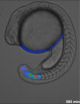
(Press-News.org) The once-powerful Super Typhoon Neoguri weakened to a tropical storm when it dropped heavy rainfall over southern Japan during the week of July 7, 2014. NASA and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission or TRMM satellite measured that soaking from its orbit in space and data was used to create a maps showing the rainfall totals.
Heavy rainfall from Neoguri fell on land that was already soaked earlier this month by a slow moving seasonal frontal system. Neoguri was reported to have caused up to five deaths and 50 injuries in Japan.
Rainfall from tropical storm Neoguri also caused a large landslide in the town of Nagiso on the main island of Honshu resulting in one death and the destruction of many buildings.
A TRMM Multi-Satellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA), produced at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Maryland, combined the rainfall estimates generated by TRMM and other satellites. The analysis showed a near-real time Multi-satellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA) for the period from July 1 to 11, 2014. The analysis indicated rainfall totals of over 520 mm (about 20.4 inches) near the western tip of the Japanese island of Kyushu. Neoguri's past locations and track are shown with red symbols.
INFORMATION:
Text credit: Harold F. Pierce
SSAI/NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
NASA adds up Tropical Storm Neoguri's deluge from space
2014-07-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Say 'no' to interruptions, 'yes' to better work
2014-07-14
Modern office workers are expected to multitask regularly, often juggling multiple projects and priorities over the course of a day. Studies have shown that the typical employee in an office environment is interrupted up to six times per hour, but how does that impact the finished product? New research published in Human Factors evaluates how ongoing interruptions can negatively affect the quality of work.
"People don't realize how disruptive interruptions can be," said Cyrus Foroughi, coauthor of "Do Interruptions Affect Quality of Work?" and a PhD candidate at George ...
Sierra Leone samples: Ebola evidence in West Africa in 2006
2014-07-14
Analysis of clinical samples from suspected Lassa fever cases in Sierra Leone showed that about two-thirds of the patients had been exposed to other emerging diseases, and nearly nine percent tested positive for Ebola virus. The study, published in this month's edition of Emerging Infectious Diseases, demonstrates that Ebola virus has been circulating in the region since at least 2006—well before the current outbreak.
First author Randal J. Schoepp, Ph.D., recently returned from Liberia and Sierra Leone, where he spent six weeks helping to set up an Ebola testing laboratory ...
Scientists deepen genetic understanding of eosinophilic esophagitis
2014-07-14
WHAT:
Scientists funded by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) have identified genetic markers associated with eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE), an inflammatory disease characterized by high levels of immune cells called eosinophils in the esophagus. Their findings suggest that several genes are involved in the development of EoE, which can cause difficulty eating and often is associated with food allergies. The findings also may help explain why the disease specifically affects the esophagus. The work was supported in part by the Consortium of Food Allergy Research, ...
The Lancet Neurology: Personal View looks back on 40 years of the Glasgow Coma Scale
2014-07-14
A group of leading brain injury specialists look back on 40 years of the Glasgow Coma Scale and outline the continuing role of the scale in research and clinical practice, in a new Personal View published in The Lancet Neurology.
The Personal View is published on the 40th anniversary of the Glasgow Coma Scale's introduction in a 1974 Lancet article*. Since this seminal publication, the Glasgow Coma Scale has provided a practical method for bedside assessment of impairment of conscious level, the clinical hallmark of acute brain injury. The scale was designed to be ...
Story tips from the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory, July 2014
2014-07-14
To arrange for an interview with a researcher, please contact the Communications staff member identified at the end of each tip. For more information on ORNL and its research and development activities, please refer to one of our media contacts. If you have a general media-related question or comment, you can send it to news@ornl.gov.
MATERIALS – Rare earth substitute …
An alloy discovered at Oak Ridge National Laboratory holds great promise for permanent magnets as the material retains its magnetic properties at higher temperatures yet contains no rare-earth elements. ...
Using competitors' brand name as a keyword can backfire, INFORMS study finds
2014-07-14
Buying keywords of a popular competitors' brand names on search engines such as Google and Bing can backfire according to a new study in the Articles in Advance section of Marketing Science, a journal of the Institute for Operations Research and the Management Sciences (INFORMS).
Firms buy specific keywords, including competitors' brand names, on search engines to reach consumers searching for those words. Online advertisements employing such keywords are called search ads. Sometimes a brand such as Nissan Altima will buy search ads to reach customers who conduct a ...
Antibiotic use prevalent in hospice patients despite limited evidence of its value
2014-07-14
CORVALLIS, Ore. – New research suggests that use of antibiotics is still prevalent among terminal patients who have chosen hospice care as an end-of-life option, despite little evidence that the medications improve symptoms or quality of life, and sometimes may cause unwanted side effects.
The use of antibiotics is so engrained in contemporary medicine that 21 percent of patients being discharged from hospitals directly to a hospice program leave with a prescription for antibiotics, even though more than one fourth of them don't have a documented infection during their ...
Timing is not only ticking
2014-07-14
This news release is available in German.
Many animals exhibit segmental patterns that manifest themselves during development. One classical example is the sequential and rhythmic formation the segmental precursors of the backbone, a process that has been linked to the ticking of an oscillator in the embryo – the "segmentation clock". Until now, this patterning process was thought to be determined simply by the time scale of genetic oscillations that periodically trigger new segment formation. However, this week in the journal Science, Max Planck researchers suggest ...
Cocaine, cash and chemistry: 4 scientifically rich facts about money (video)
2014-07-14
WASHINGTON, July 14, 2014 — Chances are those dollars in your pocket have a trace of cocaine on them. Don't worry — most bank notes in the U.S. do. Your cash also contains invisible ink and has likely been through a washing machine before it came out of the ATM. For more, watch this week's Reactions episode, which features a stack of chemistry facts about the almighty dollar. The video is available at http://youtu.be/bAIwFaPycaU.
Subscribe to the series at Reactions YouTube, and follow us on Twitter @ACSreactions to be the first to see our latest videos.
The American ...
Scientists developed new technology for the diagnosis of cancer cells
2014-07-14
Together with the company Tissuegnostics, the pathologist Lukas Kenner and his colleagues have developed a software that is able to identify cancer cells in tissue sections and demonstrate the presence of specific biomarkers on cells. The overall information provides a precise picture of the disease and leads to the most suitable treatment.
According to the results of the study, "Two independent pathologists concur with each other only in regard of every third diagnosis."
"The recently developed software offers, for the first time, the option of eliminating the so-called ...