Fields (TTF) therapy may increase median survival time and improve quality of life scores compared to best standard of care chemotherapy. Professor Zvi Ram, chairman of the Department of Neurosurgery at Tel-Aviv Sourasky Medical Center, presented the data at the Society for Neuro-Oncology (SNO) Annual Scientific Meeting.
Physicians delivered the investigational TTF therapy to patients ...
Childhood obesity linked to increased risk of adult cardiovascular and metabolic disorders
2010-11-20
New Rochelle, NY, November 19, 2010—Mounting evidence linking childhood obesity to an increasing risk of obesity, heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and other cardiovascular and metabolic disorders in adulthood is clearly presented in a comprehensive review article in the current issue of Childhood Obesity, published by Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. The article is available free online.
Authors Megan Moriarty-Kelsey, MD and Stephen Daniels, MD, PhD, Department of Pediatrics, University of Colorado School of Medicine, caution that the rising prevalence of obesity in children will ...
New path for colon cancer drug discovery
2010-11-20
An old pinworm medicine is a new lead in the search for compounds that block a signaling pathway implicated in colon cancer. The findings, reported by Vanderbilt University Medical Center researchers in the November issue of Nature Chemical Biology, suggest a fresh approach for developing therapeutics that target the pathway.
More than 90 percent of sporadic (non-inherited) colon cancers – the second deadliest type of cancer in the developed world – are caused by mutations that result in inappropriate activation of the Wnt (pronounced "wint") signaling pathway. Blocking ...
Scripps Research scientists identify first synthetic activator of 2 critical proteins
2010-11-20
JUPITER, FL, November 19, 2010 – Scientists from the Florida campus of The Scripps Research Institute have identified a novel synthetic activator of a pair of proteins that belong to a protein family playing key roles in human metabolism and immune function. The discovery could provide new and potentially more effective therapeutic approaches to diseases ranging from diabetes to osteoporosis.
The study was published in the November issue (Volume 5, Issue 11) of the journal ACS Chemical Biology.
"This new compound is particularly important because it works in vivo, ...
Invention helps students learn surgical techniques before operating on patients
2010-11-20
FORT COLLINS - In the last 50 years, modern medicine has made astounding advances in surgery, yet many of today's veterinary and human medicine students still hone basic surgical and suturing skills on carpet pads and pig's feet before transitioning to a live patient. An invention by Colorado State University veterinarians provides students with artificial body parts that look, feel, behave, and even bleed just like real skin, muscles and vessels.
The artificial replicas of sections of human and animal bodies -- such as an abdominal wall -- give students a realistic learning ...
UH physicists study behavior of enzyme linked to Alzheimer's, cancer
2010-11-20
HOUSTON, Nov. 19, 2010 – University of Houston (UH) physicists are using complex computer simulations to illuminate the workings of a crucial protein that, when malfunctioning, may cause Alzheimer's and cancer.
Margaret Cheung, assistant professor of physics at UH, and Antonios Samiotakis, a physics Ph.D. student, described their findings in a paper titled "Structure, function, and folding of phosphoglycerate kinase (PGK) are strongly perturbed by macromolecular crowding," published in a recent issue of the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, one ...
New study into bladder regeneration heralds organ replacement treatment
2010-11-20
Researchers in the United States have developed a medical model for regenerating bladders using stem cells harvested from a patient's own bone marrow. The research, published in STEM CELLS, is especially relevant for paediatric patients suffering from abnormally developed bladders, but also represents another step towards new organ replacement therapies.
The research, led by Dr Arun Sharma and Earl Cheng from the Feinberg School of Medicine at Northwestern University and Children's Memorial Research Center, focused on bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) taken from ...
Busy microbial world discovered in deepest ocean crust ever explored
2010-11-20
CORVALLIS, Ore. – The first study to ever explore biological activity in the deepest layer of ocean crust has found bacteria with a remarkable range of capabilities, including eating hydrocarbons and natural gas, and "fixing" or storing carbon.
The research, just published in the journal PLoS One, showed that a significant number and amount of bacterial forms were present, even in temperatures near the boiling point of water.
"This is a new ecosystem that almost no one has ever explored," said Martin Fisk, a professor in the College of Oceanic and Atmospheric Sciences ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
Electric field tunes vibrations to ease heat transfer
[Press-News.org] New microscope reveals ultrastructure of cellsHZB researchers can take images of small cellular components in their natural environment -- while the cell remains intact