(Press-News.org) In contrast to their negative reputation as disease causing agents, some viruses can perform crucial biological and evolutionary functions that help to shape the world we live in today, according to a new report by the American Academy of Microbiology.
"Viruses participate in essential Earth processes and influence all life forms on the planet, from contributing to biogeochemical cycles, shaping the atmospheric composition, and driving major speciation events," states Marilyn Roossinck of Pennsylvania State University, a member of the steering committee that helped to organize the colloquium.
The report, 'Viruses Throughout Life & Time: Friends, Foes, Change Agents,' is based on the deliberation of a group of scientific experts who gathered for two days in San Francisco, CA in July 2013 to answer a series of questions regarding the variety of roles that viruses play in the natural world.
"The inspiration for holding the colloquium was that recent metagenomics studies of viruses have indicated we know very little about the real world of viruses. Almost all published research is about the viruses that cause disease in humans and their domesticated plants and animals. This certainly represents only a very small fraction of the viruses that really exist," says Roossinck. "It is very important to understand the real world of viruses, as this can inform our basic understanding of life and its origins, as well as major earth phenomena like carbon cycling."
Beyond their pathogenic impact, the report examines in depth the size of the virosphere, the origin of viruses, the overlooked biological and microbial ecological role of viruses, and how these live forms have contributed to evolution. Additional highlights from the report explain how some viruses are commensal organisms or symbionts, their functioning in microbial communities, and their role in maintaining the biosphere. The array of responsibilities taken on by viruses is due to their incredible sequence diversity and genomic plasticity, referred to as "viral dark matter".
The report concludes by stimulating the readers to think about key questions: "What if viruses had never existed on Earth? Would life have evolved quite differently"? Continued viral research will help to answer these enticing questions.
INFORMATION:
The American Academy of Microbiology is the honorific leadership group of the American Society for Microbiology. The mission of the Academy is to recognize scientific excellence, as well as foster knowledge and understanding in the microbiological sciences. A full list of Academy colloquia reports can be found at http://academy.asm.org/index.php/browse-all-reports. For more information about the American Society for Microbiology, visit http://www.asm.org.
Report on viruses looks beyond disease
2014-07-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Radio frequency ID tags on honey bees reveal hive dynamics
2014-07-22
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Scientists attached radio-frequency identification (RFID) tags to hundreds of individual honey bees and tracked them for several weeks. The effort yielded two discoveries: Some foraging bees are much busier than others; and if those busy bees disappear, others will take their place.
The findings are reported in the journal Animal Behaviour.
Tagging the bees revealed that about 20 percent of the foraging bees in a hive brought home more than half of the nectar and pollen gathered to feed the hive.
"We found that some bees are working very, very hard ...
Vanderbilt study shows therapeutic bacteria prevent obesity in mice
2014-07-22
A probiotic that prevents obesity could be on the horizon. Bacteria that produce a therapeutic compound in the gut inhibit weight gain, insulin resistance and other adverse effects of a high-fat diet in mice, Vanderbilt University investigators have discovered.
"Of course it's hard to speculate from mouse to human," said senior investigator Sean Davies, Ph.D., assistant professor of Pharmacology. "But essentially we've prevented most of the negative consequences of obesity in mice, even though they're eating a high-fat diet."
Regulatory issues must be addressed before ...
Enhanced NIST instrument enables high-speed chemical imaging of tissues
2014-07-22
A research team from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), working with the Cleveland Clinic, has demonstrated a dramatically improved technique for analyzing biological cells and tissues based on characteristic molecular vibration "signatures." The new NIST technique is an advanced form of the widely used spontaneous Raman spectroscopy, but one that delivers signals that are 10,000 times stronger than obtained from spontaneous Raman scattering, and 100 times stronger than obtained from comparable "coherent Raman" instruments, and uses a much larger ...
NASA's TRMM satellite measures up Super Typhoon Rammasun
2014-07-22
NASA's TRMM satellite measured up Super Typhoon Rammasun's rainfall rates, rainfall totals and cloud heights providing a look at the inner workings and aftermath of the storm.
Super Typhoon Rammasun struck the southern coast of China on Friday, July 18 as a very powerful super typhoon with sustained winds estimated at 135 knots (~155 mph or equivalent to a Category 5 hurricane on the US Saffir-Simpson scale), making it the strongest typhoon to hit the area in several decades.
Rammasun made landfall at 3:30 p.m. (local time) on Hainan Island where the southern half of ...
Preschoolers can reflect on what they don't know
2014-07-22
Contrary to previous assumptions, researchers find that preschoolers are able to gauge the strength of their memories and make decisions based on their self-assessments. The study findings are published in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science.
"Previously, developmental researchers assumed that preschoolers did not introspect much on their mental states, and were not able to reflect on their own uncertainty when problem solving," says psychological scientist Emily Hembacher of the University of California, Davis, lead author of ...
Extra exercise helps depressed smokers kick the habit faster
2014-07-22
This news release is available in French. Montreal, July 22, 2014 — People diagnosed with depression need to step out for a cigarette twice as often as smokers who are not dealing with a mood disorder. And those who have the hardest time shaking off the habit may have more mental health issues than they are actually aware of.
Those insights were among the collective findings recently published in the journal Nicotine & Tobacco Research by a team of researchers based in part at Concordia University.
While nearly one in five North American adults are regular smokers, ...
CEOs who motivate with 'fightin' words' shoot themselves in the foot
2014-07-22
Heading into the war room to fire up the troops? Declaring war on the competition to boost sales? Well, CEO, you might want to tamp down them's fightin' words—you could be shooting yourself in the foot.
A new Brigham Young University business study finds that bosses who try to motivate their employees with violent rhetoric—think of Steve Jobs declaring "thermonuclear war" on Samsung—end up motivating rival employees to play dirty.
"Business executives use violent language all the time," said David Wood, BYU professor of accounting and one of two BYU authors on the paper. ...
Dangers of desert dust: New diagnostic tool for valley fever
2014-07-22
VIDEO:
In this video, biodesign researcher Krupa Navalkar describes a new diagnostic technique for pinpointing Valley Fever.
Click here for more information.
On July 5, 2011, a massive wall of dust, ("haboob," in Arabic), blanketed Phoenix, Arizona, creating an awesome spectacle, (or stubborn nuisance, depending on your perspective). Dust storms are a common occurrence in the arid desert environments of the American Southwest.
But windborne dust can be a serious health risk, ...
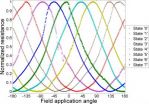
A new multi-bit 'spin' for MRAM storage
2014-07-22
WASHINGTON D.C., June 22, 2014 -- Interest in magnetic random access memory (MRAM) is escalating, thanks to demand for fast, low-cost, nonvolatile, low-consumption, secure memory devices. MRAM, which relies on manipulating the magnetization of materials for data storage rather than electronic charges, boasts all of these advantages as an emerging technology, but so far it hasn't been able to match flash memory in terms of storage density.
In the journal Applied Physics Letters, from AIP Publishing, a France-U.S. research team reports an intriguing new multi-bit MRAM storage ...
Fly-inspired sound detector
2014-07-22
WASHINGTON D.C., June 22, 2014 – Even within a phylum so full of mean little creatures, the yellow-colored Ormia ochracea fly is distinguished among other arthropods for its cruelty -- at least to crickets. Native to the southeastern U.S. states and Central America, the fly is a most predatory sort of parasite. It swoops onto the back of a singing male cricket, deposits a smear of larvae, and leaves its wicked brood to invade, kill and consume the cricket from inside out.
None of this would be possible without the fly's ability to find a cricket -- the cornerstone of ...