(Press-News.org) CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Scientists are searching through a massive collection of 20-million-year-old amber found in the Dominican Republic more than 50 years ago, and the effort is yielding fresh insights into ancient tropical insects and the world they inhabited.
When the collection is fully curated, a task that will take many years, it will be the largest unbiased Dominican amber collection in the world, the researchers report.
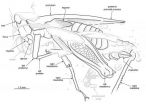
Perhaps the most striking discovery thus far is that of a pygmy locust, a tiny grasshopper the size of a rose thorn that lived 18- to 20-million years ago and fed on moss, algae and fungi. The specimen is remarkable because it represents an intermediate stage of evolution in the life of its subfamily of locusts (known as the Cladonotinae). The most ancient representatives of this group had wings, while modern counterparts do not. The newly discovered locust has what appear to be vestigial wings — remnant structures that had already lost their primary function.
The discovery is reported in the journal ZooKeys.
"Grasshoppers are very rare in amber and this specimen is extraordinarily well-preserved," said Sam Heads, a paleontologist at the Illinois Natural History Survey, a division of the Prairie Research Institute at the University of Illinois.
Heads, laboratory technician Jared Thomas and study co-author Yinan Wang found the new specimen a few months after the start of their project to screen more than 160 pounds of Dominican amber collected in the late 1950s by former INHS entomologist Milton Sanderson. Sanderson described several specimens from the collection in a paper in Science in 1960, a report that inspired a generation of scientists to seek out and study Dominican amber, Heads said.
The bulk of the Sanderson amber collection remained in storage, however, until Heads uncovered it in 2010.
Heads has named the new pygmy locust Electrotettix attenboroughi, the genus name a combination of electrum (Latin from Greek, meaning "amber") and tettix (Greek, meaning "grasshopper"). The species is named for Sir David Attenborough, a British naturalist and filmmaker (not to be confused with Richard Attenborough, David's actor brother who appeared in the movie "Jurassic Park").
"Sir David has a personal interest in amber, and also he was one of my childhood heroes and still is one of my heroes and so I decided to name the species in his honor -- with his permission of course," Heads said. (Attenborough narrates and appears in a new video about the Sanderson collection and the specimen that bears his name.)
The process of screening the amber is slow and painstaking. Much of the amber is clouded with oxidation, and the researchers must carefully cut and polish "windows" in it to get a good look at what's inside. In addition to the pygmy locust, Heads and his colleagues have found mating flies, stingless bees, gall midges, Azteca ants, wasps, bark beetles, mites, spiders, plant parts and even a mammal hair.
The pygmy locust was found in a fragment that also contained wasps, ants, midges, plant remnants and fungi. Such associations are rich in information, Heads said, offering clues about the creatures' physiological needs and the nature of their habitat.
"Fossil insects can provide lots of insight into the evolution of specific traits and behaviors, and they also tell us about the history of the time period," Heads said. "They're a tremendous resource for understanding the ancient world, ancient ecosystems and the ancient climate - better even, perhaps, than dinosaur bones."
INFORMATION:
The National Science Foundation supports this work. Heads and his colleagues are digitizing the best specimens, and will upload the images onto a publicly available website.
Editor's notes: To reach Sam Heads, call 217-244-9448; email swheads@illinois.edu.
The paper, "A remarkable new pygmy grasshopper (Orthoptera, Tetrigidae) in Miocene amber from the Dominican Republic," is available online or from the U. of I. News Bureau.
Decades-old amber collection offers new views of a lost world
2014-07-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
F1000Research brings static research figures to life
2014-07-30
F1000Research today published new research from Bjorn Brembs, professor of neurogenetics at the Institute of Zoology, Universitaet Regensburg, in Germany, with a proof-of-concept figure allowing readers and reviewers to run the underlying code within the online article. This represents an important leap forward for scientific publishing, by demonstrating a completely novel framework for assessing the quality of a scholarly output.
Figure 3 in fact doesn't really exist. The authors submitted their data and their code to F1000Research, and the figure is generated 'on the ...
Income is a major driver of avoidable hospitalizations across New Jersey
2014-07-30
NEW BRUNSWICK, N.J. – The household income of its residents is the most important factor in whether a community has high or low rates of avoidable hospital visits – conditions that could be better managed in a doctor's office or other health care settings if treated at an early stage, according to a report released today by the Rutgers Center for State Health Policy (CSHP).
An analysis of hospital billing records and demographic data by Rutgers researchers across 13 low-income communities in New Jersey found that as an area's per capita income rises, the number of patients ...
Dimly lit working environments: Correcting your body clock is possible!
2014-07-30
This news release is available in French.
Researchers at Inserm, led by Claude Gronfier (Inserm Unit 846: Stem Cell and Brain Institute), have, for the first time, conducted a study under real conditions on the body clocks of members of the international polar research station Concordia. The researchers have shown that a particular kind of artificial light is capable of ensuring that their biological rhythms are correctly synchronised despite the absence of sunlight. The full significance of this result can be appreciated with the knowledge that disturbance to this ...
Saving seeds the right way can save the world's plants
2014-07-30
KNOXVILLE—Exotic pests, shrinking ranges and a changing climate threaten some of the world's most rare and ecologically important plants, and so conservationists establish seed collections to save the seeds in banks or botanical gardens in hopes of preserving some genetic diversity.
For decades, these seed collections have been guided by simple models that offer a one-size-fits-all approach for how many seeds to gather, such as recommending saving 50 seed samples regardless of species' pollination mode, growth habitat and population size.
A new study, however, has found ...
Neuro researchers advocate for a shift in thinking for stroke rehabilitation
2014-07-30
Los Angeles, CA (July 30, 2014) With the advent of non-surgical modalities, stimulation of the brain has become a popular science and researchers must work to ensure systematic methods for consistent results in the study of stroke rehabilitation. A new study out today in The Neuroscientist discusses a systematic shift in perspective and suggests that chronically stimulating premotor areas (PMAs) of the brain would strongly promote stroke motor recovery, for example by restoring balance between the stroke and the intact hemispheres while establishing greater widespread connectivity. ...
Money talks when it comes to acceptability of 'sin' companies, study reveals
2014-07-30
Toronto – Companies who make their money in the "sin" industries such as the tobacco, alcohol and gaming industries typically receive less attention from institutional investors and financial analysts.
But new research shows social norms and attitudes towards these types of businesses are subject to compromise when their share price looks to be on the rise. A paper from the University of Toronto's Rotman School of Management found that institutional shareholdings and analysts' coverage of sin firms were low when firm performance was low but went up with rising performance ...
Brain response to appetizing food cues varies among obese people
2014-07-30
Washington, DC—People who have the most common genetic mutation linked to obesity respond differently to pictures of appetizing foods than overweight or obese people who do not have the genetic mutation, according to a new study published in the Endocrine Society's Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism (JCEM).
More than one-third of adults are obese. Obesity typically results from a combination of eating too much, getting too little physical activity and genetics. In particular, consumption of appetizing foods that are high in calories can lead to weight gain. ...
Teen insomnia is linked with depression and anxiety
2014-07-30
A study of high school students by University of Adelaide psychology researchers has shed new light on the links between insomnia-related mental health conditions among teens.
School of Psychology PhD student Pasquale Alvaro surveyed more than 300 Australian high school students aged 12-18 to better understand their sleep habits, mental health condition and the time of day they were most active (known as their "chronotype").
The results, now published in the journal Sleep Medicine, may have implications for the clinical treatment of teens experiencing sleep and mental ...
High frequency of potential entrapment gaps in hospital beds
2014-07-30
A survey of beds within a large teaching hospital in Ireland has shown than many of them did not comply with dimensional standards put in place to minimise the risk of entrapment. The report, published online in the journal Age and Ageing, therefore emphasises the need for careful selection of patients for whom bedrails are to be used, as well as the need for monitoring and maintenance of hospital bed systems.
Bedrails are commonly used as safety devices to prevent people falling from bed. However, although the risk for any individual is extremely low, people can and ...
Chinese mosquitos on the Baltic Sea
2014-07-30
The analysis of the roughly 3,000 pieces is still in its infant stage. But it is already evident that the results will be of major significance. "Amazingly often, we are finding–in addition to Asian forms–the same insect species in Fushun amber that we found in Baltic amber," explained Bonn paleontologist Professor Dr. Jes Rust.
The Baltic amber comes from the Baltic Sea region, which is almost 10,000 kilometers from Fushun. Sites rich in finds are, e.g., the coastal regions of Mecklenburg, Poland and Belarus. The pieces from the Baltic region are slightly younger than ...