(Press-News.org) In the first study of its kind, Prapti Gautam, PhD, and colleagues from The Saban Research Institute of Children's Hospital Los Angeles found that children with fetal alcohol spectrum disorders (FASD) showed weaker brain activation during specific cognitive tasks than their unaffected counterparts. These novel findings suggest a possible neural mechanism for the persistent attention problems seen in individuals with FASD. The results of this study will be published in Cerebral Cortex on August 4.
"Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) has been used to observe brain activity during mental tasks in children with FASD, but we are the first to utilize these techniques to look at brain activation over time," says Gautam. "We wanted to see if the differences in brain activation between children with FASD and their healthy peers were static, or if they changed as children got older."
FASD encompasses the broad spectrum of symptoms that are linked to in utero alcohol exposure, including cognitive impairment, deficits in intelligence and attention and central nervous system abnormalities. These symptoms can lead to attention problems and higher societal and economic burdens common in individuals with FASD.
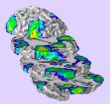
During the period of childhood and adolescence, brain function, working memory and attention performance all rapidly improve, suggesting that this is a crucial time for developing brain networks. To study how prenatal alcohol exposure may alter this development, researchers observed a group of unaffected children and a group of children with FASD over two years. They used fMRI to observe brain activation through mental tasks such as visuo-spatial attention—how we visually perceive the spatial relationships among objects in our environment —and working memory.
"We found that there were significant differences in development brain activation over time between the two groups, even though they did not differ in task performance," notes Elizabeth Sowell, PhD, director of the Developmental Cognitive Neuroimaging Laboratory at The Saban Research Institute and senior author on the manuscript. "While the healthy control group showed an increase in signal intensity over time, the children with FASD showed a decrease in brain activation during visuo-spatial attention, especially in the frontal, temporal and parietal brain regions."
These results demonstrate that prenatal alcohol exposure can change how brain signaling develops during childhood and adolescence, long after the damaging effects of alcohol exposure in utero. The atypical development of brain activation observed in children with FASD could explain the persistent problems in cognitive and behavioral function seen in this population as they mature.
INFORMATION:
About Children's Hospital Los Angeles
Children's Hospital Los Angeles has been named the best children's hospital in California and among the top five in the nation for clinical excellence with its selection to the prestigious US News & World Report Honor Roll. Children's Hospital is home to The Saban Research Institute, one of the largest and most productive pediatric research facilities in the United States, is one of America's premier teaching hospitals and has been affiliated with the Keck School of Medicine of the University of Southern California since 1932.
For more information, visit http://www.CHLA.org. Follow us on Twitter, Facebook, YouTube and LinkedIn, or visit our blog: ResearCHLAblog.org
Media Contact: Jennifer Jing, jjing@chla.usc.edu
(323) 361-1812
Prenatal alcohol exposure alters development of brain function
Researchers from The Saban Research Institute suggest neural basis for symptoms of fetal alcohol spectrum disorders
2014-08-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Mid-level scientists most likely to use new research tools, says study in INFORMS journal
2014-08-04
Scientists in the middle of the status hierarchy, not those at the top or the bottom, are the first to work with easy-to-use commercial products. They are also the most prone to imitate their prior collaborators' use of such commercial kits. These are among the findings of a study of scientists-as-customers appearing in Marketing Science, a journal of the Institute for Operations Research and the Management Sciences (INFORMS).
Nonmonotonic Status Effects in New Product Adoption is by Yansong Hu of the University of Warwick and Christophe Van den Bulte of the University ...
Animalistic descriptions of violent crimes increase punishment of perpetrators
2014-08-04
Describing criminals and criminal activities with animal metaphors leads to more retaliation against perpetrators by inducing the perception that they're likely to continue engaging in violence, a new Aggressive Behavior study suggests.
When surveying jury?eligible adults, investigators varied animalistic descriptions of a violent crime and examined its effect on the severity of the punishment for the act. Compared with non?animalistic descriptions, animalistic descriptions resulted in significantly harsher punishment for the perpetrator due to an increase in perceived ...
Evolutionary explanation for why some lessons more easily learned than others
2014-08-04
It's easy to guess why it doesn't take long to learn to avoid certain behaviors and embrace others. But how do we know what drives these predilections? A study led by Aimee Dunlap at the University of Missouri-St. Louis, and co-authored by University of Minnesota researcher David Stephens, offers insight into the evolutionary underpinning of animals' innate ability to quickly absorb critical life lessons.
Animals are flooded with stimuli, but survival often depends on their ability to form specific associations that enhance fitness while ignoring others entirely. Psychologists ...
Enhancing biofuel yields from biomass with novel new method
2014-08-04
RIVERSIDE, Calif. — A team of researchers, led by Professor Charles E. Wyman, at the University of California, Riverside's Bourns College of Engineering have developed a versatile, relatively non-toxic, and efficient way to convert raw agricultural and forestry residues and other plant matter, known as lignocellulosic biomass, into biofuels and chemicals.
The patent-pending method, called Co-solvent Enhanced Lignocellulosic Fractionation (CELF), brings researchers closer to solving the long elusive goal of producing fuels and chemicals from biomass at high enough yields ...
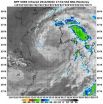
NASA catches the brief life of Tropical Storm Nakri
2014-08-04
The low pressure area known as System 96W struggled to organize for a week and finally became Tropical Storm Nakri on August 2 as the Suomi NPP satellite passed overhead. Nakri had a short life, however, as it dissipated the following day while approaching South Korea.
On Saturday, August 2, at 9 p.m. EDT, Nakri's maximum sustained winds were near 40 knots (46 mph/74 kph). At that time it was centered about 100 nautical miles southeast of Kunsan Air Base, near 35.0 north and 125.0 east. It was moving to the north at 14 knots (16.1 mph/21.9 kph).
When NASA-NOAA's Suomi ...
NASA sees Typhoon Halong's eye wink
2014-08-04
As Super Typhoon Halong tracks north through the Northwestern Pacific Ocean, NASA's Aqua and Terra satellites have seen the powerful storm appear to wink at space as it developed and "opened" an eye and then close its eye as clouds moved over it. That wink appears to be a sign of eyewall replacement in the powerful storm.
On August 2 at 01:45 UTC (August 1 at 9:45 p.m. EDT) NASA's Terra satellite captured a visible image of a wide-eyed Super Typhoon Halong moving through the Northwestern Pacific Ocean. At the time of the image, Halong was a powerful Category 5 Super Typhoon ...
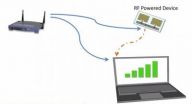
No-power Wi-Fi connectivity could fuel internet of things reality
2014-08-04
Imagine a world in which your wristwatch or other wearable device communicates directly with your online profiles, storing information about your daily activities where you can best access it – all without requiring batteries. Or, battery-free sensors embedded around your home could track minute-by-minute temperature changes and send that information to your thermostat to help conserve energy.
This not-so-distant "Internet of Things" reality would extend connectivity to perhaps billions of devices. Sensors could be embedded in everyday objects to help monitor and track ...
NASA's IBEX and Voyager spacecraft drive advances in outer heliosphere research
2014-08-04
San Antonio -- Aug. 4, 2014 -- Scientists yesterday highlighted an impressive list of achievements in researching the outer heliosphere at the 40th International Committee on Space Research (COSPAR) Scientific Assembly in Moscow.
"Between NASA's Voyager and IBEX missions, it's an incredible time for outer heliospheric science," says Dr. Dave McComas, IBEX principal investigator and assistant vice president of the Space Science and Engineering Division at Southwest Research Institute, who also will be recognized with a 2014 COSPAR Space Science Award at the assembly. "Ten ...
Children in immigrant families more likely to be sedentary
2014-08-04
Immigrant children from all racial and ethnic backgrounds are more likely to be sedentary than U.S.-born white children, according to a new study by sociologists at Rice University. The researchers said their findings should remind pediatricians and parents of children in immigrant families to encourage physical activity.
The research revealed that children of immigrants from all racial and ethnic backgrounds have lower levels of physical activity than U.S.-born white children, even when adjustments are made for socio-demographic and neighborhood characteristics. A low ...
New tools advance bio-logic
2014-08-04
Researchers at Rice University and the University of Kansas Medical Center are making genetic circuits that can perform more complex tasks by swapping protein building blocks.
The modular genetic circuits engineered from parts of otherwise unrelated bacterial genomes can be set up to handle multiple chemical inputs simultaneously with a minimum of interference from their neighbors.
The work reported in the American Chemical Society journal ACS Synthetic Biology gives scientists more options as they design synthetic cells for specific tasks, such as the production of ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Cal Poly’s fifth Climate Solutions Now conference to take place Feb. 23-27
Mask-wearing during COVID-19 linked to reduced air pollution–triggered heart attack risk in Japan
Achieving cross-coupling reactions of fatty amide reduction radicals via iridium-photorelay catalysis and other strategies
Shorter may be sweeter: Study finds 15-second health ads can curb junk food cravings
Family relationships identified in Stone Age graves on Gotland
Effectiveness of exercise to ease osteoarthritis symptoms likely minimal and transient
Cost of copper must rise double to meet basic copper needs
A gel for wounds that won’t heal
Iron, carbon, and the art of toxic cleanup
Organic soil amendments work together to help sandy soils hold water longer, study finds
Hidden carbon in mangrove soils may play a larger role in climate regulation than previously thought
Weight-loss wonder pills prompt scrutiny of key ingredient
Nonprofit leader Diane Dodge to receive 2026 Penn Nursing Renfield Foundation Award for Global Women’s Health
Maternal smoking during pregnancy may be linked to higher blood pressure in children, NIH study finds
New Lund model aims to shorten the path to life-saving cell and gene therapies
Researchers create ultra-stretchable, liquid-repellent materials via laser ablation
Combining AI with OCT shows potential for detecting lipid-rich plaques in coronary arteries
SeaCast revolutionizes Mediterranean Sea forecasting with AI-powered speed and accuracy
JMIR Publications’ JMIR Bioinformatics and Biotechnology invites submissions on Bridging Data, AI, and Innovation to Transform Health
Honey bees navigate more precisely than previously thought
Air pollution may directly contribute to Alzheimer’s disease
Study finds early imaging after pediatric UTIs may do more harm than good
UC San Diego Health joins national research for maternal-fetal care
New biomarker predicts chemotherapy response in triple-negative breast cancer
Treatment algorithms featured in Brain Trauma Foundation’s update of guidelines for care of patients with penetrating traumatic brain injury
Over 40% of musicians experience tinnitus; hearing loss and hyperacusis also significantly elevated
Artificial intelligence predicts colorectal cancer risk in ulcerative colitis patients
Mayo Clinic installs first magnetic nanoparticle hyperthermia system for cancer research in the US
Calibr-Skaggs and Kainomyx launch collaboration to pioneer novel malaria treatments
JAX-NYSCF Collaborative and GSK announce collaboration to advance translational models for neurodegenerative disease research
[Press-News.org] Prenatal alcohol exposure alters development of brain functionResearchers from The Saban Research Institute suggest neural basis for symptoms of fetal alcohol spectrum disorders