(Press-News.org) Numerous risk factors are believed to contribute to the development of autoimmune disorders such as multiple sclerosis, and new research is focusing on the role that bacteria in the gastrointestinal tract as well as other cell stress-related chemical signals could have in stimulating inflammation in the central nervous system and activating immunostimulatory cytokines. Two comprehensive Review articles are part of a focus on "Cytokines in Neuroinflammation and Immunity" in a special issue of Journal of Interferon & Cytokine Research (JICR), a peer-reviewed publication from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The articles are available free on the JICR website.
Kiel Telesford and Lloyd Kasper, Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth University (Lebanon, NH) and Javier Ochoa-Repáraz, University of California-Santa Barbara, describe three key characteristics of the gut microbiome related to immune cell activity and cytokine production that may be relevant to susceptibility to and treatment of autoimmune disorders such as multiple sclerosis. In the article "Gut Commensalism, Cytokines, and Central Nervous System Demyelination," the authors note that our understanding of the biology of the gut microbiome and the immunoregulatory potential of bacteria and parasites in the gut is still in its infancy.
In the Review article "Interferons, Signal Transduction Pathways, and the Central Nervous System," Shreeram Nallar and Dhan Kalvakolanu, University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, explore in detail the latest research pointing to the role of cytokines, and in particular interferons, in contributing to the development of diseases affecting the central nervous system. The authors discuss the potential effects of either an excess or lack of interferons, the inflammatory effects of cytokines, and new therapeutic research strategies.
"The communications between the microbial community in the gut and the host immune system is turning out to be remarkably complex and is likely to impact on many aspects of both health and disease," says Editor-in-Chief Thomas A. Hamilton, PhD, Chairman, Department of Immunology, Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Ohio.
INFORMATION:
About the Journal
Journal of Interferon & Cytokine Research (JICR), led by Editors-in-Chief Ganes C. Sen, PhD, Chairman, Department of Molecular Genetics, Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Ohio, and Thomas A. Hamilton, PhD, is an authoritative peer-reviewed journal published monthly online with Open Access options and in print that covers all aspects of interferons and cytokines from basic science to clinical applications. JICR, celebrating 35 years of publication in 2015, is an official journal of the International Cytokine & Interferon Society. Complete tables of content and a sample issue may be viewed on the JICR website.
About the Publisher
Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers is a privately held, fully integrated media company known for establishing authoritative peer-reviewed journals in many promising areas of science and biomedical research, including Viral Immunology, AIDS Research and Human Retroviruses, and DNA and Cell Biology. Its biotechnology trade magazine, Genetic Engineering & Biotechnology News (GEN), was the first in its field and is today the industry's most widely read publication worldwide. A complete list of the firm's 80 journals, books, and newsmagazines is available on the Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers website.
Is the gut microbiome a potential cause and therapeutic target for autoimmune diseases like multiple sclerosis?
2014-08-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Satellite shows Bertha merged with frontal system in North Atlantic
2014-08-07
A visible satellite image from NOAA's GOES-East satellite shows that Post-Tropical Storm Bertha was merging with a frontal system in the North Atlantic Ocean.
The visible image from 1200 UTC (8 a.m. EDT) on August 6 was created at the NASA GOES Project, located at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The image was created from data from NOAA's GOES-East satellite and the circulation center of Bertha is barely discernable. Bertha's circulation was connected to a stationary front that stretched from northeastern Canada to the Bahamas creating what ...
Adult myelination -- Wrapping up neuronal plasticity
2014-08-07
The adult CNS is remarkably adaptable – it retains the ability to generate and integrate new cells, and remodel pre-existing circuits. Intense research over the last 25 years has provided critical insight into the cell generation and differentiation potential of endogenous neural stem and progenitor cells, and has described three core CNS plasticity mechanisms. While we are still a long way from fully understanding how neural plasticity is regulated from the level of the individual cell, through to the level of the neural network, there is growing evidence to support the ...
Eating at fast food, full service restaurants linked to more calories, poorer nutrition
2014-08-07
ATLANTA – August 7, 2014 –For adults, eating at both fast-food and full-service restaurants is associated with significant increases in the intake of calories, sugar, saturated fat, and sodium, according to a new study. The study, appearing early online in Public Health Nutrition, finds on days when adults ate at a restaurant, they consumed about 200 additional total daily calories whether they ate at fast- food restaurants or at full-service restaurants.
Previous studies looking at restaurant food consumption have found that adults who reported eating fast food consumed ...
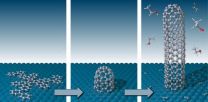
Synthesis of structurally pure carbon nanotubes using molecular seeds
2014-08-07
For 20 years, carbon nanotubes (CNTs) have been the subject of intensive fundamental as well as applied research. With their extraordinary mechanical, thermal and electronic properties, these tiny tubes with their graphitic honeycomb lattice have become the paragon of nanomaterials. They could help to create next-generation electronic and electro-optical components that are smaller than ever before, and thus to achieve even faster switching times.
As uniform as possible
With a diameter of roughly one nanometre, single-wall CNTs (or SWCNTs) need to be considered as quantum ...
Researcher finds companies' religious affiliation can buffer negative reactions
2014-08-07
While companies like Hobby Lobby and Chick-fil-A are at the forefront of debate over the religious rights of employers, a new study by a Grand Valley State University researcher shows religious affiliation can safeguard companies against negative reactions to store policies. The findings were published in the Journal of Services Marketing.
The research, led by Kelly Cowart, assistant professor of marketing at Grand Valley State University, examines the effect of a firm's religious association on customer perceptions of the firm, especially when a service failure occurs. ...
The economy of bitcoins
2014-08-07
This news release is available in German. Anyone who strolls around the Kreuzberg district of Berlin, can't help but notice them – the small signs on the doors of shops and cafes "Bitcoins accepted". Customers pay for their shirt or their cappuccino with their Smartphone instead of with bank notes or credit cards. The digital currency Bitcoin makes all this possible. "The image of Bitcoin has changed fundamentally", explains David Garcia, a post-doctoral researcher with the Chair of Systems Design held by Professor Frank Schweitzer. "Bitcoins used to be the reserve ...
Excavation of ancient well yields insight into Etruscan, Roman and medieval times
2014-08-07
TALLAHASSEE, Fla. -- During a four-year excavation of an Etruscan well at the ancient Italian settlement of Cetamura del Chianti, a team led by a Florida State University archaeologist and art historian unearthed artifacts spanning more than 15 centuries of Etruscan, Roman and medieval civilization in Tuscany.
"The total haul from the well is a bonanza," said Nancy de Grummond, the M. Lynette Thompson Professor of Classics at Florida State. De Grummond, who has performed work at the site since 1983, is one of the nation's leading scholars of Etruscan studies.
"This ...
Newsroom journalists at increased risk of PTSD and depression from images of extreme violence
2014-08-07
Journalists working with images of extreme violence submitted to newsrooms by the public are at increased risk of adverse psychological consequences, including post-traumatic stress disorder. New research, published today by JRSM Open, shows that frequent, repetitive viewing of traumatic images by journalists working with 'live' or User Generated Content material can be closely linked to anxiety, depression, PTSD and alcohol consumption. Frequency rather than duration of exposure to images of graphic violence is more emotionally distressing to journalists processing User ...
Diamonds are a quantum computer's best friend
2014-08-07
This news release is available in German.
The Quantum Computer is the Holy Grail of quantum technology. Its computing power would eclipse even the fastest classical computers we have today. A team of researchers from TU Wien (Vienna) the National Institute for Informatics (Tokyo) and NTT Basic Research Labs in Japan has now proposed a new architecture for quantum computing, based on microscopic defects in diamond. A reliable quantum computer capable of solving complex problems would have to consist of billions of quantum systems, and such a device is still out of ...
Study: Attending a more selective college doesn't mean a better chance of graduating
2014-08-07
WASHINGTON, D.C., August 7, 2014 ─ It is commonly argued that students should attend the most academically selective college possible, since, among other reasons, highly selective institutions graduate students at higher rates. However, is it the institutions themselves that succeed in getting students through to degree completion, or is degree completion merely a result of the quality of the students entering the institutions?
New research published today in the American Educational Research Journal (AERJ), a peer-reviewed journal of the American Educational Research ...