(Press-News.org) Meet the seven new dwarf galaxies.
Yale University astronomers, using a new type of telescope made by stitching together telephoto lenses, recently discovered seven celestial surprises while probing a nearby spiral galaxy. The previously unseen galaxies may yield important insights into dark matter and galaxy evolution, while possibly signaling the discovery of a new class of objects in space.
For now, scientists know they have found a septuplet of new galaxies that were previously overlooked because of their diffuse nature: The ghostly galaxies emerged from the night sky as the team obtained the first observations from the "homemade" telescope.
The discovery came quickly, in a relatively small section of sky. "We got an exciting result in our first images," said Allison Merritt, a Yale graduate student and lead author of a paper about the discovery in the Astrophysical Journal Letters. "It was very exciting. It speaks to the quality of the telescope."
Pieter van Dokkum, chair of Yale's astronomy department, designed the robotic telescope with University of Toronto astronomer Roberto Abraham. Their Dragonfly Telephoto Array uses eight telephoto lenses with special coatings that suppress internally scattered light. This makes the telescope uniquely adept at detecting the very diffuse, low surface brightness of the newly discovered galaxies.
"These are the same kind of lenses that are used in sporting events like the World Cup. We decided to point them upward instead," van Dokkum said. He and Abraham built the compact, oven-sized telescope in 2012 at New Mexico Skies, an observatory in Mayhill, N.M. The telescope was named Dragonfly because the lenses resemble the compound eye of an insect.
"We knew there was a whole set of science questions that could be answered if we could see diffuse objects in the sky," van Dokkum said. In addition to discovering new galaxies, the team is looking for debris from long-ago galaxy collisions.
"It's a new domain. We're exploring a region of parameter space that had not been explored before," van Dokkum said.
The Yale scientists will tackle a key question next: Are these seven newly found objects dwarf galaxies orbiting around the M101 spiral galaxy, or are they located much closer or farther away, and just by chance are visible in the same direction as M101?
If it's the latter, Merritt said, these objects represent something entirely different. "There are predictions from galaxy formation theory about the need for a population of very diffuse, isolated galaxies in the universe," Merritt said. "It may be that these seven galaxies are the tip of the iceberg, and there are thousands of them in the sky that we haven't detected yet."
Merritt stressed that until they collect more data and determine the distances to the objects, researchers won't know their true nature. But the possibilities are intriguing enough that the team has been granted the opportunity to use the Hubble Space Telescope for further study.
"I'm confident that some of them will turn out to be a new class of objects," van Dokkum said. "I'd be surprised if all seven of them are satellites of M101."
Meanwhile, there is also more work to be done with the new telescope. "We are collecting new data with the Dragonfly telescope every clear night. We're all curious to see what other surprises the night sky has in store for us," Merritt said.
INFORMATION:
Astronomers find 7 dwarf galaxies with new telescope
2014-07-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study provides new approach to forecast hurricane intensity
2014-07-10
VIDEO:
This is the one-of-a-kind, Alfred C. Glassell, Jr., SUSTAIN research facility at the UM Rosenstiel School of Marine and Atmospheric Science, where Haus and colleagues will conduct further studies on...
Click here for more information.
MIAMI – New research from University of Miami (UM) Rosenstiel School of Marine and Atmospheric Science suggests that physical conditions at the air-sea interface, where the ocean and atmosphere meet, is a key component to improve forecast ...
Extinct sea scorpion gets a Yale eye exam, with surprising results
2014-07-10
Poor peepers are a problem, even if you are a big, bad sea scorpion.
One minute, you're an imperious predator, scouring the shallow waters for any prey in sight. The next, thanks to a post-extinction eye exam by Yale University scientists, you're reduced to trolling for weaker, soft-bodied animals you stumble upon at night.
Such is the lot of the giant pterygotid eurypterid, the largest arthropod that ever lived. A new paper by Yale paleontologists, published in the journal Biology Letters, dramatically re-interprets the creature's habits, capabilities, and ecological ...
Despite setback, 'Mississippi Baby' represents significant breakthrough in effort to end AIDS
2014-07-10
Washington, D.C.—July 10, 2014—In response to today's announcement that the "Mississippi Baby," believed to have been functionally cured of HIV, has now been found to have detectable levels of the virus, the Elizabeth Glaser Pediatric AIDS Foundation (EGPAF) expresses disappointment in this setback but remains hopeful that the scientific breakthrough that allowed the child's HIV levels to remain undetectable for more than two years will continue to help researchers understand how to control HIV and ultimately develop a cure.
"Although we had high hopes that the child ...
Hubble spots spiral bridge of young stars linking two ancient galaxies
2014-07-10
NASA's Hubble Space Telescope has photographed an unusual structure 100,000 light years long, which resembles a corkscrew-shaped string of pearls and winds around the cores of two colliding galaxies.
The unique structure of the star spiral may yield new insights into the formation of stellar superclusters that result from merging galaxies and gas dynamics in this rarely seen process.
"We were surprised to find this stunning morphology. We've long known that the 'beads on a string' phenomenon is seen in the arms of spiral galaxies and in tidal bridges between interacting ...
Active shooter training increases comfort level of emergency responders
2014-07-10
(Boston) – Emergency Medical Service (EMS) responders felt better prepared to respond to an active shooter incident after receiving focused tactical training according to a new study in the journal Prehospital and Disaster Medicine. This is the first study to specifically examine the EMS provider comfort level with respect to entering a scene where a shooter has not yet been neutralized or working with law enforcement personnel during that response.
Incidents such as the Columbine High School shooting, the Virginia Tech campus shooting, the 2009 Fort Hood shooting, the ...
Scorpions are master architects, according to new research from Ben-Gurion University
2014-07-10
BEER-SHEVA, Israel – Ben-Gurion University of the Negev scientists have discovered that scorpions create a platform in their burrows where they warm up before the evening hunt.
As ectothermic animals, scorpions rely on energy from the environment to regulate
their internal temperature. The researchers believe that this platform provides a safe, warm spot for the scorpions to increase their body temperature before they leave their hiding places to forage at night.
After trapping the wild large-clawed scorpions (Scorpio maurus palmatus) in Israel's Negev desert the ...
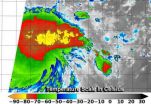
NASA-NOAA Suomi NPP satellite sees power within newborn Tropical Depression 09W
2014-07-10
As the Northwestern Pacific is bidding goodbye to Tropical Cyclone Neoguri, another tropical depression has formed. NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite passed over Tropical Depression 09W (TD09W) and captured infrared data on the storm indicating some powerful thunderstorms within.
Because TD09W is close to land areas, watches are already in effect. On July 10, a tropical storm watch is in force for Guam, Rota, Tinian and Saipan.
Tropical depression 09W was formerly known as low pressure System 92W. VIIRS instrument aboard NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite taken July 10 at ...
Scripps Florida scientists shed new light on nerve cell growth
2014-07-10
JUPITER, FL, July 10, 2014 – Amidst the astounding complexity of the billions of nerve cells and trillions of synaptic connections in the brain, how do nerve cells decide how far to grow or how many connections to build? How do they coordinate these events within the developing brain?
In a new study, scientists from the Florida campus of The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) have shed new light on these complex processes, showing that a particular protein plays a far more sophisticated role in neuron development than previously thought.
The study, published in the journal ...
On the link between periodontitis and atherosclerosis
2014-07-10
Chronic oral infection with the periodontal disease pathogen, Porphyromonas gingivalis, not only causes local inflammation of the gums leading to tooth loss but also is associated with an increased risk of atherosclerosis. A study published on July 10th in PLOS Pathogens now reveals how the pathogen evades the immune system to induce inflammation beyond the oral cavity.
Like other gram-negative bacteria, P. gingivalis has an outer layer that consists of sugars and lipids. The mammalian immune system has evolved to recognize parts of this bacterial coating, which then ...
New research finds ocean's most abundant organisms have clear daily cycles
2014-07-10
Imagine the open ocean as a microbial megacity, teeming with life too small to be seen. In every drop of water, hundreds of types of bacteria can be found. Now scientists have discovered that communities of these ocean microbes have their own daily cycles—not unlike the residents of a bustling city who tend to wake up, commute, work, and eat at the same times.
What's more, it's not all about the sun. Light-loving photoautotrophs—bacteria that need solar energy to help them photosynthesize food from inorganic substances—have been known to sun themselves on a regular schedule. ...