(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON D.C., July 15, 2014 -- From your hot car to your warm laptop, every machine and device in your life wastes a lot of energy through the loss of heat. But thermoelectric devices, which convert heat to electricity and vice versa, can harness that wasted heat, and possibly provide the green tech energy efficiency that's needed for a sustainable future.
Now, a new study shows how porous substances can act as thermoelectric materials—pointing the way for engineering the use of such materials in thermoelectric devices of the future.
About 70 percent of all the energy generated in the world is wasted as heat, said Dimitris Niarchos of the National Center for Scientific Research Demokritos in Athens, Greece. He and Roland Tarkhanyan, also of NCSR Demokritos, have published their analysis in the journal APL Materials, from AIP Publishing.
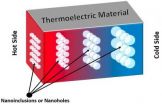
To create the technology needed to capture this heat, researchers around the world have been trying to engineer more efficient thermoelectric materials. One promising material is one that's filled with tiny holes that range in size from about a micron (10-6 meters) to about a nanometer (10-9 meters). "Porous thermoelectrics can play a significant role in improving thermoelectrics as a viable alternative for harvesting wasted heat," Niarchos said.
Heat travels through a material via phonons, quantized units of vibration that act as heat-carrying particles. When a phonon runs into a hole, it scatters and loses energy. Phonons thus can't carry heat across a porous material as efficiently, giving the material a low thermal conductivity, which turns out to increase the efficiency of heat-to-electricity conversion. The more porous the material, the lower the thermal conductivity, and the better it is as a thermoelectric material.
So far, however, researchers have yet to systematically model how porous materials maintain low thermal conductivity, Niarchos said. So he and Tarkhanyan studied the thermal properties of four simple model structures of micro-nano porous materials. This analysis, Niarchos says, provides a rough blueprint for how to design such materials for thermoelectric devices.
Overall, the researchers found that the smaller the pores and the closer they're packed together, the lower the thermal conductivity. Their calculations match data from other experiments well, Niarchos said. They also show that, in principle, micro-nano porous materials can be several times better at converting heat to electricity than if the material had no pores.
The first model describes a material filled with holes of random sizes, ranging from microns to nanometers in diameter. The second is one with multiple layers in which each layer contains pores of different size scales, which gives it a different porosity. The third is a material that's composed of a three-dimensional cubic lattice of identical holes. The fourth is another multilayered system. But in this case, each layer contains a cubic lattice of identical holes. The size of the holes is different in each layer.
According to the analysis, the first and fourth models have lower thermal conductivities than the second. The third model seems to be the best one, as it also has a lower thermal conductivity than the fourth model.
Except for the first model, however, all the models aren't practical because they represent idealized situations with a perfect arrangement of pores, Niarchos said. It's also practically impossible to create precisely equal-sized pores. The first model is thus the most realistic.
Still, he said, all the distinct models demonstrate the importance of porosity in thermoelectric materials. Built upon simple and general analytical formulas, the models allow for a very fast and accurate computation of the effective lattice thermal conductivity of a porous material and the systematic analysis of such materials.
INFORMATION:
The article, "Reduction of thermal conductivity in porous 'gray' materials," is authored by Roland H. Tarkhanyan and Dimitris Niarchos. It appears in the journal APL Materials on July 15, 2014. After that date, it can be accessed at: http://scitation.aip.org/content/aip/journal/aplmater/2/7/10.1063/1.4886220
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
APL Materials is a new open access journal featuring original research on significant topical issues within the field of materials science. See: http://aplmaterials.aip.org
New materials for future green tech devices
2014-07-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Widespread support for rapid HIV testing in dental surgeries -- new study
2014-07-15
More than 80 per cent of oral health patients are willing to receive rapid HIV-testing in dental settings, which could help reduce the spread of the HIV according to a groundbreaking study revealed today at a Sydney University HIV Testing Symposium.
The first of its kind study of 521 Sydney-based dental patients assessed patients' willingness to undergo rapid HIV testing in dental settings, their preference for HIV testing-type type and their willingness to pay for the test.
Rapid HIV testing is a screening test that swiftly detects the presence of HIV antibodies in ...
Hear Jane read: Rutgers University-Newark researcher gives new meaning to semantics
2014-07-15
For years a key way of diagnosing dyslexia has been how well a person reads aloud. Similarly, the reading skills of adult readers also have been assessed by having them read words aloud. "The idea is that the more you read in English, the more you will encounter words that don't follow standard rules of pronunciation, so it's an index of reading exposure and, presumably, ability," explains researcher William W. Graves. But are you a better reader if you pronounce a word based on its meaning, or based on its spelling? Does it make a difference? And why? Those are the ...
Genetic testing for alcohol dependence risk in African Americans
2014-07-15
New Rochelle, NY, July 15, 2014—Alcohol dependence (AD) has a genetic component and testing can determine a person's genetic risk for susceptibility to AD. A new study shows that while more than 85% of the African American adults expressed an interest in genetic testing for AD susceptibility, many had ethical, privacy, and procedural concerns, as reported in Genetic Testing and Molecular Biomarkers, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available on the Genetic Testing and Molecular Biomarkers website.
Denise Scott and coauthors ...
New statement on 'PEG' feeding tubes in children published by Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology
2014-07-15
July 15, 2014– Placement of a percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy tube has become an "essential" technique for children and young people with a wide range of problems with feeding and nutrition, according to a position statement in the Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition, official journal of the European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition (ESPGHAN) and the North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition. The journal is published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, a part of Wolters Kluwer Health. ...
Identifying newly diagnosed HIV-infected people using electronic medical records
2014-07-15
New Rochelle, NY, July 15, 2014—A new, validated software-based method for identifying patients with newly diagnosed HIV using electronic medical records (EMRs) is described in AIDS Research and Human Retroviruses, a peer-reviewed journal published by Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available free on the AIDS Research and Human Retroviruses website at http://online.liebertpub.com/doi/full/10.1089/aid.2013.0287 until August 15, 2014.
Providing medical care early on to people with newly diagnosed HIV infection is important for improving clinical outcomes. ...
Researchers find organic pollutants not factor in turtle tumor disease
2014-07-15
For nearly four decades, scientists have suspected that persistent organic pollutants (POPs) contributed to a green turtle's susceptibility to the virus that causes fibropapilomatosis (FP), a disease that forms large benign tumors that can inhibit the animal's sight, mobility and feeding ability. In a new study,* researchers from the Hollings Marine Laboratory (HML), a government-university partner facility in Charleston, S.C., and from university and federal collaborators in Hawaii demonstrated POPs are not, in fact, a co-factor linked to the increasing number of green ...
Experts voice concerns over arsenic in rice, reports Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition
2014-07-15
July 15, 2014 – Inorganic arsenic in rice and rice-based foods poses health concerns in infants and young children, and steps should be taken to minimize exposure, according to a commentary in the Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition, official journal of the European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition (ESPGHAN) and the North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition. The journal is published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, a part of Wolters Kluwer Health.
The inorganic arsenic levels ...
Oetzi's 'non-human' DNA
2014-07-15
Much of what we know about Oetzi – for example what he looked like or that he suffered from lactose intolerance – stems from a tiny bone sample which allowed the decoding of his genetic make-up. Now, however, the team of scientists have examined more closely the part of the sample consisting of non-human DNA. "What is new is that we did not carry out a directed DNA analysis but rather investigated the whole spectrum of DNA to better understand which organisms are in this sample and what is their potential function", is how Frank Maixner, from the EURAC Institute for Mummies ...
New mite species from a Caribbean mesophotic coral ecosystem named after J.Lo
2014-07-15
During a recent survey of organisms collected from Bajo de Sico, a mesophotic coral reef ecosystem in Mona Passage off Puerto Rico, one pontarachnid mite species new to science was discovered. The new species was named after the famous Puerto Rican singer Jennifer Lopez. The study was published in the open access journal ZooKeys.
"The reason behind the unusual choice of name for the new species", explains the lead author Vladimir Pešić, Department of Biology, University of Montenegro, "is that J.Lo's songs and videos kept the team in a continuous good mood when writing ...
Hidden variations in neuronal networks may explain differences in brain injury outcomes
2014-07-15
ATLANTA–A team of researchers at the Neuroscience Institute at Georgia State University has discovered that hidden differences in the properties of neural circuits can account for whether animals are behaviorally susceptible to brain injury. These results could have implications for the treatment of brain trauma.
People vary in their responses to stroke and trauma, which impedes the ability of physicians to predict patient outcomes. Damage to the brain and nervous system can lead to severe disabilities, including epilepsy and cognitive impairment.
If doctors could ...