(Press-News.org) A new approach to measuring biodiversity has uncovered some biologically important but currently unprotected areas in Western Australia, while confirming the significance of the world heritage listed Wet Tropics rainforests in the country's north-east.
In a paper published yesterday (Friday 18 July) in Nature Communications, scientists from CSIRO, University of California, University of Canberra, the Australian Tropical Herbarium at James Cook University and University of New South Wales applied the new method to Australia's iconic Acacia.
The genus Acacia includes Australia's floral emblem the golden wattle, Acacia pycnantha.
"In this study we've taken our newfound knowledge of the genetics of Acacia and its extended family tree and combined it with Australia's comprehensive botanical and environmental databases," explained co-author Dr Andrew Thornhill.
"It's 21st Century botany, using genetics to tell us about Acacia's evolutionary history – its family pedigree."
Lead author Professor Brent Mishler from the University of California, Berkeley, said the approach taken – phylogenetic analysis – gave a much more complex and complete picture of diversity.
"It takes into account not just the number of plant species in an area, but also their rarity in the landscape and the rarity of their close relatives. We're looking at whole branches of the tree of life, rather than just a species out at the end of a branch," he said.
Professor Darren Crayn, Director of the Australian Tropical Herbarium at James Cook University in Cairns, said the research would not have been possible without the decades of groundwork involved in digitising the specimen information held by Australia's herbaria.
"The results of that world-leading collaboration are now shared through public resources like the Atlas of Living Australia and the Australia's Virtual Herbarium," Professor Crayn said.
"It puts us at the forefront, globally, in identifying important areas of biodiversity by combining cutting-edge genetic analysis with the information contained in scientific collections compiled over centuries."
The study involved complex analysis of mountains of data.
"We introduced randomisation to test the accuracy of our calculations, and that made this a massive statistical exercise," Dr Thornhill said. "We used CSIRO's supercomputer to do calculations on the genetics and distribution of around 120,000 recorded plants."
The researchers created a new model to pinpoint areas that are the cradles of new species (neo-endemics) and those where the remaining members of ancient lineages (paleo-endemics) have taken refuge.
The model is called CANAPE, or Categorical Analysis of Neo- and Paleo-Endemism.
"With CANAPE we're looking beyond whether or not a species is rare," Dr Thornhill said.
"We're using the plant's DNA to investigate its evolutionary tree and establish whether it's restricted to a particular area because it's a relatively new species that developed there, or whether this is a previously wide-spread plant that has retreated to the area as its suitable habitat has shrunk.
"That's valuable information for conservation, particularly in light of the pressures of climate change and development."
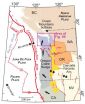
The study confirms Queensland's Wet Tropics in north-eastern Australia as having high values for paleo-endemism, providing refuge for plants that were probably once more widely distributed across the continent.
"Using CANAPE we've also identified places of Acacia 'super-endemism', where the old and new co-exist – places that are both cradles for new species and refuges for older plants," Dr Thornhill said.
"Some of these extremely significant sites in the north-west of Western Australia are currently unprotected.
"We hope this study, and investigation of other significant plant groups using this new method, will help focus attention on these sites and lead to the conservation of more of the diversity of life on Earth."
Dr Thornhill and his colleagues are now focussing similar studies on Australian eucalypts, conifers and ferns.
INFORMATION:
A new measure of biodiversity
Phylogenetic analysis gives a much more complex and complete picture of the diversity of Australia's national plant
2014-07-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Getting a grip on robotic grasp
2014-07-18
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- Twisting a screwdriver, removing a bottle cap, and peeling a banana are just a few simple tasks that are tricky to pull off single-handedly. Now a new wrist-mounted robot can provide a helping hand — or rather, fingers.
Researchers at MIT have developed a robot that enhances the grasping motion of the human hand. The device, worn around one's wrist, works essentially like two extra fingers adjacent to the pinky and thumb. A novel control algorithm enables it to move in sync with the wearer's fingers to grasp objects of various shapes and sizes. Wearing ...
Biomarker discovery may lead to new HIV treatment
2014-07-18
Further analysis of a Phase II study of therapeutic HIV vaccine candidate Vacc-4x revealed a potential biomarker associated with participants who experienced a more profound viral load reduction after receiving the vaccine. The results of this exploratory, ad hoc, subset analysis by St George's, University of London and Bionor Pharma were announced today at the AIDS 2014 Conference in Melbourne, Australia.
If confirmed, the biomarker may be able to predict which patients will benefit most from the therapeutic HIV vaccine candidate Vacc-4x, which is being developed by ...
'Nanocamera' takes pictures at distances smaller than light's own wavelength
2014-07-17
VIDEO:
This is a video demonstrating scanning-stage-based exposure, whereby programmed
motion of a microscope stage is used to write the University's "Block I " logo into the plasmonic film. Each bar in the...
Click here for more information.
Researchers at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign have demonstrated that an array of novel gold, pillar-bowtie nanoantennas (pBNAs) can be used like traditional photographic film to record light for distances that ...
Tiniest catch: University of Arizona scientists' fishing expedition reveals viral diversity in the sea
2014-07-17
A fishing expedition of microscopic proportions led by University of Arizona ecologists revealed that the lines between virus types in nature are less blurred than previously thought.
Using lab-cultured bacteria as "bait," a team of scientists led by Matthew Sullivan has sequenced complete and partial genomes of about 10 million viruses from an ocean water sample in a single experiment.
The study, published online on July 14 by the journal Nature, revealed that the genomes of viruses in natural ecosystems fall into more distinct categories than previously thought. This ...
Lunar pits could shelter astronauts, reveal details of how 'man in the moon' formed
2014-07-17
VIDEO:
This video shows images from NASA's LRO spacecraft of various lunar pits.
Click here for more information.
While the moon's surface is battered by millions of craters, it also has over 200 holes – steep-walled pits that in some cases might lead to caves that future astronauts could explore and use for shelter, according to new observations from NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) spacecraft.
The pits range in size from about 5 meters (~5 yards) across to more than ...
Older adults who walk out of necessity are at highest risk for outdoor falls
2014-07-17
Older adults are at a greater danger of falling when walking for utilitarian purposes such as shopping and appointments than when walking for recreation, according to a study from UMass Medical School.
"Older adults have two times the risk of falling while walking out of necessity than walking for recreation, and four times greater risk of injury from a fall on a sidewalk than in a recreational area," said Wenjun Li, PhD, associate professor of medicine in the Division of Preventive and Behavioral Health at UMMS and lead author of the study "Utilitarian Walking, Neighborhood ...
Estimating earthquake frequency and patterns in the Puget Lowland
2014-07-17
Boulder, Colo. - The hazard posed by large earthquakes is difficult to estimate because they often occur hundreds to thousands of years apart. Because written records for the Puget Lowland of northwestern Washington cover less than 170 years, the size and frequency of the largest and oldest earthquakes on the Seattle and Tacoma faults are unknown. Past earthquakes can only be estimated through geologic studies of sediments and landforms that are created when faults break the ground surface.
Along the Cascadia margin, the cities of Seattle and Tacoma occupy the Puget ...
Discovery may make it easier to develop life-saving stem cells
2014-07-17
Not unlike looking for the proverbial needle in a haystack, a team of Michigan State University researchers have found a gene that could be key to the development of stem cells – cells that can potentially save millions of lives by morphing into practically any cell in the body.
The gene, known as ASF1A, was not discovered by the team. However, it is at least one of the genes responsible for the mechanism of cellular reprogramming, a phenomenon that can turn one cell type into another, which is key to the making of stem cells.
In a paper published in the journal Science, ...
Losing sleep over your divorce? Your blood pressure could suffer
2014-07-17
Those who experience persistent sleep problems after a divorce stand to suffer from more than just dark circles. They might also be at risk for potentially harmful increases in blood pressure, a new study finds.
A growing body of research links divorce to significant negative health effects and even early death, yet few studies have looked at why that connection may exist.
Divorce-related sleep troubles may be partly to blame, suggest the authors of a new study to be published in a forthcoming issue of the journal Health Psychology.
"In the initial few months after ...
Choosing cheese
2014-07-17
Go ahead and call Rachel Dutton's research cheesy if you must. As far as she's concerned, it's anything but an insult.
A Bauer Fellow at the Faculty of Arts and Sciences' Center for Systems Biology, Dutton and her lab study cheese – or more precisely – the bacteria and fungi that live on cheese, in an effort to better understand how microbial communities form.
After studying 137 varieties of cheese collected in 10 different countries, Dutton has been able to identify three general types of microbial communities that live on cheese, opening the door to using each as ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
Robotic wing inspired by nature delivers leap in underwater stability
[Press-News.org] A new measure of biodiversityPhylogenetic analysis gives a much more complex and complete picture of the diversity of Australia's national plant